Water Module theory: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Tag: Manual revert |
||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
The following topics are described on this page: | The following topics are described on this page: | ||
* | * {{inlink|Introduction to the Water Module Theory}} | ||
* [[#Calculation Models|Calculation modules]] | * [[#Calculation Models|Calculation modules]] {{inlink|Calculation Models}} | ||
* [[#Formulas|Theories and formulas ]] | * [[#Formulas|Theories and formulas ]] | ||
* [[#Calculation related information|Computational structure and sequences]] | * [[#Calculation related information|Computational structure and sequences]] | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
===Introduction to the Water Module Theory === | ===Introduction to the Water Module Theory === | ||
The [[Water Module]] in the {{software}} is an implementation of a 2D grid based shallow water model, based on the 2D Saint Venant equations (see [[Surface model (Water Overlay)|Surface Model]]). The module is further enhanced with infiltration, evaporation, groundwater flow and hydraulic structures. | The [[Water Module]] in the {{software}} is an implementation of a 2D grid based shallow water model, based on the 2D Saint Venant equations (see [[Surface model (Water Overlay)|Surface Model]]). The module is further enhanced with infiltration, evaporation, groundwater flow and hydraulic structures. | ||
To perform the calculations, the project area is first rasterized into a [[Grid overlay|large grid of cells]]. Each cell has a specific quantity of water and specific hydrological parameters based on the data in the project. The total time which should be simulated is divided into discrete [[Timestep formula (Water Overlay)|timesteps]]. Per timestep, each cell communicates with its adjacent cells to exchange water, based on it's water level, surface height, current flow direction and other factors. Accuracy and reliability is obtained by dividing the project area and simulation time into sufficiently small cells and steps, at the cost of more computation time. Take a look at the [[Testbed_water_module|testbed water module]] project, available in all domains, to see some of the components of the [[Water Module]] in a project. | To perform the calculations, the project area is first rasterized into a [[Grid overlay|large grid of cells]]. Each cell has a specific quantity of water and specific hydrological parameters based on the data in the project. The total time which should be simulated is divided into discrete [[Timestep formula (Water Overlay)|timesteps]]. Per timestep, each cell communicates with its adjacent cells to exchange water, based on it's water level, surface height, current flow direction and other factors. Accuracy and reliability is obtained by dividing the project area and simulation time into sufficiently small cells and steps, at the cost of more computation time. Take a look at the [[Testbed_water_module|testbed water module]] project, available in all domains, to see some of the components of the [[Water Module]] in a project. | ||
The Water Module enables users to implement a water model for their project which is accurate and delivers fast results. To ensure accuracy, the Water Module is repeatedly tested against multiple (internationally) acknowledged hydrological [[Water module benchmarks|benchmarks and tests]]. Fast results are achieved by executing the water calculations on High performance GPU servers. | The Water Module enables users to implement a water model for their project which is accurate and delivers fast results. To ensure accuracy, the Water Module is repeatedly tested against multiple (internationally) acknowledged hydrological [[Water module benchmarks|benchmarks and tests]]. Fast results are achieved by executing the water calculations on High performance GPU servers. | ||
<gallery widths=500px heights=300px> | |||
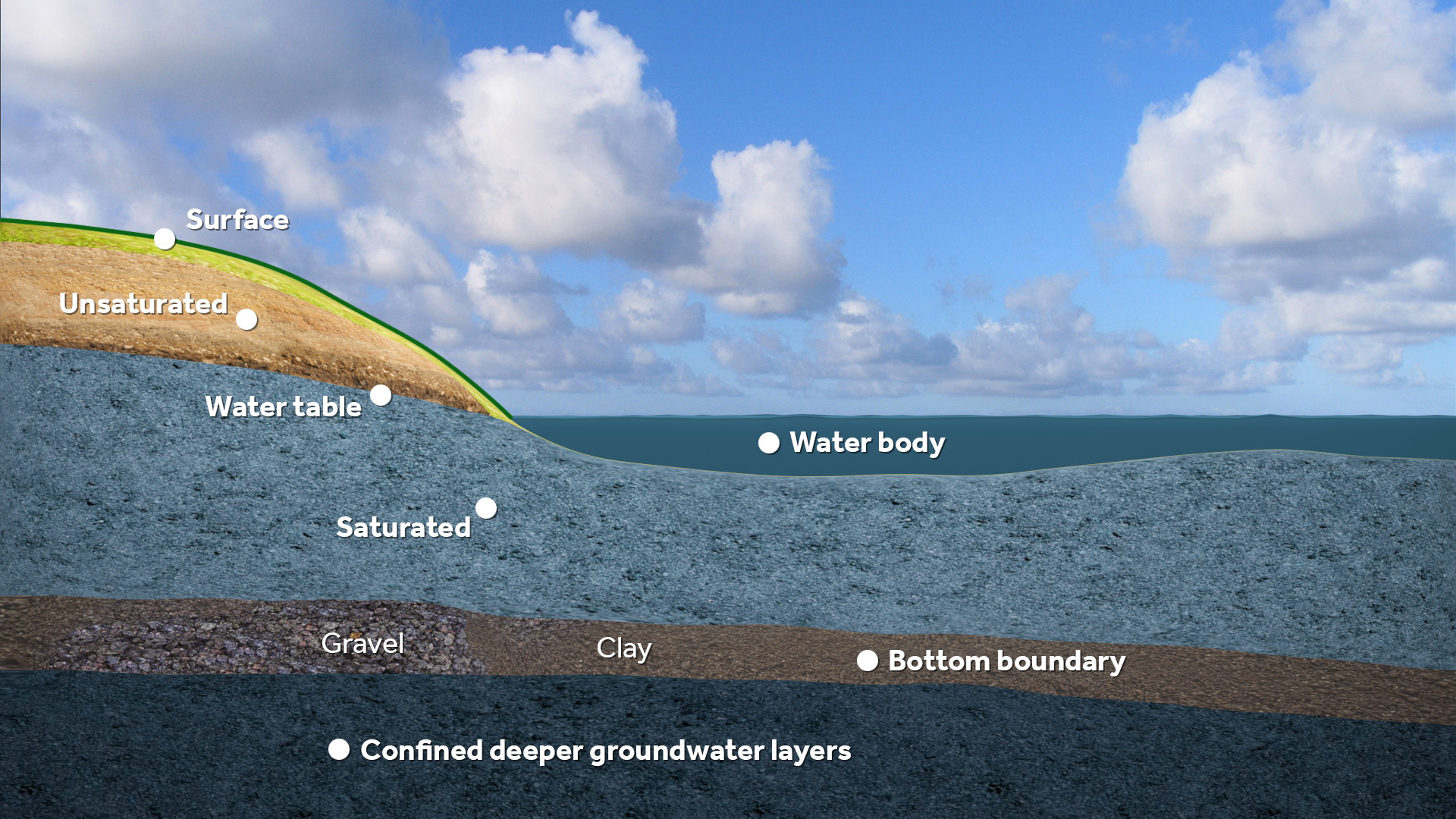
File:Water_module_layers.jpeg|Supported layers in rain, flooding and ground water calculations. | |||
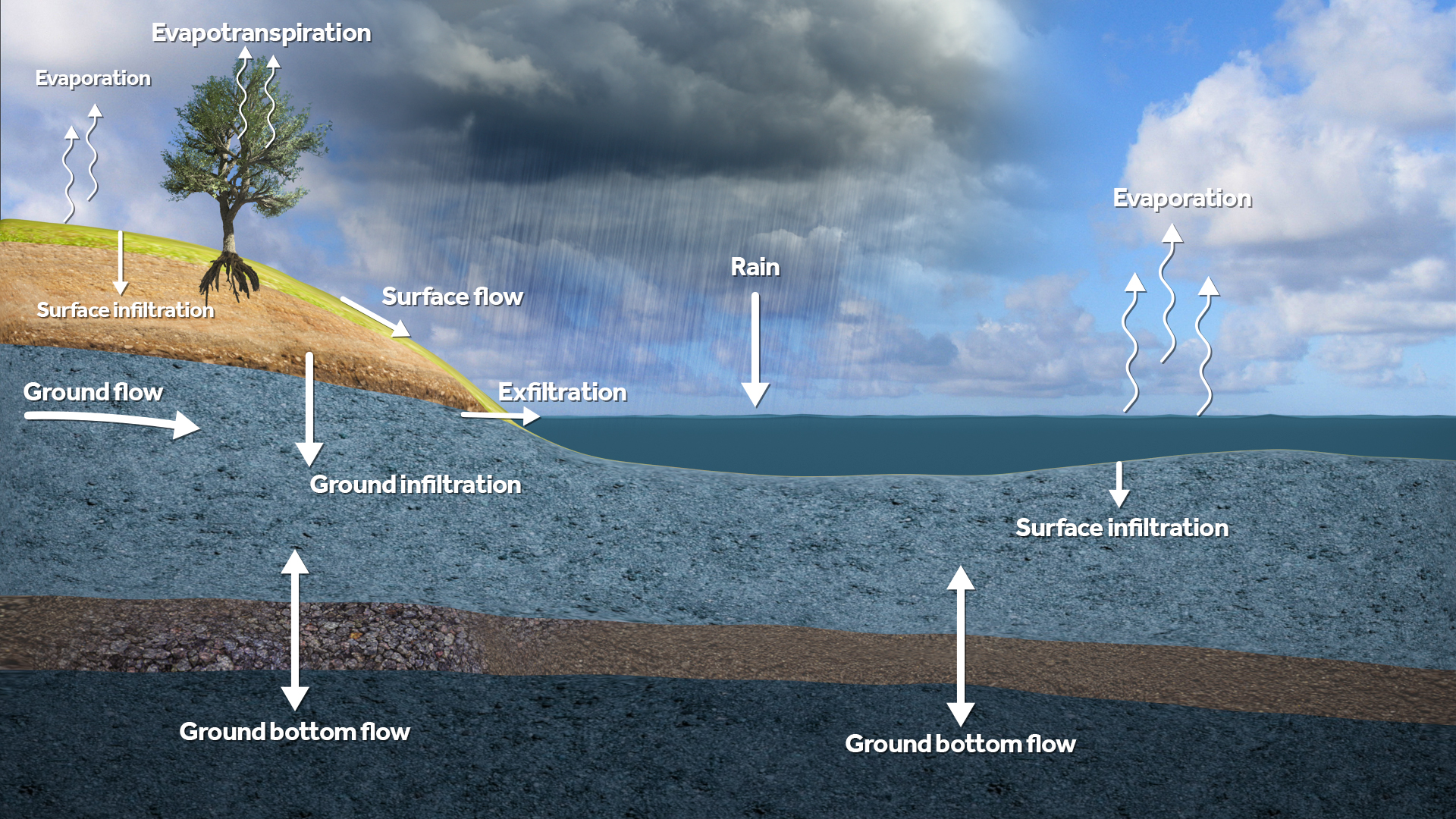
File:Water_module_flows.jpeg|Supported flows between the layers in rain, flooding and ground water calculations. | |||
</gallery> | |||
===Calculation Models=== | ===Calculation Models=== | ||
| Line 22: | Line 25: | ||
Multiple models are implemented which in conjunction form the water model in its entirety. | Multiple models are implemented which in conjunction form the water model in its entirety. | ||
<div style="column-count:2"> | |||
* [[Surface model (Water Overlay)]] | |||
* [[Ground model (Water Overlay)]] | |||
* [[Elevation model (Water Overlay)]] | |||
* [[Rain model (Water Overlay)]] | |||
* [[Infiltration model (Water Overlay)]] | |||
* [[Evaporation model (Water Overlay)]] | |||
* [[Storage model (Water Overlay)]] | |||
* [[Sewer model (Water Overlay)]] | |||
* [[Tracer flow model (Water_Overlay)]] | |||
* [[Border model (Water Overlay)]] | |||
* [[Breach model (Water Overlay)]] | |||
</div> | |||
===Formulas=== | |||
The precise calculations which govern the water overlay's simulation are many and varied, and based as much as possible on available expert knowledge. | The precise calculations which govern the water overlay's simulation are many and varied, and based as much as possible on available expert knowledge. | ||
Model | ====Model flow formulas==== | ||
* [[Surface water level formula (Water Overlay) | <div style="column-count:2"> | ||
* [[ | * [[Surface water level formula (Water Overlay)]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Surface flow formula (Water Overlay)]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Surface infiltration formula (Water Overlay)]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Surface evaporation formula (Water Overlay)]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Groundwater level formula (Water Overlay)]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Ground flow formula (Water Overlay)]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Ground infiltration formula (Water Overlay)]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Ground evaporation formula (Water Overlay)]] | ||
* [[Ground bottom flow formula (Water Overlay)]] | |||
</div> | |||
Hydraulic structure related | ====Hydraulic structure related formulas==== | ||
<div style="column-count:2"> | |||
* {{linkappend |postd= formula |post= formula (Water Overlay) | Culvert }} | * {{linkappend |postd= formula |post= formula (Water Overlay) | Culvert }} | ||
* {{linkappend |postd= formula |post= formula (Water Overlay) | Weir }} | * {{linkappend |postd= formula |post= formula (Water Overlay) | Weir }} | ||
| Line 57: | Line 65: | ||
* {{linkappend |postd= formula |post= formula (Water Overlay) | Inlet }} | * {{linkappend |postd= formula |post= formula (Water Overlay) | Inlet }} | ||
* {{linkappend |postd= formula |post= formula (Water Overlay) | Drainage }} | * {{linkappend |postd= formula |post= formula (Water Overlay) | Drainage }} | ||
</div> | |||
Module related | ====Module related formulas==== | ||
* [[Timestep formula (Water Overlay) | * [[Timestep formula (Water Overlay)]] | ||
* [[Season formula (Water Overlay)]] | |||
====Calculation related information==== | ====Calculation related information==== | ||
* [[Order of calculations (Water Overlay)|Order of calculations]] | * [[Order of calculations (Water Overlay)|Order of calculations]] | ||
{{ | {{WaterOverlay formula nav}} | ||
Latest revision as of 12:36, 5 March 2024
The following topics are described on this page:
- Introduction to the Water Module Theory
- Calculation modules Calculation Models
- Theories and formulas
- Computational structure and sequences
- Water Model Limits (some basic rules)
Introduction to the Water Module Theory
The Water Module in the Tygron Platform is an implementation of a 2D grid based shallow water model, based on the 2D Saint Venant equations (see Surface Model). The module is further enhanced with infiltration, evaporation, groundwater flow and hydraulic structures.
To perform the calculations, the project area is first rasterized into a large grid of cells. Each cell has a specific quantity of water and specific hydrological parameters based on the data in the project. The total time which should be simulated is divided into discrete timesteps. Per timestep, each cell communicates with its adjacent cells to exchange water, based on it's water level, surface height, current flow direction and other factors. Accuracy and reliability is obtained by dividing the project area and simulation time into sufficiently small cells and steps, at the cost of more computation time. Take a look at the testbed water module project, available in all domains, to see some of the components of the Water Module in a project.
The Water Module enables users to implement a water model for their project which is accurate and delivers fast results. To ensure accuracy, the Water Module is repeatedly tested against multiple (internationally) acknowledged hydrological benchmarks and tests. Fast results are achieved by executing the water calculations on High performance GPU servers.
Calculation Models
The Water Module performs a large number of calculations to form a complete hydrological simulation. Depending on the desired viewpoint, both the overarching concepts as well as the implemented formulas can be reviewed for detailed insight into how the water overlay works.
Multiple models are implemented which in conjunction form the water model in its entirety.
- Surface model (Water Overlay)
- Ground model (Water Overlay)
- Elevation model (Water Overlay)
- Rain model (Water Overlay)
- Infiltration model (Water Overlay)
- Evaporation model (Water Overlay)
- Storage model (Water Overlay)
- Sewer model (Water Overlay)
- Tracer flow model (Water_Overlay)
- Border model (Water Overlay)
- Breach model (Water Overlay)
Formulas
The precise calculations which govern the water overlay's simulation are many and varied, and based as much as possible on available expert knowledge.
Model flow formulas
- Surface water level formula (Water Overlay)
- Surface flow formula (Water Overlay)
- Surface infiltration formula (Water Overlay)
- Surface evaporation formula (Water Overlay)
- Groundwater level formula (Water Overlay)
- Ground flow formula (Water Overlay)
- Ground infiltration formula (Water Overlay)
- Ground evaporation formula (Water Overlay)
- Ground bottom flow formula (Water Overlay)