Waterway level change benchmark (Water Module): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
The formula erf is the complementary error function. | The formula erf is the complementary error function. | ||
<math> erf(z) = \frac{2}{\sqrt(\pi} | <math> erf(z) = \frac{2}{\sqrt(\pi}}e^(-t^2)dt</math> | ||
<math> erfc(z) = 1 - erf(z)</math> | <math> erfc(z) = 1 - erf(z)</math> | ||
Revision as of 09:20, 11 December 2020
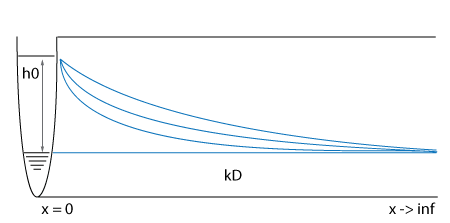 Initially, the ground water table is the same as the water level in the waterway. Suddenly the level in the waterway rises with h0 meters. This causes water to infiltrate into the ground, raising the ground water table.
Initially, the ground water table is the same as the water level in the waterway. Suddenly the level in the waterway rises with h0 meters. This causes water to infiltrate into the ground, raising the ground water table.
Formulas
When the water level in the water way changes, the water table level will also change over time. The relation between water level in the waterway and the ground water table at distance x from the water way is described by the following formulas: Water level raised:
Water level lowered:
The formula erf is the complementary error function. Failed to parse (syntax error): {\displaystyle erf(z) = \frac{2}{\sqrt(\pi}}e^(-t^2)dt}
where:
- : change in freatic groundwater table (m)
- : change in water level in the waterway(m)
- : distance to the water way (m)
- : time since the water level change
- : transmissivity of the aquifer (m2 / day)
- : freatic water storage fraction.








