Attribute Overlay: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
[[File:Overlays-right-attributeoverlay.jpg|framed|left|The [[Right Panel]] when an attribute overlay is selected.]] | [[File:Overlays-right-attributeoverlay.jpg|framed|left|The [[Right Panel]] when an attribute overlay is selected.]] | ||
By default, the overlay does not display any relevant information. The properties of this overlay must be configured first, most notably the attribute based on which to highlight data. | By default, the overlay does not display any relevant information. The properties of this overlay must be configured first, most notably the attribute based on which to highlight data. | ||
==Create an Attribute Overlay== | ==Create an Attribute Overlay== | ||
Revision as of 09:13, 13 September 2018
What the Average overlay is
The attribute overlay is an overlay which displays the presence of a specific attribute in a data layer. A data type, such as buildings, neighborhoods, or areas, is checked. If the data has the specified attribute, it is highlighted in the 3D world by the overlay.
Additional information displayed in hover panel
[[File:|thumb|250px|left|The attribute overlay of the xxx.]]
When a specific (highlighted) location in the 3D world is clicked, the hover panel can display additional information on the underlying data. The name of the data item being highlighted is displayed, as well as the value of the attribute based on which it is being highlighted. For example, if buildings are highlighted with the TRAFFIC_FLOW, it will display the name of the building, some information on its size, and the TRAFFIC_FLOW value.
Purpose of the Attribute Overlay
The primary purpose of the attribute overlay is to highlight data with a specific attribute. This allows for simple, slightly dynamic visualizations of data such as:
- Buildings with traffic data.
- Zones with building height restrictions.
The overlay can be further enhanced with some in-software calculations or external processing. By calculating the desired color which should be used to display data (either using excels and TQL statements, or by preprocessing data in an external program and then loading the results in your project), it's possible to differentiate data in the map using multiple colors. This can allow you to visualize data such as:
- The ages of constructions.
- The types of buildings in the world.
- Self-calculated scores for areas or neighborhoods
For more information on how to realize the more dynamic use-cases, check the articles on Excel, TQL, the Geo Data Wizard, and color attributes.
Configuring the overlay
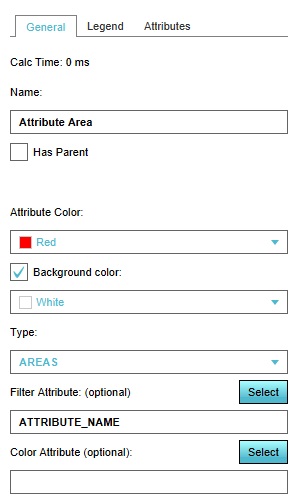
By default, the overlay does not display any relevant information. The properties of this overlay must be configured first, most notably the attribute based on which to highlight data.
Create an Attribute Overlay
- Select in the editor 'Geo Data' from the ribbon
- Select 'Overlays' from the ribbon bar
- Select the 'Add Attribute' overlay
- XXX
Selection type
Select attribute value
Select Layer
Attributes can be assigned to one of more layers in the 3D model: Buildings, Terrains, Areas and Neighborhoods. In this step you can select the following options for choosing which attribute values you would like to see:
- Filter occurrence in Layers: an attribute value is selected from order of occurrence in the model data layers mentioned above
- Minimum values in Layers. The minimum value is selected from all layers above
- Maximum values in Layers. The maximum value is selected from all layers above
- Specific Layer only. A specific layer can be selected.
- Select in the editor 'Geo Data' from the ribbon
- Select 'Overlays' from the ribbon bar
- Select the desired overlay from the list of active overlays on the left panel
- Select 'remove' from the bottom of the left panel
- Confirm the removal in the pop up confirmation message
