Exporting Blender models to CityJSON: Difference between revisions
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
4. Add a new shapefile layer and choose polygon as mode of drawing.<br><br> | 4. Add a new shapefile layer and choose polygon as mode of drawing.<br><br> | ||
[[File:Nieuwe_kaartlaag.png|300px]]<br>''Add new shapefile layer.''<br><br> | [[File:Nieuwe_kaartlaag.png|300px]]<br>''Add new shapefile layer.''<br><br> | ||
5. Activate the Edit setting (The yellow pencil icon) and add a new object. This will start polygon drawing on the map.<br> | |||
6. Draw a square polygon or any shape to outline where your 3d model should ultimately fit in the location. We will use this polygon as a reference in Blender to move our 3d object on to.<br><br> | |||
[[File:Draw_polygon.jpg|300px]]<br><br> | |||
7. Click on the save edit icon next to the edit object icon (yellow pencil). This will save any edits for this object. Note that this is a different save than the normal file save.<br><br> | |||
[[File:Edit_tools.png|300px]] | |||
Revision as of 11:54, 29 March 2021
Introduction
It is possible to import CityGML file into the Tygron Platform. This article deals with exporting a Blender model to CityJSON so that it can be imported into the Tygron Platform via the CityGML importer.
(Blender is the free and open source 3D creation suite. To learn more about blender visit https://www.blender.org/ or https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blender_(software))
In order to export Blender models to CityJSON we first need to install the Up3date exporter and install it as an add-on in to Blender. This add-on was originally developed by Konstantinos Mastorakis (konmast3r) as part of their research orientation project for the MSc Geomatics programme of TU Delft. Its functionality was further developed for the needs of their MSc thesis An integrative workflow for 3D city model versioning.
To read the documentation go to https://github.com/cityjson/Up3date#exporting-a-3d-city-model.
Setting up the exporter in Blender.
1. Visit https://github.com/cityjson/Up3date and download the zip file from the green Code dropdown menu on the right side.
2. Open Blender and go to Edit -> Preferences.
3. In the preference dialog click on "Add-ons". You can see a list of the add-ons which are available for Blender.
4. Click on "Install" in the top right and select the zip file which you have downloaded.
5. After install the exporter will be available in the list. (Import-Export: Import CityGML)
6. Click on the checkbox next to it to activate the exporter.
7. Close the Preferences dialog.
Preparing your model for export
There is a small setup needed in order to export your model succesfully to CityJSON. This consists of naming conventions and custom properties that need to be added to your model and Blender environment. Another important issue is the Levels of Detail that need to be setup. CityGML supports 4 levels. from 0 to 4. 0 is the most low resolution version of the model. This means the polycount is very small. 4 is the most dense. Levels of Detail are primarily used in real time engines like the Tygron Platform to load the appropriate size model for the particular zoom level. This helps reduce memory when a large area is displayed. In this setup we will be using the Level of Detail 2. If you have have more the workflow is the same and just repeat it for the other levels. (Consult screenshots for more clarification)
1. Rename your collection (name of the group the model is in) in the outliner to "LoD2" by double clicking on it. Make sure that your model is part of this collection.
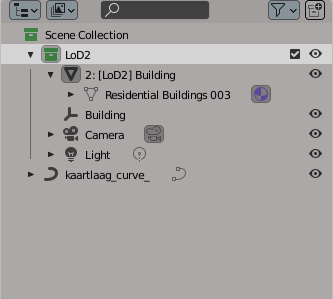
The outliner in Blender.
2. Rename your model to the following specification: 0: [LoD0] ID_of_object. The "0" represents the LOD and "ID-of_object" represents the name of the object. So for example a level 2 house model could be renamed as: 2: [LoD2] Building
3. In the object properties add 2 new custom properties to your model:
- type: the_surface_type (Surface, MultiSurface, CompositeSurface and Solid are accepted)
- lod : the_number_of_lod
So for this example the type would be "Solid" and the lod would be "2"
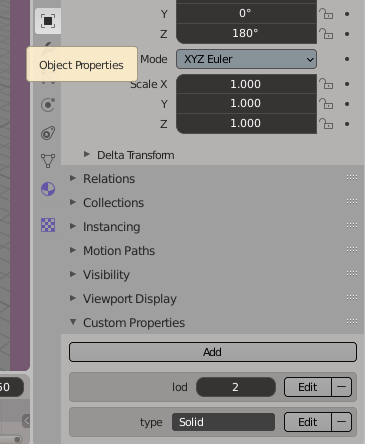
Add object properties.
4. Add an empty object to the Lod2 Collection and rename it to the "ID_of_object". So in this example it would be "Building".
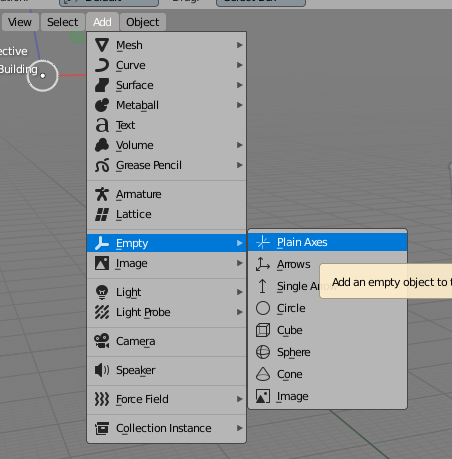
Add empty object.
5. Add a custom property to the empty object:
- type: Building
You could add more properties to the object as needed such as "address.PostalCode: 0000AB". This depends on what meta information you would like to export with your model.
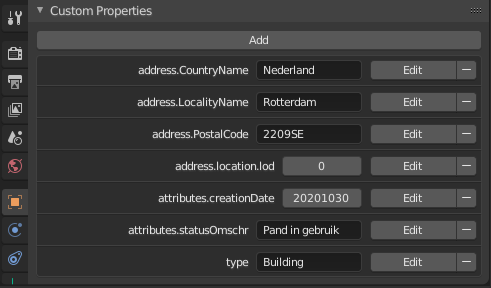
An example of more properties.
6. Finally add a new property to the Environment settings in Blender. Here we will tell the exporter to export the georeference coordinate system which we want. In this example we will be using: CRS:urn:ogc:def:crs:EPSG::3857
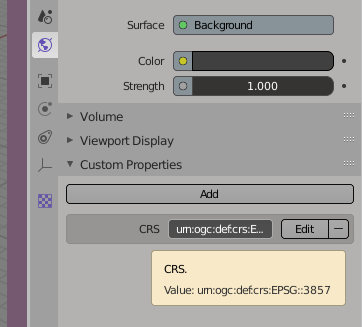
Add environment properties.
7. If you have any materials add a new property to the material under the custom properties section in the materials tab. Make sure you have the material selected. If you have multiple materials add custom properties to these as well. You can choose the following: type: Semantic_name (WallSurface, RoofSurface, GroundSurface) So for this example we will use only Wallsurface and add the property as this: type:WallSurface.
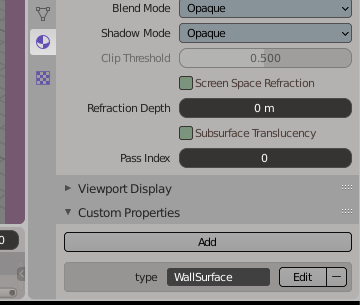
Add material property
Georeference your model
One of the issues when dealing with non-GIS based 3d modelling software is the absence of any Georeference systems. This means that a model exists only in "Blender" local space and not necessarily in an geographic location. Most reference systems work with degrees and not with metric or imperial units. So how do we know where our model should be located when exporting it from Blender with the correct reference system. Remember we used in this example the CRS:urn:ogc:def:crs:EPSG::3857 system. To fix the location we will need different GIS enabled software to help us out. In this example we will be using QGIS which is an open source package which handles georeferencing with ease. To download QGIS go to: https://qgis.org/en/site/
This walkthrough assumes you have some knowledge with QGIS.
1. Make a new project.
2. Connect to a WMS service and choose the background map which should be shown.
3. Make sure you choose the "WGS 84 / Pseudo Mercator" "EPSG:3857" Reference System for use with this example by going to project settings and choosing the right system in the CRS tab. If you use a different system make sure that the sysytem is added as a property in step 6 of "preparing your model for export" (This will correspond with the system we have added as a property to the Blender Environment, namely: CRS:urn:ogc:def:crs:EPSG::3857).
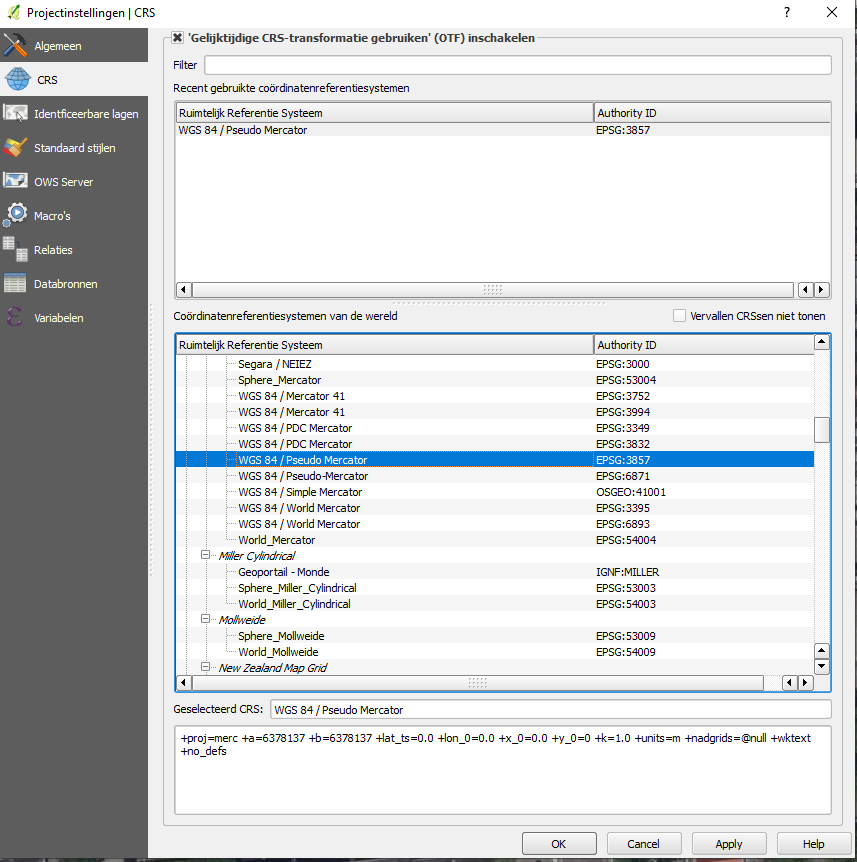
CRS settings.
4. Add a new shapefile layer and choose polygon as mode of drawing.
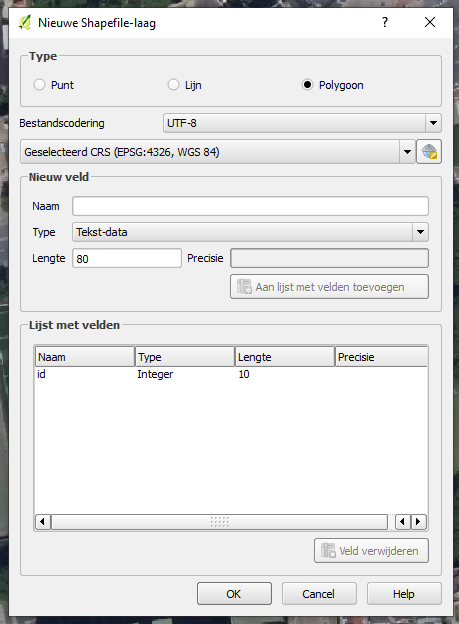
Add new shapefile layer.
5. Activate the Edit setting (The yellow pencil icon) and add a new object. This will start polygon drawing on the map.
6. Draw a square polygon or any shape to outline where your 3d model should ultimately fit in the location. We will use this polygon as a reference in Blender to move our 3d object on to.
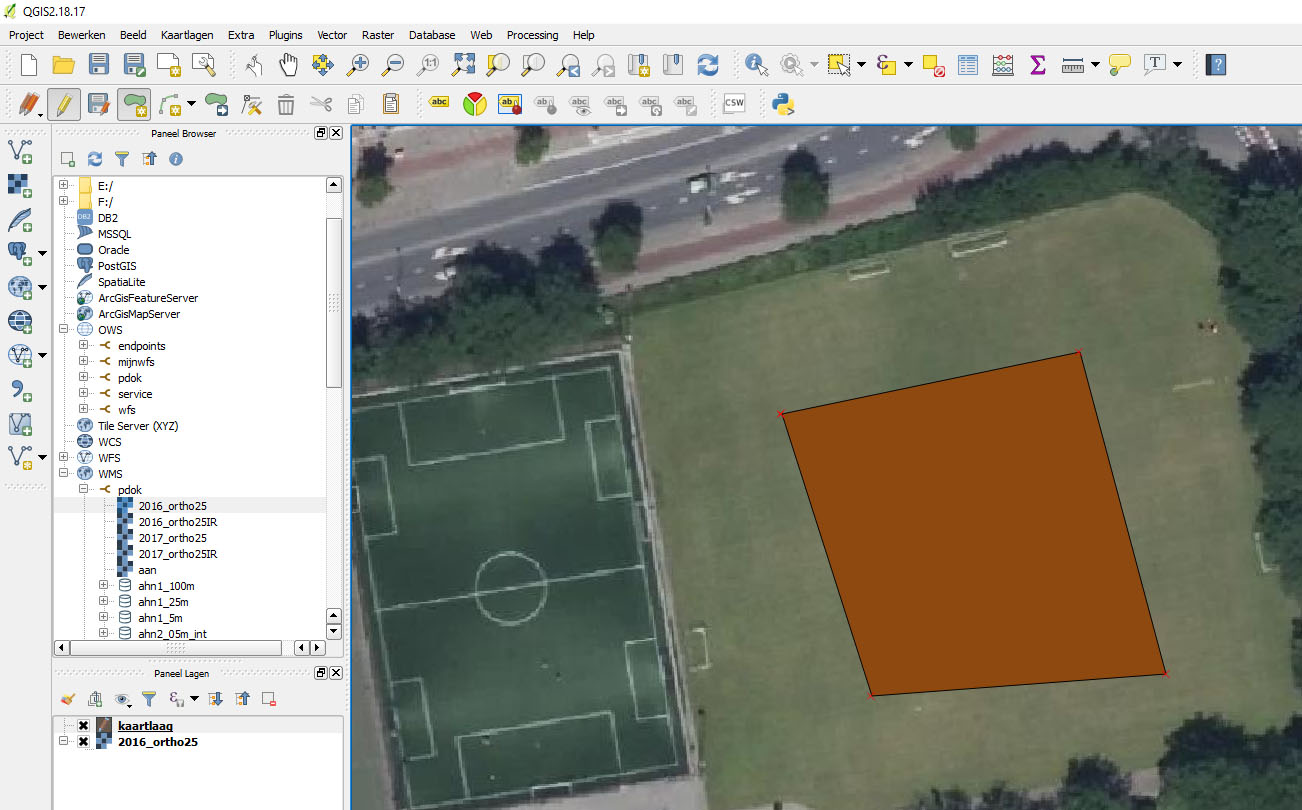
7. Click on the save edit icon next to the edit object icon (yellow pencil). This will save any edits for this object. Note that this is a different save than the normal file save.