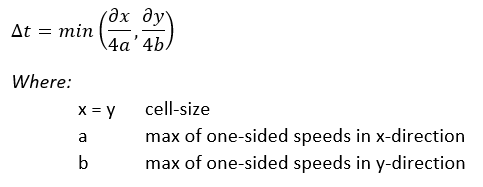Flooding Overlay: Difference between revisions
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
The Tygron Engine Inundation module relies on an explicit finit volume method, taken from Kurganov and Petrova (2007). This scheme relies on a reconstruction of cell bottom, water level and velocity at the interfaces between computational cells as proposed by Lax and Wendroff (see Rezzolla, 2011). The reconstruction method, taken from Bolderman et all (2014) ensures numerical stability at the wetting and drying front of a flood wave. | The Tygron Engine Inundation module relies on an explicit finit volume method, taken from Kurganov and Petrova (2007). This scheme relies on a reconstruction of cell bottom, water level and velocity at the interfaces between computational cells as proposed by Lax and Wendroff (see Rezzolla, 2011). The reconstruction method, taken from Bolderman et all (2014) ensures numerical stability at the wetting and drying front of a flood wave. | ||
=== | ===Computation time step=== | ||
An adaptive timestep is implemented according to Kurganov and Petrova (2007). At every timestep, the courant-number is kept smaller than 0.25 for every active computation cell: | |||
[[File:Inundation_overlay_03.PNG]] | |||
===Calculation Preferences (General Tab)=== | ===Calculation Preferences (General Tab)=== | ||
Revision as of 14:16, 2 August 2018
What is the Inundation overlay
The inundation is developed for the computation of surface (water) flow in a wide range of applications. These applications include large scale inundations due to dike breaches and inundations at the bottom of hill-slopes. Therefore the commonly applied 2D Saint Venant Equations are implemented on a highly parallel applicable explicit numerical scheme suitable for Tygron GPU clusters.
Adding and removing
To add an inundation overlay go to the Overlays menu in the GEO DATA ribbon and select Add Inundation. To remove the overlay, press Remove below the overlays list.
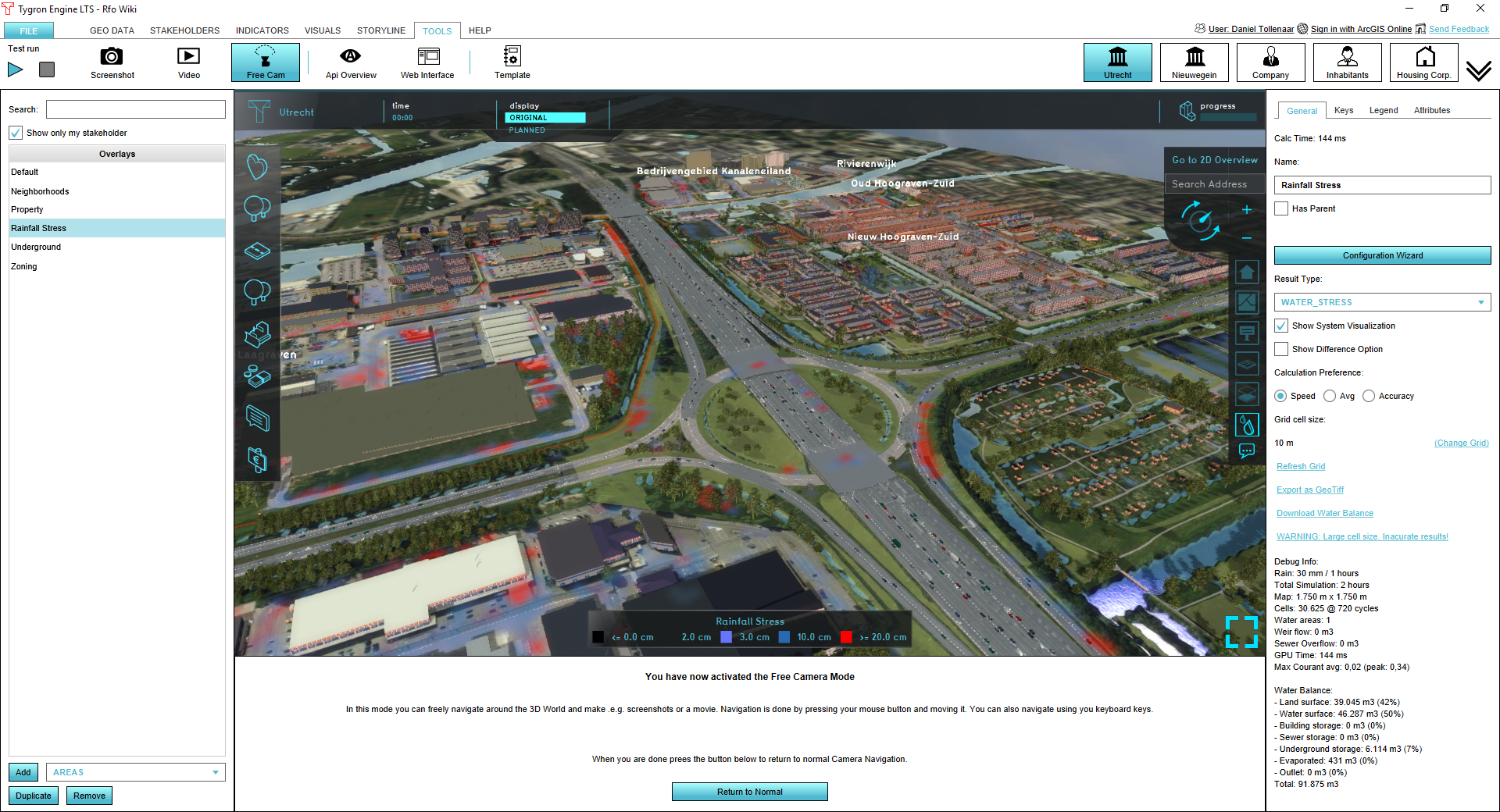
Result types
The rainfall overlay is a grid overlay showing results of heavy rainfall on the surface (flooding), sub-surface (groundwater), open water and sewer system. The following results are produced:
| Result type | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BASE_GROUNDWATER_DISTANCE | m (below surface) | Initial groundwater level relative to the surface level (NL: ontwateringsdiepte). |
| BASE_TYPES | nominal value | Division of gridcells in water, land or sewer areas that are connected to the sewer. |
| EVAPORATED | m (mm)¹ | Total evaporation over the simulation period |
| IMPACTED_BUILDINGS | nominal value | Constructions impacted by flood: the value from the function value indicator is assigned to a building if the water depth at a grid-cell surrounding the building exceeds the overlay attribute value IMPACT_FLOOD_TRESHOLD_M |
| SEWER_LAST_VALUE | m (mm)¹ | The amount of water in the sewer storage at the end of simulation |
| SEWER_MAX_VALUE | m (mm)¹ | Maximum amount of water in the sewer storage during the simulation |
| SURFACE_DURATION | s (min)¹ | The amount of time the water depth in a cell exceeds the value set in the overlay attribute value SHOW_DURATION_FLOOD_LEVEL_M |
| SURFACE_FLOW | m3/m2 | Total volume of water passed a grid-cell, scaled by the cell surface (grid cell-size^2) |
| SURFACE_LAST_VALUE | m (min)¹ | Water depth at the end of simulation |
| SURFACE_MAX_VALUE | m (min)¹ | Maximum water depth during the simulation |
| UNDERGROUND_FLOW | m³/m² | Totall infiltration amount from the surface to groundwater |
| UNDERGROUND_LAST_VALUE | m (mm) | The amount by which the groundwater table has risen above the initial groundwater level at the end of simulation |
| UNDERGROUND_MAX_VALUE | m (mm) | The maximum amount by which the groundwater table has risen above the initial groundwater during the simulation |
| WATER_STRESS | m (mm) | The Maximum water depth during the simulation. At water cells only a water depth is shown if the depth exceeds the overlay attribute value ALLOWED_WATER_INCREASE_M |
¹ the units between () are as displayed in the 3D client. If exported to GTiff the SI-convention is used: meters (m) and seconds (s).
Inundation Model
2D Saint Venant equations
The 2D Saint Venant equations describe the conservation of mass in a gridcell and the conservation of momentum in both x and y, direction:
File:Inundation overlay 01.PNG
The Saint Venant equations describe the following processes:
- friction
- bed slope
- water pressure
- convection (changes in bathemetry over space)
- inertia (increase or decrease of velocity over time)
Numerical scheme
The Tygron Engine Inundation module relies on an explicit finit volume method, taken from Kurganov and Petrova (2007). This scheme relies on a reconstruction of cell bottom, water level and velocity at the interfaces between computational cells as proposed by Lax and Wendroff (see Rezzolla, 2011). The reconstruction method, taken from Bolderman et all (2014) ensures numerical stability at the wetting and drying front of a flood wave.
Computation time step
An adaptive timestep is implemented according to Kurganov and Petrova (2007). At every timestep, the courant-number is kept smaller than 0.25 for every active computation cell:
Calculation Preferences (General Tab)
Overlay Keys
References
- Rezzolla L (2011) ∙ Numerical Methods for the Solution of Partial Differential Equations
- Bollermann A, Chen G, Kurganov A and Noelle S (2014) ∙ A Well-Balanced Reconstruction For Wetting/Drying Fronts ∙ found at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/269417532_A_Well-balanced_Reconstruction_for_Wetting_Drying_Fronts (last visited 2018-06-29)
- Kurganov A, Petrova G (2007) ∙ A Second-Order Well-Balanced Positivy Preserving Central-Upwind Scheme for the Saint-Venant System ∙ found at: http://www.math.tamu.edu/~gpetrova/KPSV.pdf (last visited 2018-06-29)