Ground flow formula (Water Overlay): Difference between revisions
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
where: | where: | ||
: <math>w_{n,t}</math> = The [[Groundwater level formula (Water Overlay)|underground water level]] of cell <math>n</math> at time <math>t</math>. | : <math>w_{n,t}</math> = The [[Groundwater level formula (Water Overlay)|underground water level]] of cell <math>n</math> at time <math>t</math>. | ||
: <math>KD_n</math> = The hydraulic conductivity of the cell, multiplied with the thickness of the layer, defined in [[Terrain hydraulic conductivity with thickness md (Water Overlay)|HYDRAULIC_CONDUCTIVITY_WITH_THICKNESS_MD]] of the underground terrain. | : <math>KD_n</math> = The hydraulic conductivity of the cell, multiplied with the thickness of the layer, defined in [[Terrain hydraulic conductivity with thickness md (Water Overlay)|HYDRAULIC_CONDUCTIVITY_WITH_THICKNESS_MD]] of the underground terrain. | ||
: <math>\Delta w</math> = Underground water level difference at time <math>t</math>. | : <math>\Delta w</math> = Underground water level difference at time <math>t</math>. | ||
Revision as of 12:30, 25 January 2024
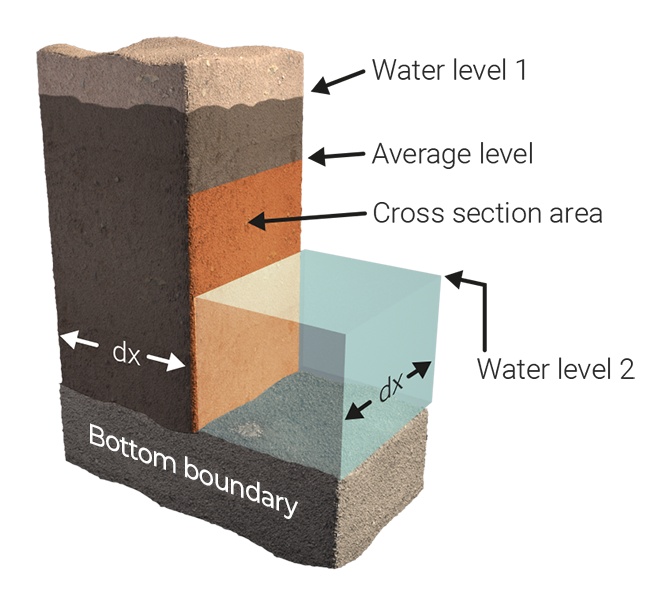
Underground flow is different from surface flow, since it has to account for the slowdown and porousness of the medium. In general, horizontal underground flow is calculated using formulas described in Harbaugh 2005[1][2]. However, when an aquifer is present, the Aquifer formula is applied.
It depends on the configuration of the HYDRAULIC_CONDUCTIVITY_WITH_THICKNESS attribute value in the Water Overlay what Hydraulic Conductivity formula is used:
- A value means Hydraulic Conductivity without Thickness formula will be used.
- A value means Hydraulic Conductivity with Thickness formula will be used.
Hydraulic Conductivity without Thickness
The flow between the two cells is calculated as:
where:
- = The underground water level of cell at time .
- = the datum height of the surface of cell c, set by the elevation or a Terrain elevation prequel.
- = The hydraulic conductivity of the cell, defined in HYDRAULIC_CONDUCTIVITY_MD of the underground terrain.
- = The ground bottom distance of the cell c, defined by a Bottom distance prequel or a general GROUND_BOTTOM_DISTANCE_M of the Water Overlay.
- = Area of conductance at time .
- = Underground water level difference at time .
- = Computational timestep.
- = Size of grid cell.
- = Averaged underground water level at time , based on water levels in underground, WATER_STORAGE_PERCENTAGE and potentially the surface water level, when the underground is filled to the top.
- = The amount of water to be transported at time between one cell and the other.
Hydraulic Conductivity with Thickness
The flow between the two cells is calculated as:
where:
- = The underground water level of cell at time .
- = The hydraulic conductivity of the cell, multiplied with the thickness of the layer, defined in HYDRAULIC_CONDUCTIVITY_WITH_THICKNESS_MD of the underground terrain.
- = Underground water level difference at time .
- = Computational timestep.
- = Size of grid cell.
- = The amount of water to be transported at time between one cell and the other.
Aquifer formula
When an aquifer is present, its hydraulic diffusivity is used to calculate the water flow.
Based on conditions being true, the calculated volume of water that is transported through the aquifer is calculated as:
Where:
- = Ground water level in cell at time ;
- = the datum height of the aquifer at the cell.
- = Volume in that flows between the two adjacent cells due to the aquifer at time .
- = Ground water level difference between the two adjacent cells at time ;
- = Computational timestep.
- = The AQUIFER_KD attribute of aquifer.
- = The calculated amount of water to be transported at time between one cell and the other.
Related
The following topics are related to this formula.
- Features
- Aquifer
- Formulas
- Groundwater level formula
- Underground infiltration formula
- Models
- Underground model
- Infiltration model
- Tracer flow model
See also
References
- ↑ Harbaugh, A.W., 2005, MODFLOW-2005, the U.S. Geological Survey modular ground-water model-the Ground-Water Flow Process: U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods 6-A16, variously paginated.
- ↑ Langevin, C.D., Hughes, J.D., Banta, E.R., Niswonger, R.G., Panday, Sorab, and Provost, A.M. (2017) ∙ Documentation for the MODFLOW 6 Groundwater Flow Model: U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods, book 6, chap. A55 ∙ p 31 ∙ found at: https://doi.org/10.3133/tm6A55 (last visited 2019-02-04)