How to configure the Water Overlays: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
==Multi Breach simulation== | ==Multi Breach simulation== | ||
It is also possible to simulate multiple breaches. | |||
Therefore we also make use of the variable Outlet Q as mentioned above in the previous use case. | |||
==Import data with waterdepths== | ==Import data with waterdepths== | ||
Revision as of 12:45, 24 October 2018
Please note: This page is currently being updated.
This page describes several use cases and examples of configurations in the Flooding Overlay.
Time-controlled flow rate in a Breach area
To create a variable Outlet Q in a breach area, a CSV (comma-separated values) file can be imported. Below the steps on how to create such a breach area. For this example we create the CSV in Excel, but you can also use another program to create the CSV.
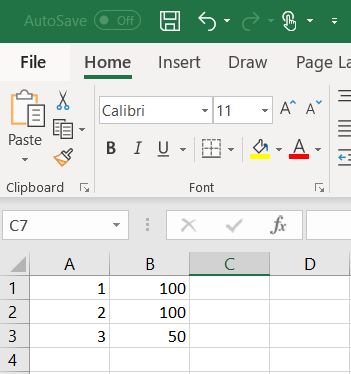
How to set-up your CSV in Excel:
- Open Excel.
- In the first column, define your time steps. This can be in seconds, minutes, hours or days.
- Add the corresponding flow rates per step in the second column.
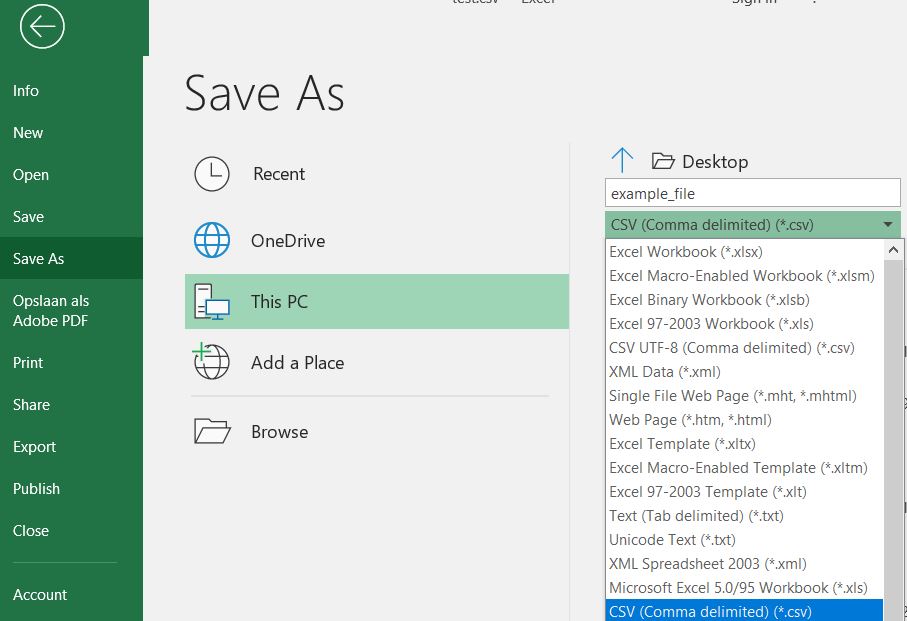
- Save the Excel as a CSV.
How to import the CSV as the flow rate:
- Either add a breach area or have your GeoJSON file with your breach area ready. The area should have at least a breach floor attribute.
- Add a Flooding Overlay.
- Go to the Configuration Wizard of the Flooding Overlay.
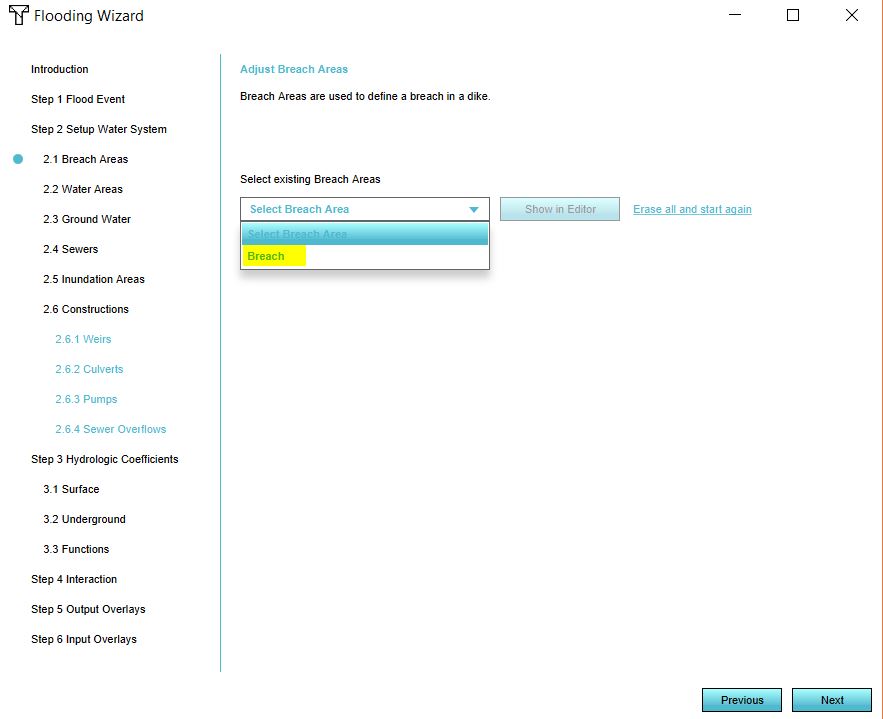
- In step 2.1 either select the attribute that specifies your breach_floor or import your GeoJSON file.
- Click on Next.
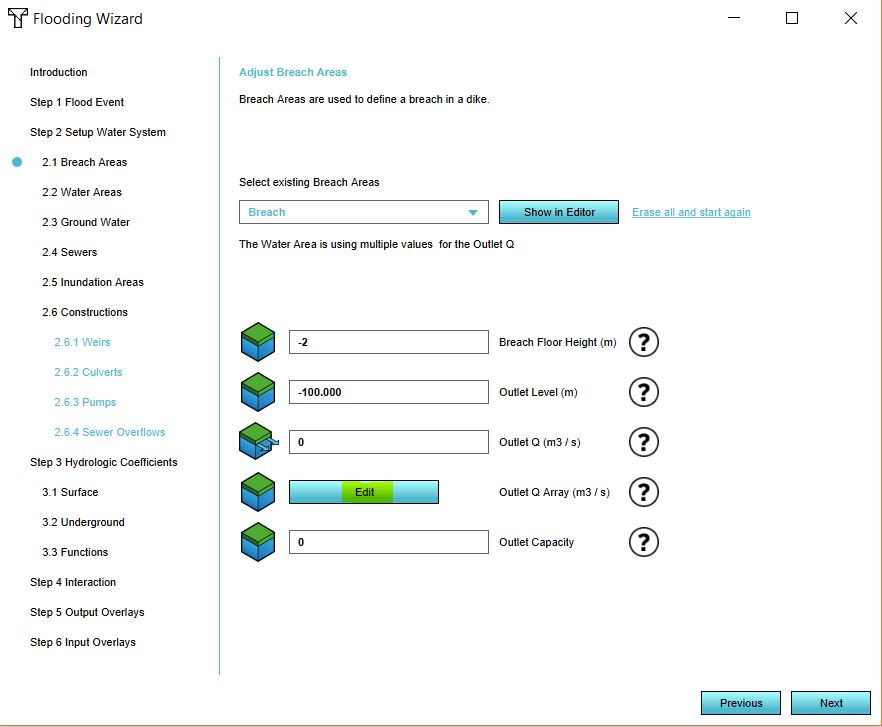
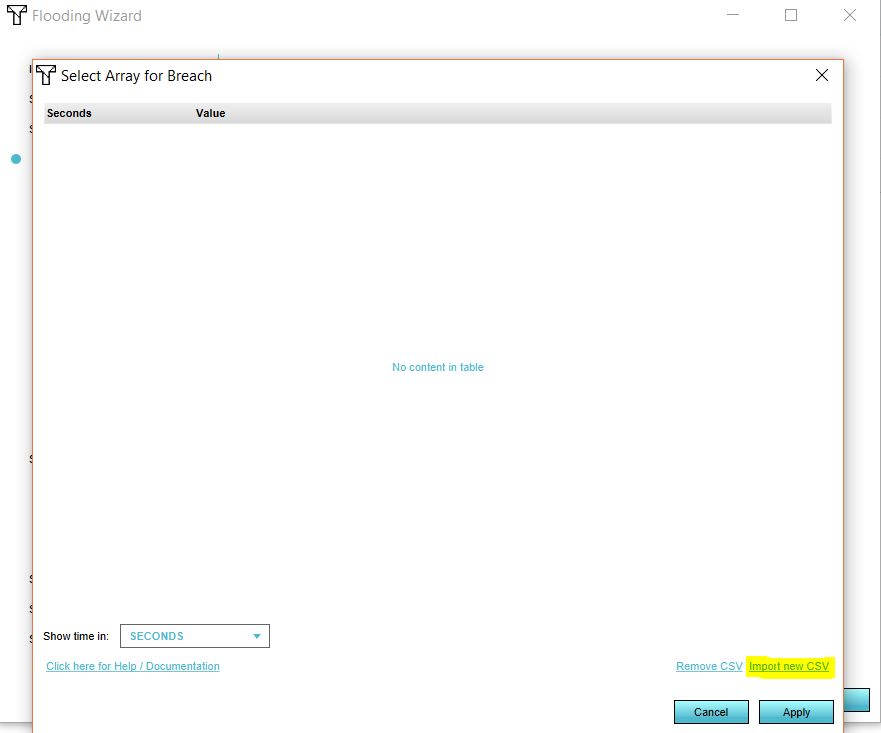
- In the dropdown menu, select your breach area. Now click on Edit.
- Import your CSV file by selecting the CSV file.
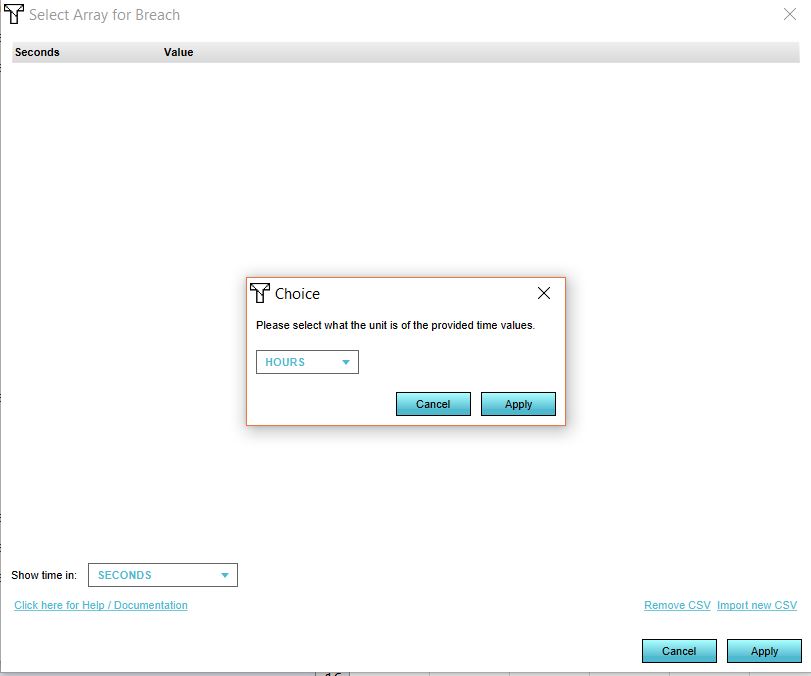
- Select the time units in your file.
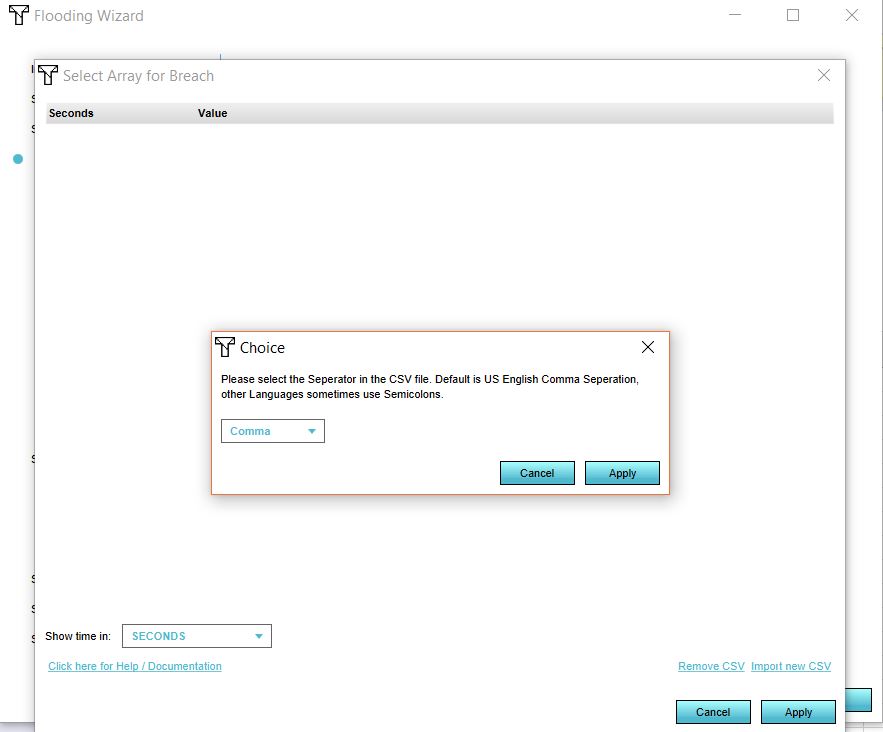
- Select the seperator for your file.
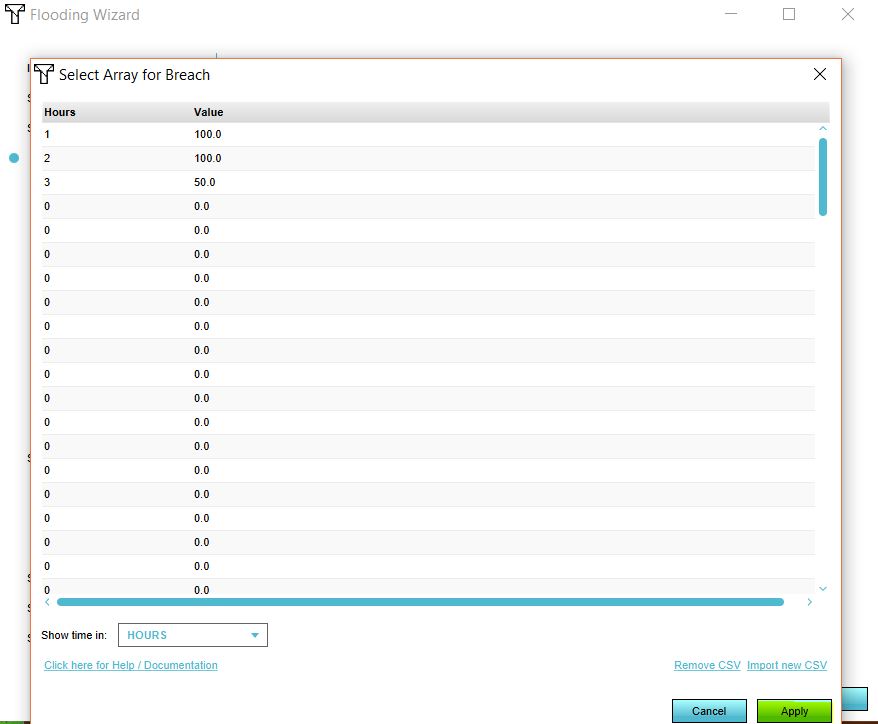
- Click on Apply.
Multi Breach simulation
It is also possible to simulate multiple breaches. Therefore we also make use of the variable Outlet Q as mentioned above in the previous use case.