Sky view factor calculation model (Heat Overlay): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Sky limiters== | |||
The model starts by determining per grid cell what the height of obstacles are on that grid cell. An obstacle can be: | |||
* a building, | |||
* foliag. ,The top of foliage is used as the obstacle height. | |||
* terrain height. | |||
[[File:Sky_view_limiters.png|500px]] | [[File:Sky_view_limiters.png|500px]] | ||
Next, for each grid cell, the sky view sections are calculated for each consecutive pair of rays. In the previous image, you can see one such section. | |||
==Sky exposure versus sky view area== | |||
In literature, two sky parameters are mentioned that are sometimes confused: Sky exposure and sky view factor. | |||
Where the sky exposure is related to the sky view dome (3D) the sky view factor is related to the projection of the view dome to the horizontal plane. We can call the projected circle the view circle. | |||
In the second image, you can distinguish a sky view section on the dome and a section projected on the view circle. | |||
[[File:Sky_view_sections.png|500px]] | [[File:Sky_view_sections.png|500px]] | ||
== Sky view factor == | |||
The sky view factor can be calculated by dividing the sky view area by the area of the circle of the horizontal plane. | |||
The sky view area is simply the sum of the areas of each section. Each section area is calculated as an arc section. | |||
[[File:Sky_view_area.png|500px]] | |||
==Notes== | |||
* The size of the dome and sky circle do not matter, they can simply be a unit sphere and circle. Only the angle between the ray and the horizontal plane determine the sky view sections. | |||
Revision as of 12:22, 16 September 2019
Sky limiters
The model starts by determining per grid cell what the height of obstacles are on that grid cell. An obstacle can be:
- a building,
- foliag. ,The top of foliage is used as the obstacle height.
- terrain height.
Next, for each grid cell, the sky view sections are calculated for each consecutive pair of rays. In the previous image, you can see one such section.
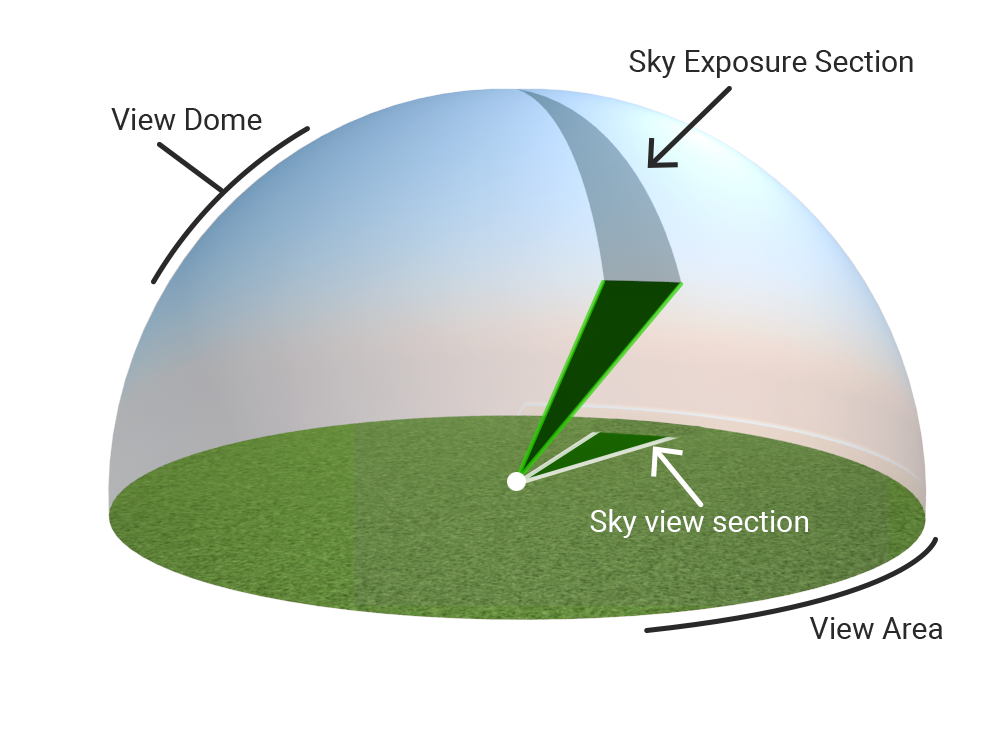
Sky exposure versus sky view area
In literature, two sky parameters are mentioned that are sometimes confused: Sky exposure and sky view factor.
Where the sky exposure is related to the sky view dome (3D) the sky view factor is related to the projection of the view dome to the horizontal plane. We can call the projected circle the view circle.
In the second image, you can distinguish a sky view section on the dome and a section projected on the view circle.
Sky view factor
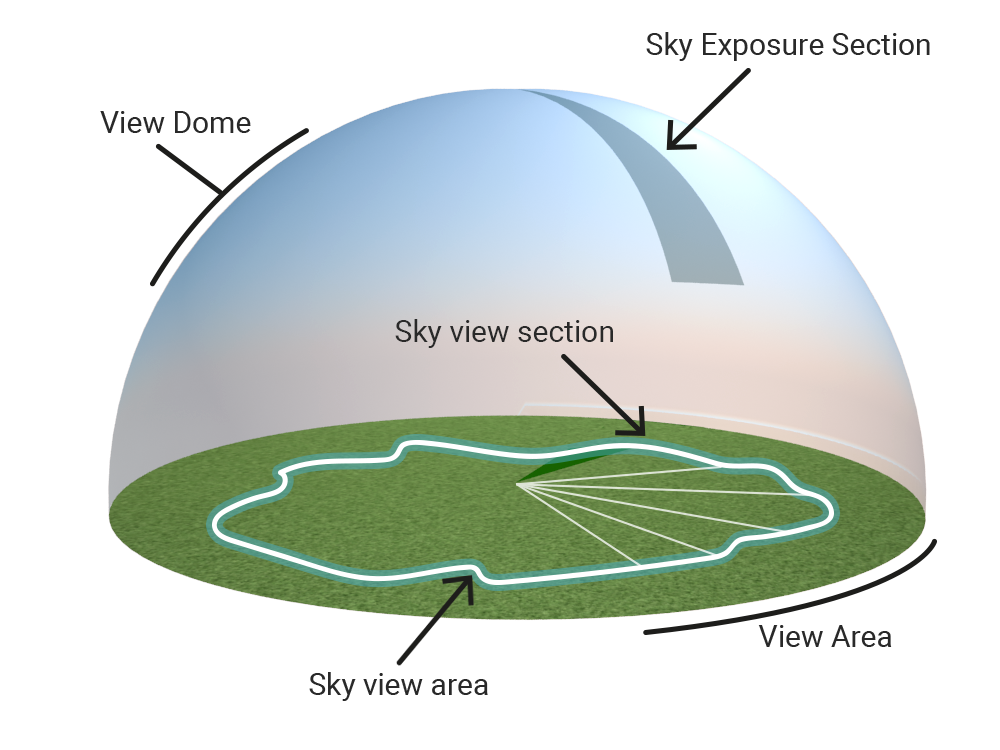
The sky view factor can be calculated by dividing the sky view area by the area of the circle of the horizontal plane.
The sky view area is simply the sum of the areas of each section. Each section area is calculated as an arc section.
Notes
- The size of the dome and sky circle do not matter, they can simply be a unit sphere and circle. Only the angle between the ray and the horizontal plane determine the sky view sections.
