Neural Network (Inference Overlay): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
Neural Networks are stored in the {{software}} as data [[item]]s with a reference to an [[ONNX]]-file (Open Neural Network Exchange format<ref name="ONNX"/>). | Neural Networks are stored in the {{software}} as data [[item]]s with a reference to an [[ONNX]]-file (Open Neural Network Exchange format<ref name="ONNX"/>). | ||
Input and output for neural networks is handled using data tensors. These tensors are multi-dimensional data arrays. They are automatically identified when selecting or adding a new Neural Network. | [[Input tensor (Inference Overlay)|Input]] and [[Output tensor (Inference Overlay)|output]] for neural networks is handled using data tensors. These tensors are multi-dimensional data arrays. They are automatically identified when selecting or adding a new Neural Network. | ||
Whether a Neural Network classifies or detects objects given an input depends on its inference model. Such a model consists using AI-software, such as [[PyTorch]]. | Whether a Neural Network classifies or detects objects given an input depends on its inference model. Such a model consists using AI-software, such as [[PyTorch]]. | ||
Revision as of 15:18, 8 October 2024
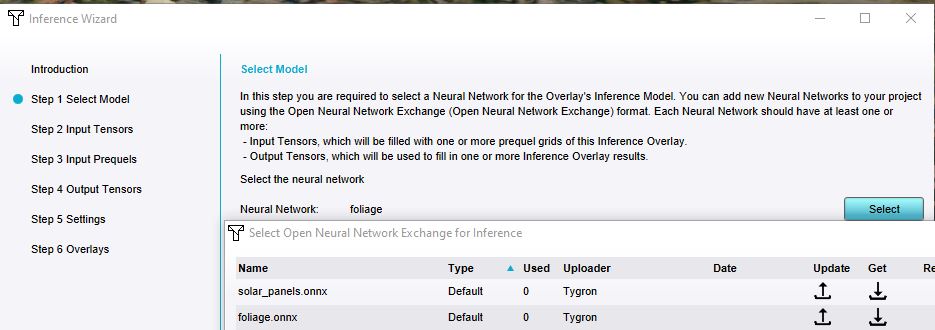
A Neural Network in the Tygron Platform is a pre-trained convolution network[1] that can be used by an AI Inference Overlay to classify or detect patterns and features given one or more input Overlays. Neural Networks are stored in the Tygron Platform as data items with a reference to an ONNX-file (Open Neural Network Exchange format[2]).
Input and output for neural networks is handled using data tensors. These tensors are multi-dimensional data arrays. They are automatically identified when selecting or adding a new Neural Network.
Whether a Neural Network classifies or detects objects given an input depends on its inference model. Such a model consists using AI-software, such as PyTorch.
Supported Convolution Types
- Image Classification
- Classifies a picture
- Predicts probability of object
- Detection (with masks and bounding boxes)
- Detects up to several objects in a picture
- Predicts probabilities of objects and where they are located
See also
References
- ↑ Cheatsheet ∙ found at: https://stanford.edu/~shervine/teaching/cs-230/cheatsheet-convolutional-neural-networks (last visited: 2024-09-21)
- ↑ ONNX ∙ found at: https://onnx.ai/ (last visited: 2024-09-21)




