Attribute: Difference between revisions
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
==Attributes in relation to the Tygron Engine== | ==Attributes in relation to the Tygron Engine== | ||
A number of spatial components, such as [[neighborhood]]s, [[area]]s, [[construction]]s and [[zone]]s, can be provided attributes. These components have attributes to provide information, often defined by the user, in addition to the default properties the components have. The Tygron Engine also stores or reflects a number of standard properties as attributes, meaning that these properties can easily be inspected or changed in the same way user-defined data can. | A number of spatial components, such as [[neighborhood]]s, [[area]]s, [[construction]]s and [[zone]]s, can be provided attributes. These components have attributes to provide information, often defined by the user, in addition to the default properties the components have. The Tygron Engine also stores or reflects a number of standard properties as attributes, meaning that these properties can easily be inspected or changed in the same way user-defined data can. | ||
[[Globals]] behave similarly to attributes, except that they are not part of any specific component in the project, but part of the project as a whole. | |||
==Attribute values== | ==Attribute values== | ||
Revision as of 11:13, 9 August 2016
What is an Attribute?
An attribute is a characteristic or (additional) property of something. Attributes are a common way to provide additional information or configuration for elements of data in software.
Attributes in relation to the Tygron Engine
A number of spatial components, such as neighborhoods, areas, constructions and zones, can be provided attributes. These components have attributes to provide information, often defined by the user, in addition to the default properties the components have. The Tygron Engine also stores or reflects a number of standard properties as attributes, meaning that these properties can easily be inspected or changed in the same way user-defined data can.
Globals behave similarly to attributes, except that they are not part of any specific component in the project, but part of the project as a whole.
Attribute values
An attribute always consists of a name and a value. The name of an attribute is usually written in capital letters, and uses underscores in place of spaces. The value must always be a number. It can be either a positive or a negative number. The number can also be a decimal number (I.e., the value is not necessarily a whole number).
Each component which can have attributes has their own list of attributes. When a given area has an attribute with a specific name, another area may or may not have an attribute with the same name as well. When 2 components have an attribute with the same name, their values are also still set per component. That means that they may coincidentally have the same value, but when the value of the attribute of one component is changed, the value of the attribute of the other component is not automatically changed as well.
Attribute values during a session
Attributes can be read during a session. Primarily, it is possible to read attributes of components using TQL. By requesting the value of an attribute of a component using TQL, the value of that attribute can be used in, for example, Excel calculations.
It is possible that, when requesting the value of an attribute of a component, that attribute does not exist for that component. In this case, the value of that attribute is deemed to be "0".
Note that this means that an attribute value of 0 can mean that the proper value of the attribute is 0, or that the attribute does not exist.
Attributes can also be changed during a session. This can be done either via Events or via TQL. Events, such as AREA_SET_ATTRIBUTE or ZONE_SET_ATTRIBUTE, can be used in the Engine to change the values of attributes. Attributes can also be changed using TQL, which means that attributes can be changed as a result of a calculation.
How to add and remove attributes
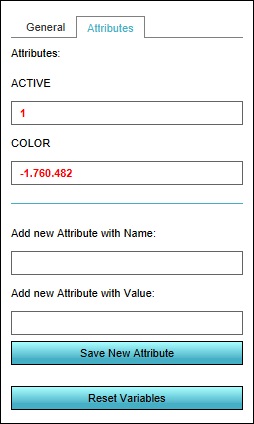
Attributes can be added to neighborhoods, areas, constructions and zones. In order to add, remove, or change an attribute for one of these Engine components, select the component in the left panel, and then select the attributes tab in the right panel. The attributes of that component will be displayed.
Adding attributes

To create a new attribute, enter the desired name for the new attribute in the "Add new Attribute with Name" field.
To create a new attribute, enter the desired value for the new attribute in the "Add new Attribute with Value" field.

Once an attribute name and a valid attribute value have been entered in the appropriate fields, the "Save New Attribute" button becomes available. Selecting it will add the attribute to the list of existing attributes for the component.
Removing attributes

To remove all attributes from a component, select the "Reset Variables" button.
Note that when you remove attributes which are related to properties of the component, the value of the properties will be changed as well, as though the attribute was set to "0".
It is currently not possible to remove individual attributes from a component. When desired, it is possible to set individual attributes to "0".
- Enter a name for the new attribute.
- Enter a value for the new attribute.
- Select "Save New Attribute".
- Select "Reset Variables".
Importing Attributes
When creating areas using GeoJSON, it is possible to have attributes created based on the same file. In the GeoJSON import window, you will have the option to select attributes of the imported shapes, and to store them as attributes in areas. The same restrictions apply for importing attributes as when normally creating or editing attributes. I.e. the values must be valid numbers.
- Option 1) Select the GeoJSON file in the folder Option 2)
Hoover over the desired component in the Editor and Select import GeoJSON file - In of case option 1 Drag and Drop the file in the Tygron Engine
- Select the desired input
- Make sure the attribute checkbox is checked
- Select the right attribute name
- Select the right attributes to import
- Select Send to import the attributes together with the imported area.
- Option 1) Select the GeoJSON file in the folder Option 2)
Edit attributes

The value of any attribute can be changed after it has been added to a component. In the list of attributes, the value field for any attribute can be selected. The value can be changed by entering a different value in the field. The value must be a valid number, or the new value is rejected immediately.
- Select the value of the attribute you wish to change.
- Change the value to a valid value.
- Press "Enter" to set the value.
Special attribute values
Some attributes may have a more exact spectrum of values which are valid. For example, the ACTIVE attribute is either 1 or a 0.
Note that for attributes like these, other number values are not automatically rejected. When the engine or a user-defined calculation depends on the attribute being within a specific range of values, and the actual value is a different, valid number, no guarantees can be made about the result.
Active
- Applies to: Areas
Some components may have an "active" property. When that property indicates the component is active, the "ACTIVE" attribute's value is "1". When the component is inactive, the attribute's value is "0".
Color
- Applies to: Areas, Neighborhoods, Zones
Many components with attributes automatically have a "COLOR" attribute added to them, the value of which is the same as the color property of that component. When that color property is changed, the attribute is changed, and vice versa.
The numeric value of the attribute corresponds with an RGB color value, calculated by combining the red, green and blue values of the desired color together, multiplied by powers of 256. The amount of red, green, and blue are values between 0 and 255, inclusive. These are added to a base value of -16777216. A proper color value can be calculated as follows: -16777216 + (red * 256²) + (green * 256) + (blue).
Urbanization
- Applies to: Neighborhoods
The "URBANIZATION" attribute is an indication of how deep within a city a neighborhood lies. It ranges from 1 (dense urbanization) to 5 (virtually no urbanization).
Nature Reserve
- Applies to: Areas
The "NATURE_RESERVE" attribute indicates whether an area is a protected area of nature. This usually means the allowance for pollution and noise is lower. Areas with an "NATURE_RESERVE" attribute value of "1" are deemed protected nature. When the attribute's value is 0, the area is not necessarily deemed protected nature.