Tygron for Decision-Making: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
You can find the presentations here: | You can find the presentations here: | ||
#[[IHS_ScenarioAnalysis_session1]] | #[[IHS_ScenarioAnalysis_session1.pdf]] | ||
# | #[[IHS_ScenarioAnalysis_session2.pdf]] | ||
[[ | |||
It is also worth mentioning that this year: | It is also worth mentioning that this year: | ||
| Line 81: | Line 79: | ||
*#the CPU and memory power of laptops, in addition to the graphic cards. | *#the CPU and memory power of laptops, in addition to the graphic cards. | ||
*Due to the corona measures, it was not possible to hold any interactive sessions inside the classroom. | *Due to the corona measures, it was not possible to hold any interactive sessions inside the classroom. | ||
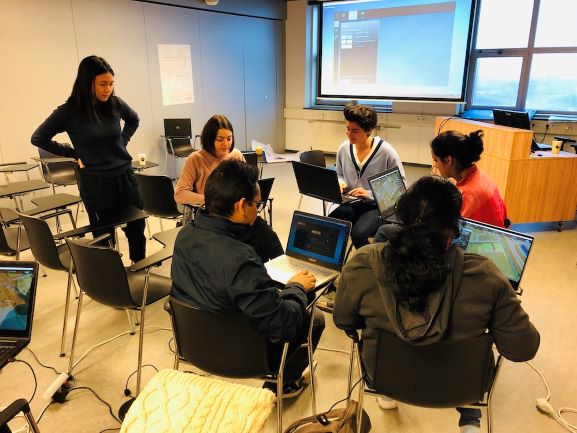
[[file:IHSTygron.jpg|350px|frame|center|IHS students discussing their projects]] | |||
==Outcome and Assessment== | ==Outcome and Assessment== | ||
==Feedback and Recommendations== | ==Feedback and Recommendations== | ||
Revision as of 11:30, 26 February 2021
Use-case 5: “Scenario Building for Sustainable Cities”
For a few years now, IHS has been using Tygron as a scenario building tool within its s"Urban Management Tools for Climate Change" short courses. During this course, the Tygron support team would join the students for half a day to help them play the Climate Game. Last year (2019-2020), IHS decided to experiment with implementing Tygron for one of its Masters specializations. The course was given as an elective for 15 students, and the implementation was completely successful. This success has pushed IHS team to design and implement a mandatory course using Tygron as part of the new curriculum. Contrary to last year, due to the COVID-19 restrictions, the course was completely done online this year.
Content of the course
General information
- Name of the course: "Scenario Building for Sustainable Cities"
- Study-block: "Applications of ICT for Smart and Sustainable Cities"
- Study Programme: Masters in Urban Environment Sustainability and Climate Change.
- Educational Institute: Institute for Housing and Urban Development Studies (IHS) of the Erasmus University Rotterdam.
Target students
- The course is designed for 30 students coming from different backgrounds
- The students do not have any prior knowledge of Tygron or other geodesign software.
- The students are expected to have some knowledge in decision-making.
- No specific skill sets or tools are required upon entering this course.
Objectives and desired outcome
The students are expected to learn planning and decision making for sustainable cities in a multi-stakeholder environment.
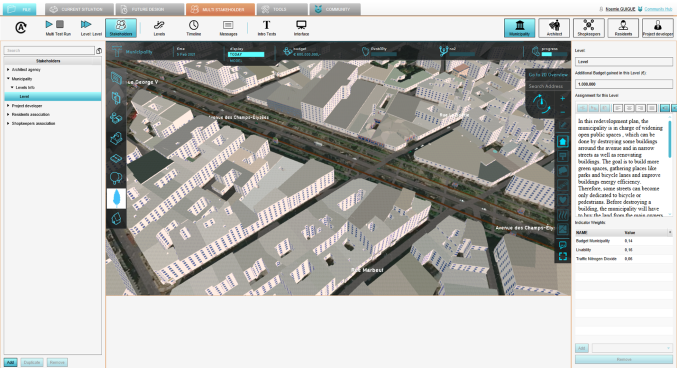
To do that, the lecturer and the teaching assistant have created a model case study based on the Champs-Elysées area in Paris using Tygron.
They called the model the "Paris Game". It is inspired from an existing redevelopment plan of the Paris municipality, with modified objectives.
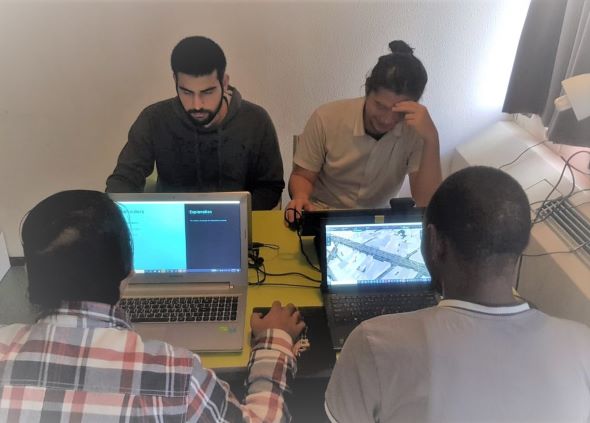
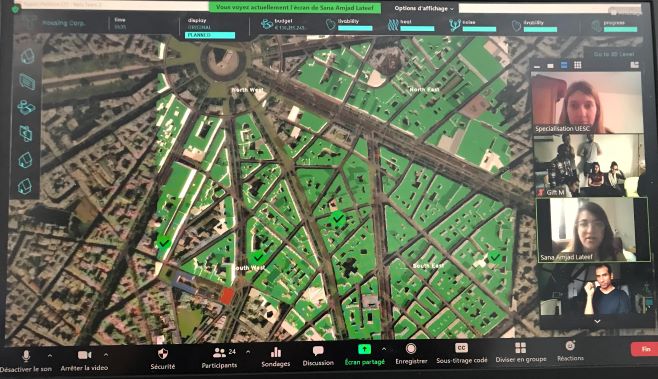
The students are expected to form teams of 4-5, and design scenarios for improving sustainability of a chosen or given area, while creating a multi-stakeholder decision making environment.
More-specifically, each team is expected to develop its own scenario for this area by:
- Creating a story; defining the potential involved stakeholders, their indicators, their goals, their budget, etc.
- Simulate the interaction between stakeholders by playing the "game' as if in real life.
Design of the Course
Syllabus and logistics
As mentioned previously, this course is part of a study-block, so it is designed to take place over 4.5 days.
The following steps explain how the course goes:
- In the first day, students get introduced to the assignment, and immediately start experimenting with Tygron individually.
- They then form their own teams of 4-5 members and begin working on their assignments.
- Every team is assigned to improve livability and sustainability of one identical area (A section of Champs-Elyse street Paris). The case is inspired from local government’s plan for improving greenery in the neighborhood. However, the goals are expanded in order to make the assignment more challenging. This also allows to compare the approach of different groups with a common aim of addressing sustainability challenges in the same area.
- They start by defining the stakeholder roles, land pricing, goals, budgets, and indicators.
- Later, they host a multi-stakeholder session, with each team member as a stakeholder.
- At the end of the course, they go through a final discussion.
You can read more about the Paris case-study by downloading this document that IHS has created: File:Model case study Paris game.pdf.
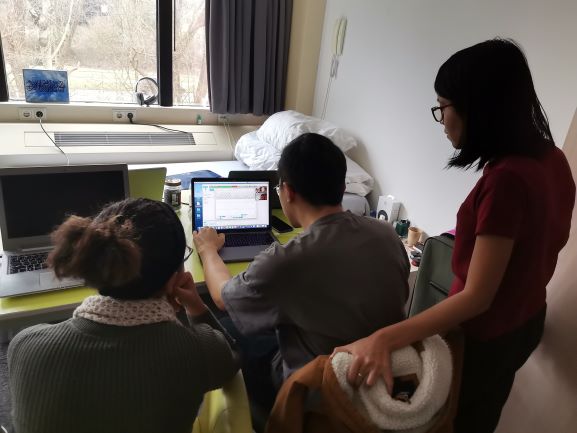
- IHS students working on their group assignments from home
Guidance and resources
For this course, lecturer Somesh Sharma and academic assistant Noémie Guigue created their own game. It took them around one month of research and preparation to get the Paris Game ready for the participants.
- First, they selected a location to focus on
- They then went over the online support material including the wiki, the forum, the demo projects and video tutorials.
- They found a relevant case-study that helped them develop the assignment
- They prepared the project, by loading the location & relevant data into Tygron, and edited it using mostly functions like overlays, attributes, stakeholders and actions.
- At the end, they produced their own presentations to guide students on the proper use of Tygron for the assignment.
You can find the presentations here:
It is also worth mentioning that this year:
- The presentations were delivered online.
- The teams had to work remotely, so they had to consider the following in forming the teams:
- the proximity to other team members. Students living in the same student housing often worked together
- the distribution of Windows and Apple-Mac laptops among team members
- the CPU and memory power of laptops, in addition to the graphic cards.
- Due to the corona measures, it was not possible to hold any interactive sessions inside the classroom.