Ground water depth formula (Subsidence Overlay): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (29 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
At the start of a simulation, the ground water depth is initialized with the [[Ground water | {{deprecated}} | ||
At the start of a simulation, the ground water depth is initialized with the [[Ground water GeoTIFF (Subsidence Overlay)|ground water depth GeoTIFF]] (if provided) and is optionally overwritten by (managed) water areas' water level. | |||
Furthermore, the ground water level can be managed with [[Drainage | Furthermore, the ground water level can be managed with [[Drainage feature (Subsidence Overlay)|drainages]] (provided as underground buildings), either [[Drainage (Subsidence Overlay)|actively]] or [[Low passive_drainage (Subsidence Overlay)|passively]]. | ||
Additionally the terrain height can change due to subsidence that occurred in previous years and due to actions taken that raised the terrain. Managed water | Additionally the terrain height can change due to subsidence that occurred in previous years and due to actions taken that raised the terrain. Managed water areas can react to these changes when indexation is configured. For indexation, see [[Indexation formula (Subsidence Overlay)|indexation formula]]. | ||
The [[Ground water depth formula (Subsidence Overlay)|following formulas]] describe how the yearly adjusted ground water depths are obtained. | The [[Ground water depth formula (Subsidence Overlay)|following formulas]] describe how the yearly adjusted ground water depths are obtained. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 18: | ||
where | where | ||
: <math>d_{gw,y}</math> is the calculated ground water depth of a grid cell at year y. | |||
: <math>d_{d,active}</math> is the ground water depth actively maintained by a drainage | |||
: <math>d_{a}</math> is the ground water depth of the managed water area. | |||
: <math>\Delta{d_{a,y}}</math> is the area water level adjustment for year y. | |||
: <math>d_{d, passive}</math> is the ground water level passively maintained by drainages. | |||
: <math>\Delta{d_{a,s,y}}</math> is the [[#Ground water level managed by water areas|ground water level increase]] calculated based on the are water level adjustment due to indexation and the subsidence in the previous year. | |||
====Ground water level managed by water | ====Ground water level managed by water areas==== | ||
[[File:ground-water-graph.jpg|400px|thumb|right|The effect of changes of managed surface water levels (by water | [[File:ground-water-graph.jpg|400px|thumb|right|The effect of changes of managed surface water levels (by water areas) on the ground water level. The x-axis indicates the relative depth of the managed surface water level. The y-axis indicates the meters of change to the ground water level, per meter change in surface water level. The smaller the relative depth is, the less the ground water level equalizes with changes in the managed surface water level.]] | ||
The ground water level can also be managed by water | The ground water level can also be managed by water areas, which control the surface water levels. To make sure ground water levels do not rise (too much), surface water levels in the water areas can be lowered automatically with respect to the subsidence. This process is called indexation. The new ground water level can then be estimated based on the indexation on the managed water level of surface water and the calculated subsidence of the previous year. The increment in ground water level is rarely exactly the adjustment of the managed surface water level and is often less, depending on the relative depth of the surface water level. The following formulas have been developed to estimate the increase of the ground water level. | ||
The new relative surface water level depth is calculated as: | The new relative surface water level depth is calculated as: | ||
<math>\Delta{d_{inc}} = - \Delta{d_{a,y}} - s_{y-1}</math> | <math>\Delta{d_{inc}} = - \Delta{d_{a,y-1}} - s_{y-1}</math> | ||
<math>d_{a,adj} = d_{a} + \Delta{d_{inc}}</math> | <math>d_{a,adj} = d_{a} + \Delta{d_{inc}}</math> | ||
| Line 36: | Line 37: | ||
Next, based on the old and new depths, the ground water depth change is divided into three sections, each which its own rate of contribution. | Next, based on the old and new depths, the ground water depth change is divided into three sections, each which its own rate of contribution. | ||
<math>\Delta{d_{low}} = 0.6 \cdot | <math>\Delta{d_{low}} = 0.6 \cdot min(0.6, d_{a,adj})- min(0.6, d_{a})</math> | ||
<math>\Delta{d_{mid}} = \frac{\max(0.6, min(1.0, d_{a,adj}))+ max(0.6, min(1.0, d_{a}))}{2.0} \cdot (\max(0.6, min(1.0, d_{a,adj}))- max(0.6, min(1.0, d_{a})))</math> | <math>\Delta{d_{mid}} = \frac{\max(0.6, min(1.0, d_{a,adj}))+ max(0.6, min(1.0, d_{a}))}{2.0} \cdot (\max(0.6, min(1.0, d_{a,adj}))- max(0.6, min(1.0, d_{a})))</math> | ||
| Line 44: | Line 45: | ||
Finally, the ground water depth change is calculated and the new ground water depth is obtained: | Finally, the ground water depth change is calculated and the new ground water depth is obtained: | ||
<math>\Delta{d_{ | <math>\Delta{d_{gw,y}} = \Delta{d_{low}}+\Delta{d_{mid}}+\Delta{d_{high}}</math> | ||
<math>d_{gw,y} = max(0.0, d_{gw} + \Delta{d_{ | <math>d_{gw,y} = max(0.0, d_{gw,0} + \Delta{d_{gw,y}})</math> | ||
<noinclude> | where | ||
===Ground Water change examples=== | : <math>d_{a} </math> is the current relative water depth of water area a. | ||
: <math>d_{a,adj}</math> is the adjusted relative water depth of water area a. | |||
: <math>\Delta{d_{a,y-1}}></math> is the water level adjustment for indexation of current year y. | |||
: <math>s_{y-1}</math> is the subsidence that occurred up to year y. | |||
: <math>d_{gw,y}</math> is the calculated adjusted ground water depth for year y, based on the occurred subsidence and indexation of previous years. | |||
: <math>d_{gw,0}</math> is the initial ground water depth at the start of the simulation. | |||
: <math>\Delta{d_{gw,y}}</math> is the estimated change of the ground water level based on occurred subsidence and indexation.<noinclude> | |||
====Inundation==== | |||
Initially, or due to subsidence, the surface height of a cell can be lower than the configured water level. In such case, for certain situations, it can be said that the cell is therefore inundated by water from the nearby waterway. When inundated, the cell's ground water level will most certainly raise to the surface level. | |||
This option is can be turned on and off using the subsidence overlay model attribute [[Inundate land below water level (Subsidence Overlay)|Inundate land below water level]]. | |||
In case this option is turned on, the following case is handled before drainage and ground water depth adjustments are considered. | |||
<math> | |||
\begin{cases} | |||
d_{gw,y} = | |||
0, & \text{if } d_{a} + \Delta{d_{inc}} < 0 \\ | |||
d_{gw,y}, & \text{otherwise} \\ | |||
\end{cases} | |||
</math> | |||
: <math>d_{a} </math> is the current relative water depth of water area a. | |||
: <math>d_{gw,y}</math> is the calculated adjusted ground water depth for year y, based on the occurred subsidence and indexation of previous years. | |||
: <math>\Delta{d_{inc}}</math> is the estimated change of the ground water level based on occurred subsidence and indexation, described in the previous section. | |||
====Ground Water change examples==== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! Terrain height (m) | ! Terrain height (m) | ||
! Water area level (m, start) | ! Water area level (m, start) | ||
! Water area level (m, changed) | ! Water area level (m, changed) | ||
! Difference between ground water level and surface water level | ! Difference (m) between ground water level and surface water level | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2.4 | | 2.4 | ||
| Line 74: | Line 101: | ||
This method of ground water level adjustment is applied when, during a session, the surface water level changes. This can be due to user input (i.e.: the user changes the water level attribute of an area), or because indexation (or lack thereof) moves the surface water level (and thus the ground water level) relative to the surface. | This method of ground water level adjustment is applied when, during a session, the surface water level changes. This can be due to user input (i.e.: the user changes the water level attribute of an area), or because indexation (or lack thereof) moves the surface water level (and thus the ground water level) relative to the surface. | ||
= | {{article end | ||
|notes= | |||
* Which ground water level should be taken depends on the use-case. For subsidence the lowest ground water level (Mean Lowest Watertable, or MLW, in English. GLG in Dutch.) is most commonly used. It is preferred because oxidation occurs more easily when the ground water level is lower.<br>However, the highest (adjusted) ground water level overlay is also available as an overlay result. (Mean Highest Watertable, or MHW, in English. GHG in Dutch.)<br>See also (PDF): [[Media:Wind (1986) Slootpeilverlaging en grondwaterstandsdaling in veenweidegebieden.pdf|Wind (1986) Slootpeilverlaging en grondwaterstandsdaling in veenweidegebieden (Ditch water level reduction and groundwater level decrease in peat meadow areas - Dutch only)]] | |||
See also (PDF): [[Media:Wind (1986) Slootpeilverlaging en grondwaterstandsdaling in veenweidegebieden.pdf|Wind (1986) Slootpeilverlaging en grondwaterstandsdaling in veenweidegebieden (Ditch water level reduction and groundwater level decrease in peat meadow areas - Dutch only)]] | |seealso= | ||
* [[Drainage feature (Subsidence Overlay)|Drainage]] | |||
* [[Hi ground water result type (Subsidence Overlay)|Hi ground water result type]] | |||
* [[Low ground water result type (Subsidence Overlay)|Low ground water result type]] | |||
}} | |||
{{Template:SubsidenceOverlay_nav}} | |||
Latest revision as of 08:01, 9 October 2025
At the start of a simulation, the ground water depth is initialized with the ground water depth GeoTIFF (if provided) and is optionally overwritten by (managed) water areas' water level.
Furthermore, the ground water level can be managed with drainages (provided as underground buildings), either actively or passively.
Additionally the terrain height can change due to subsidence that occurred in previous years and due to actions taken that raised the terrain. Managed water areas can react to these changes when indexation is configured. For indexation, see indexation formula.
The following formulas describe how the yearly adjusted ground water depths are obtained.
Ground water level managed by drainages
where
- is the calculated ground water depth of a grid cell at year y.
- is the ground water depth actively maintained by a drainage
- is the ground water depth of the managed water area.
- is the area water level adjustment for year y.
- is the ground water level passively maintained by drainages.
- is the ground water level increase calculated based on the are water level adjustment due to indexation and the subsidence in the previous year.
Ground water level managed by water areas
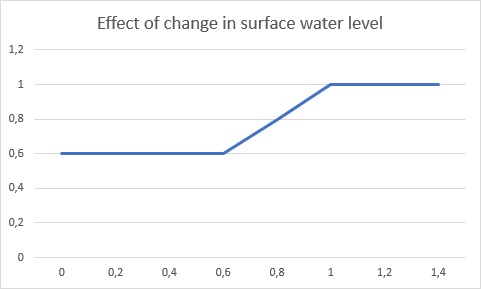
The ground water level can also be managed by water areas, which control the surface water levels. To make sure ground water levels do not rise (too much), surface water levels in the water areas can be lowered automatically with respect to the subsidence. This process is called indexation. The new ground water level can then be estimated based on the indexation on the managed water level of surface water and the calculated subsidence of the previous year. The increment in ground water level is rarely exactly the adjustment of the managed surface water level and is often less, depending on the relative depth of the surface water level. The following formulas have been developed to estimate the increase of the ground water level.
The new relative surface water level depth is calculated as:
Next, based on the old and new depths, the ground water depth change is divided into three sections, each which its own rate of contribution.
Finally, the ground water depth change is calculated and the new ground water depth is obtained:
where
- is the current relative water depth of water area a.
- is the adjusted relative water depth of water area a.
- is the water level adjustment for indexation of current year y.
- is the subsidence that occurred up to year y.
- is the calculated adjusted ground water depth for year y, based on the occurred subsidence and indexation of previous years.
- is the initial ground water depth at the start of the simulation.
- is the estimated change of the ground water level based on occurred subsidence and indexation.
Inundation
Initially, or due to subsidence, the surface height of a cell can be lower than the configured water level. In such case, for certain situations, it can be said that the cell is therefore inundated by water from the nearby waterway. When inundated, the cell's ground water level will most certainly raise to the surface level. This option is can be turned on and off using the subsidence overlay model attribute Inundate land below water level.
In case this option is turned on, the following case is handled before drainage and ground water depth adjustments are considered.
- is the current relative water depth of water area a.
- is the calculated adjusted ground water depth for year y, based on the occurred subsidence and indexation of previous years.
- is the estimated change of the ground water level based on occurred subsidence and indexation, described in the previous section.
Ground Water change examples
| Terrain height (m) | Water area level (m, start) | Water area level (m, changed) | Difference (m) between ground water level and surface water level |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.4 | 1.1 | 1.3 | -0.2 |
| 2.4 | 2.1 | 2.3 | -0.12 |
| 2.4 | 1.4 | 1.6 | -0.18 |
This method of ground water level adjustment is applied when, during a session, the surface water level changes. This can be due to user input (i.e.: the user changes the water level attribute of an area), or because indexation (or lack thereof) moves the surface water level (and thus the ground water level) relative to the surface.
Notes
- Which ground water level should be taken depends on the use-case. For subsidence the lowest ground water level (Mean Lowest Watertable, or MLW, in English. GLG in Dutch.) is most commonly used. It is preferred because oxidation occurs more easily when the ground water level is lower.
However, the highest (adjusted) ground water level overlay is also available as an overlay result. (Mean Highest Watertable, or MHW, in English. GHG in Dutch.)
See also (PDF): Wind (1986) Slootpeilverlaging en grondwaterstandsdaling in veenweidegebieden (Ditch water level reduction and groundwater level decrease in peat meadow areas - Dutch only)
See also