Trees and foliage tutorial: Difference between revisions
| Line 199: | Line 199: | ||
Click on "Update now" in the [[right panel]] to force the Overlay to recalculate. | Click on "Update now" in the [[right panel]] to force the Overlay to recalculate. | ||
[[File:tutorial trees | [[File:tutorial trees pe temperature overlay update now highlight.jpg|650px|frame|center|TODO.]] | ||
Notice that in the areas where tree data was loaded in, the calculated temperature has dropped significantly. | Notice that in the areas where tree data was loaded in, the calculated temperature has dropped significantly. | ||
Revision as of 13:03, 11 May 2023
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites should be met before starting this tutorial:
- The tutorial makes use of the Demo Heat Stress Project. If possible, a copy should be created because one of the steps involves uploading a new file. If this is undesirable, a file already present in the Project can be used.
Preparations
Take the following steps as preparation for following this tutorial:
- Start the Demo Heat Stress Project.
- If possible, use a Save as operation to create a copy of the Project.
Tree and foliage data in general
There are a number of use-cases in which having accurate green data is relevant. In urban development, green is become more and more of a required spatial aspect. But also for topics like biodiversity and heat stress the impact of the presence of green is significant. It is therefor important to have as accurate data as possible related to the presence of green in an urban environment for a variety of simulation use-cases.
The Tygron Platform will, when a new Project of a real location is generated, automatically attempt to obtain open data about trees. However, depending on the use-case more accurate datasets may be required and available. In these cases, knowing how to properly manage data about trees (or foliage thereof) will improve the quality of calculations and thus the results.
For this tutorial, there will be a focus on using trees and foliage data with and for the Heat Overlay, but the principles translate over to other use-cases as well.
Trees and foliage data in the Tygron Platform
In the Tygron Platform, trees are stored as a specific Function (or collection of Functions) of Buildings. By default, the Tygron Platform generates trees with the Function of "Default decidiuous trees". Trees can exist as either small polygons (effectively points) to symbolize a single tree in a fixed location, or as a broader polygon to symbolize a group of trees (such as a treeline or a forest).
The visualization of trees governed by a single Attribute or Function Value: FLOOR_HEIGHT_M. This Attribute, in amounts of meters, will affect how tall the tree is visualized.
For the Heat Overlay, it isn't the trees data directly which is required for the calculations, but actually the foliage of the trees. The foliage casts significant shadows and thus affects the impact of solar radiation. By default, because there isn't a general datasource for foliage, the Tygron Platform's Heat Overlay can instead derive an estimation of foliage from the trees data. This is done by effectively buffering the tree polygon with a certain amount of meters. That amount is determined by the FOLIAGE_CROWN_FACTOR, which is the ratio of foliage radius to tree height. This allows for a spatial dataset of foliage to be estimated based on the presence of trees.
For more information about how trees relate to the Heat Overlay, consult the documentation:
Preparation
For the purpose of this tutorial, 2 datasets are needed, which can be obtained from the Demo Heat Stress Project as is. The Heat Overlay will also need to have one of its settings changed, both so that there is a baseline from which a change can be seen after the process completes, but also to correctly connect the Heat Overlay with the intended datasource.
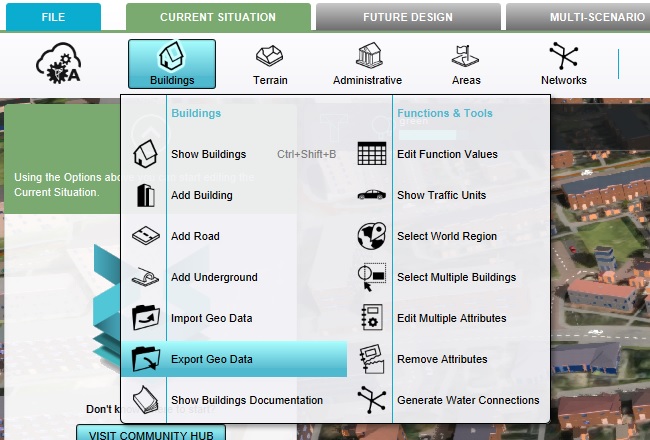
Downloading trees data from the Project
Go to:
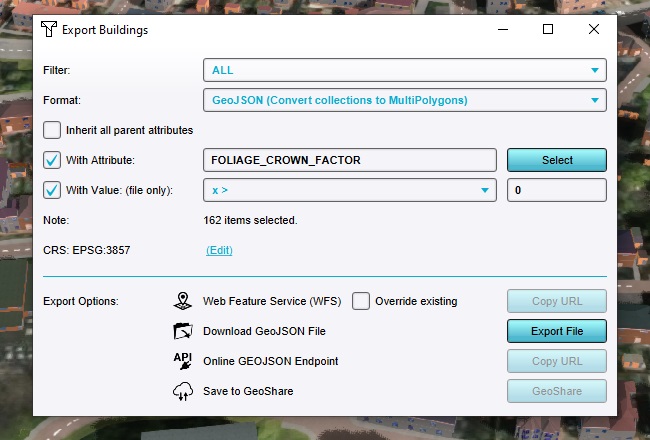
In the popup that appears, its possible to indicate which Buildings data specifically needs to be exported.
Opt to export Buildings with a specific Attribute by checking the "With Attribute" option.
As Attribute, select the Attribute FOLIAGE_CROWN_FACTOR. This is an Attribute which is only associated with trees.
Opt to check for the value of the Attribute, by checking the "With Value" option as well.
Ensure the value check is set to X > 0. This will only export Buildings which have a FOLIAGE_CROWN_FACTOR of more than 0.
Find the export option "Download GeoJSON File", and click on "Export File".
Place the file somewhere on your computer where you will be able to find it again later.
The resulting GeoJSON file is one which contains all the trees from the Project.
Downloading foliage data from the Project
The Demo Heat Stress Project also contains a number of Overlays which perform an estimation of foliage based on satellite imagery. The result is a specific Overlay with a foliage estimation, which can be downloaded as a separate file.
Go to:
In the right pane, click on "Export Grid Data".
In the popup that appears, its possible to indicate how the grid data specifically needs to be exported.
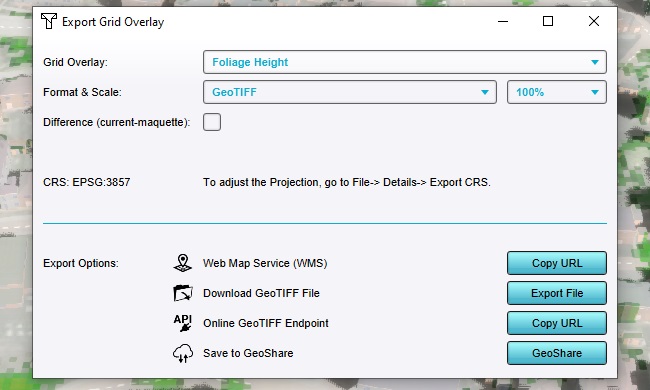
Leave all settings as they are. Find the option "Download GeoTIFF File", and click on "Export File".
Place the file somewhere on your computer where you will be able to find it again later.
The resulting GeoTIFF file is one which contains a grid of foliage from the Project.
Resetting foliage source of the Heat Overlay
Finally, it is necessary to ensure the Heat Overlay now operates from a basis where it does not have any foliage information, so that the results of importing data can be verified.
Go to:
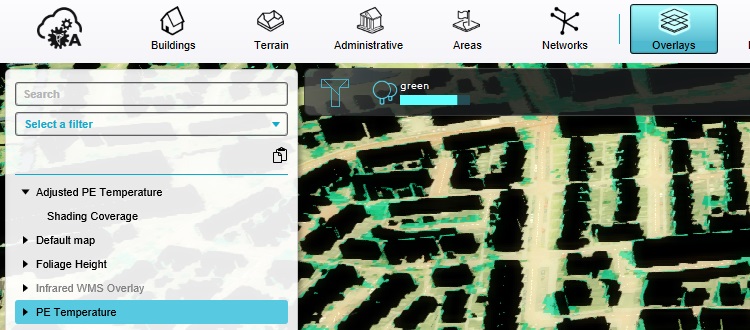
In the right panel, click on "Configuration Wizard". This opens the Heat Overlay Wizard.
Continue to the step regarding Foliage.
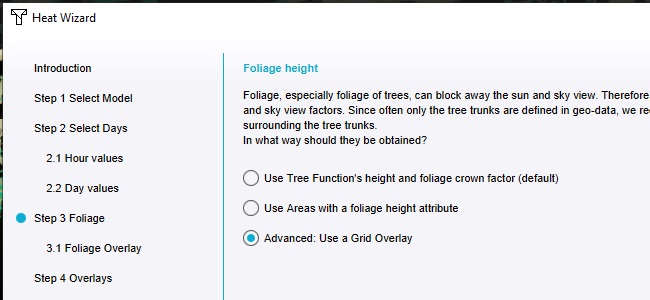
Opt to use "Tree Functions" height and foliage crown factor.
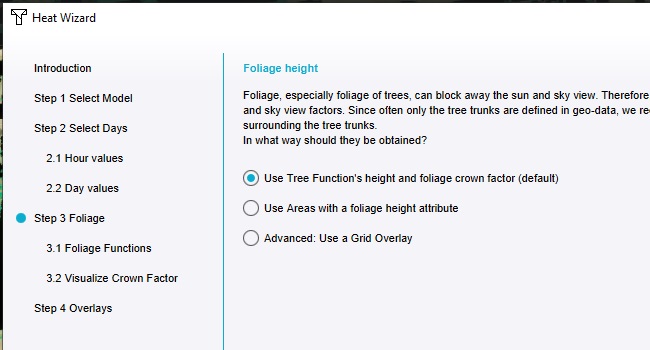
Close the Configuration Wizard.
Click on "Update now" in the right panel to force the Overlay to recalculate.
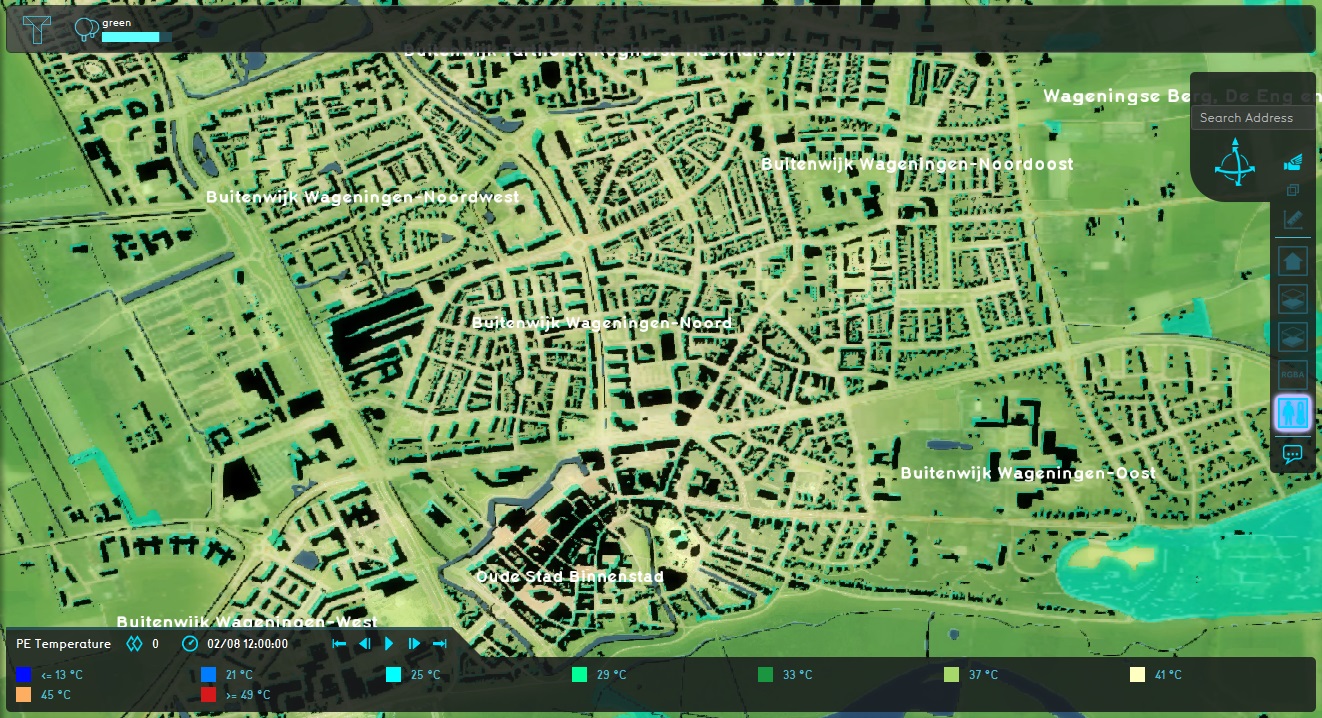
Notice the results for the Project have changed. This is because the calculation now relies on a different dataset.
Using trees data
An accurate dataset of trees will allow for an accurate counting of surface area used for the purposes of urban green. It can also be used by models such as the Heat Overlay to extrapolate foliage from, which affects the calculations for heat stress.
Removing existing trees from the Project
Before new trees data can be imported, the existing trees data should be removed. Otherwise, the original data may persist together with the new to-be-imported data, and throw off the results of calculations relying on the trees.
Go to:
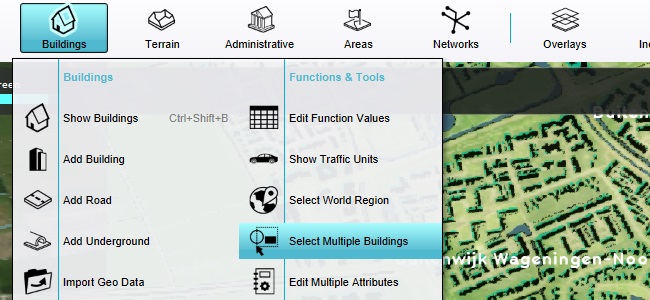
In the bottom panel, an interface now allows for the mass-manipulation of multiple Buildings at the same time, based on Function and extent.
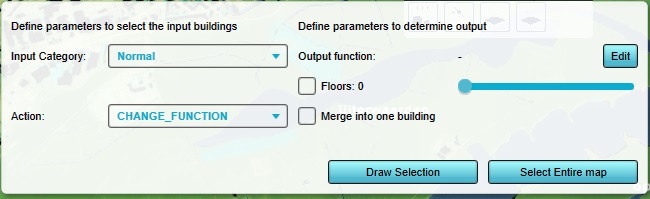
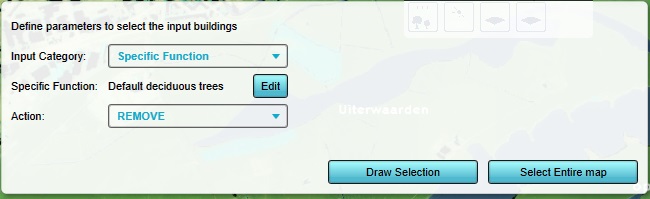
As category, select "Specific Function".
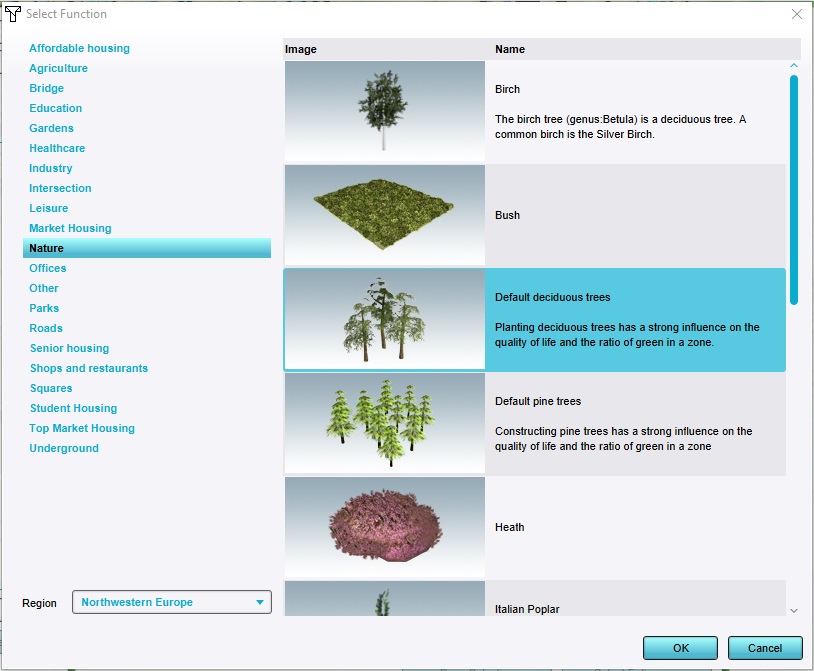
As Function, select "Default Decidiuous Trees". This is the default type of trees and means this operation will only affect trees.
As action, select "REMOVE"
Click on "Entire Map"
A prompt will appear. Confirming it will delete the 160 or so trees from the Project, leaving it without any trees data.
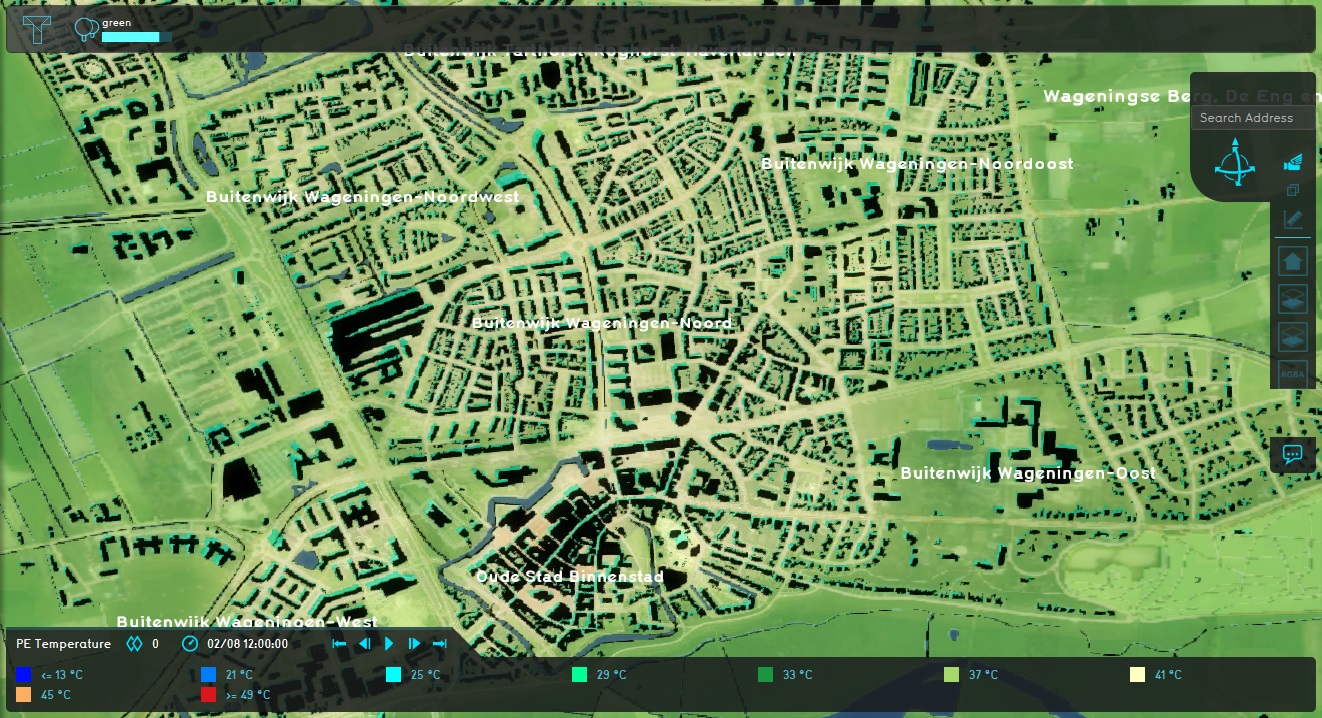
Click on "Update now" in the right panel to force the Overlay to recalculate.

Notice the results for the entire Project are now significantly hot. This is because there is now no foliage data for the Heat Overlay to work with.
Importing trees data
Go to:
This opens the Geo Data Wizard.
As import method, select "GeoJSON file".
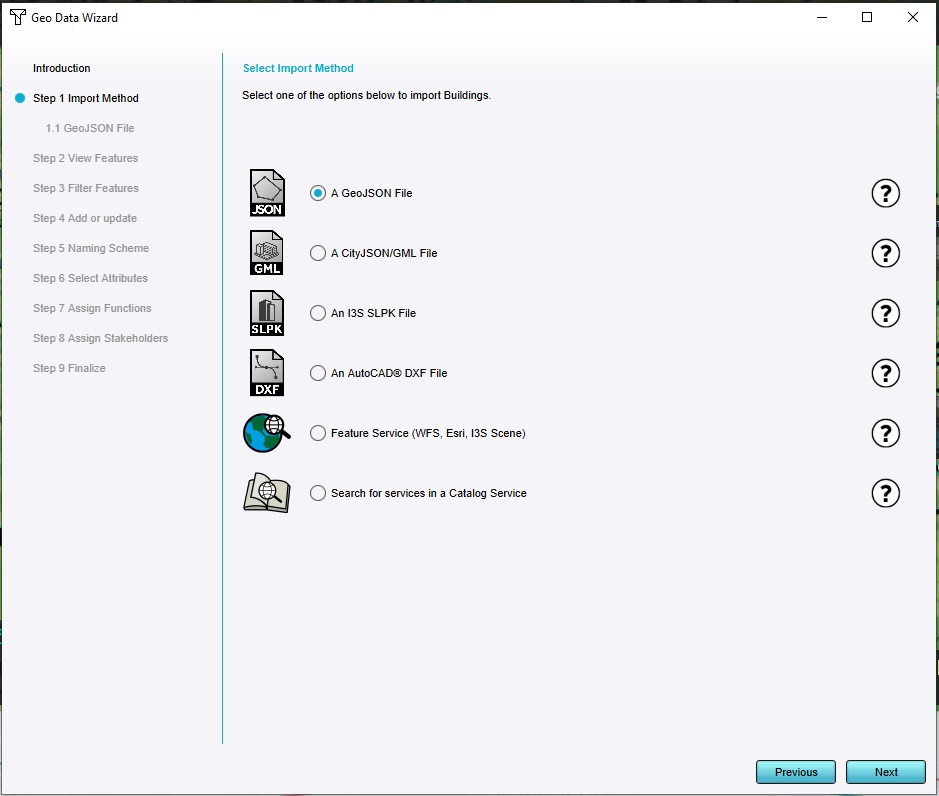
As GeoJSON file, click on "select local file". Select the previously downloaded trees geojson file.
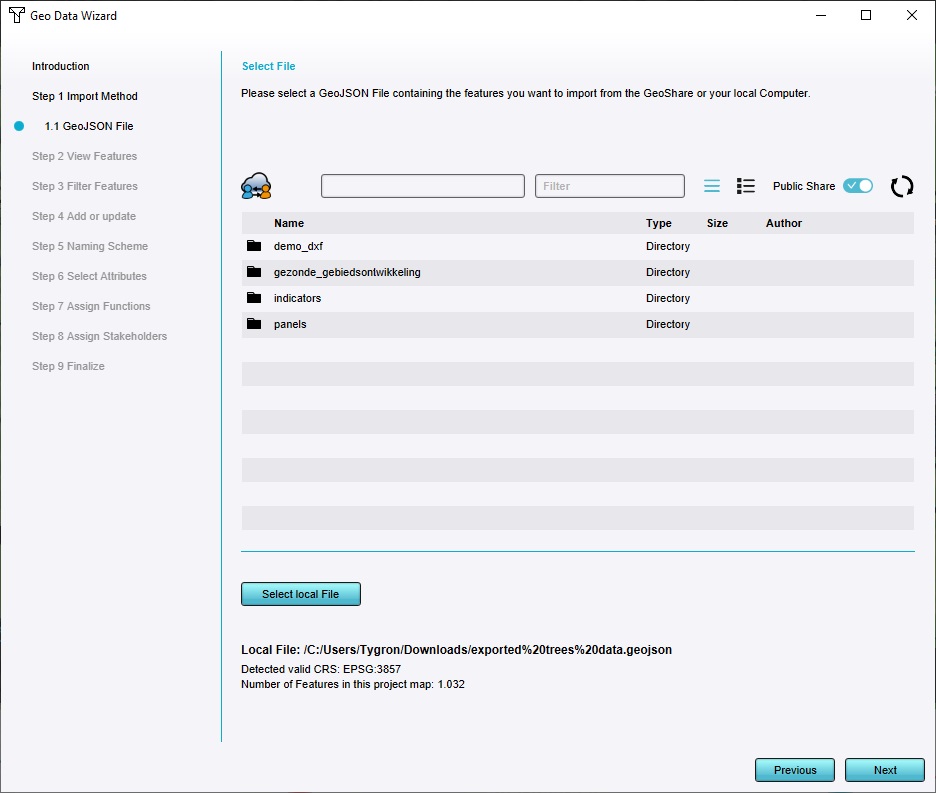
Take note of the "View features" step, where the locations of all trees are shown.
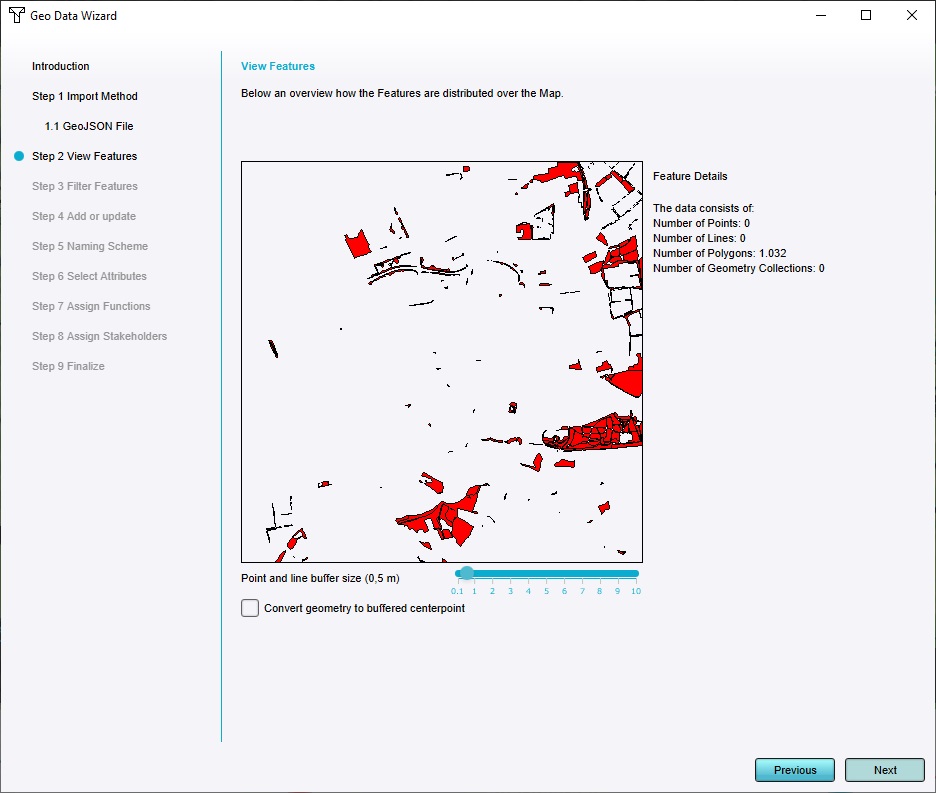
Also take note of the "buffer size" slider. when the dataset consists of points, all points will be buffered with the size indicated by the slider. By default all such points end up as polygons of exactly 1m² in size. Any polygons in the dataset will remain as-is.
Skip through the step for filtering features (all features are desired), adding or updating features (the default is to add, which is what we nat to do), and the naming scheme (names are not relevant for calculations).
In the "Select Attributes" step, take note of the Attribute FLOOR_HEIGHT_M. This Attribute determines the height of the trees which are imported. If the dataset of trees has a different Attribute which indicates the tree height of features, find that Attribute in the list of [[Attribute] names, and then edit the name of the Attribute as it is imported using the text input fields in the middle of the screen.
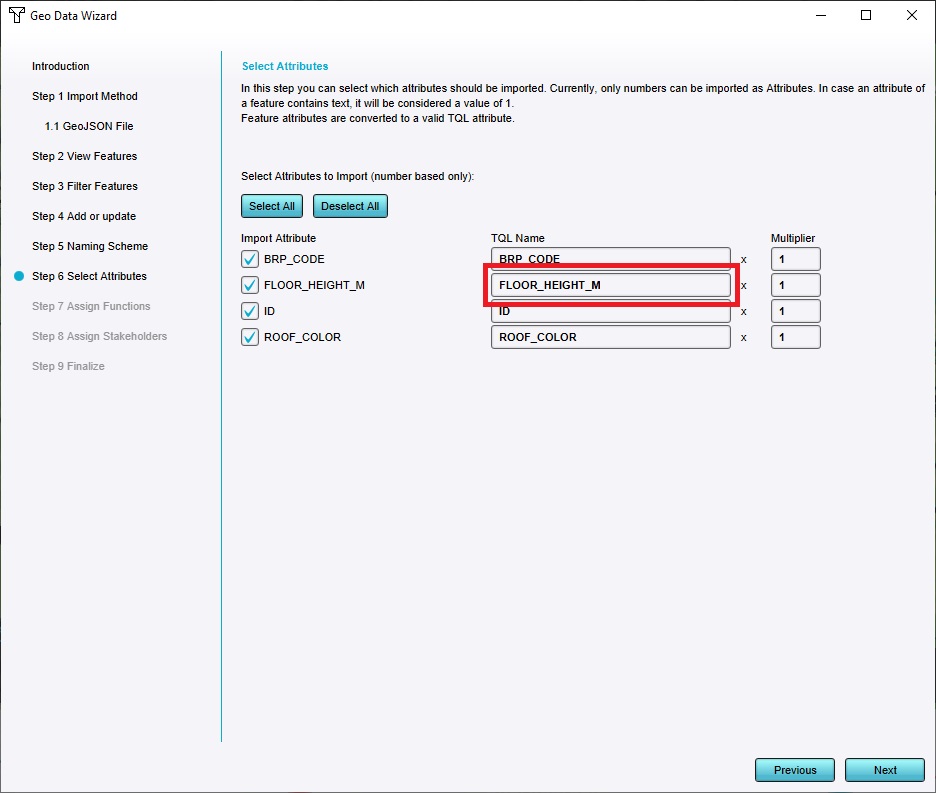
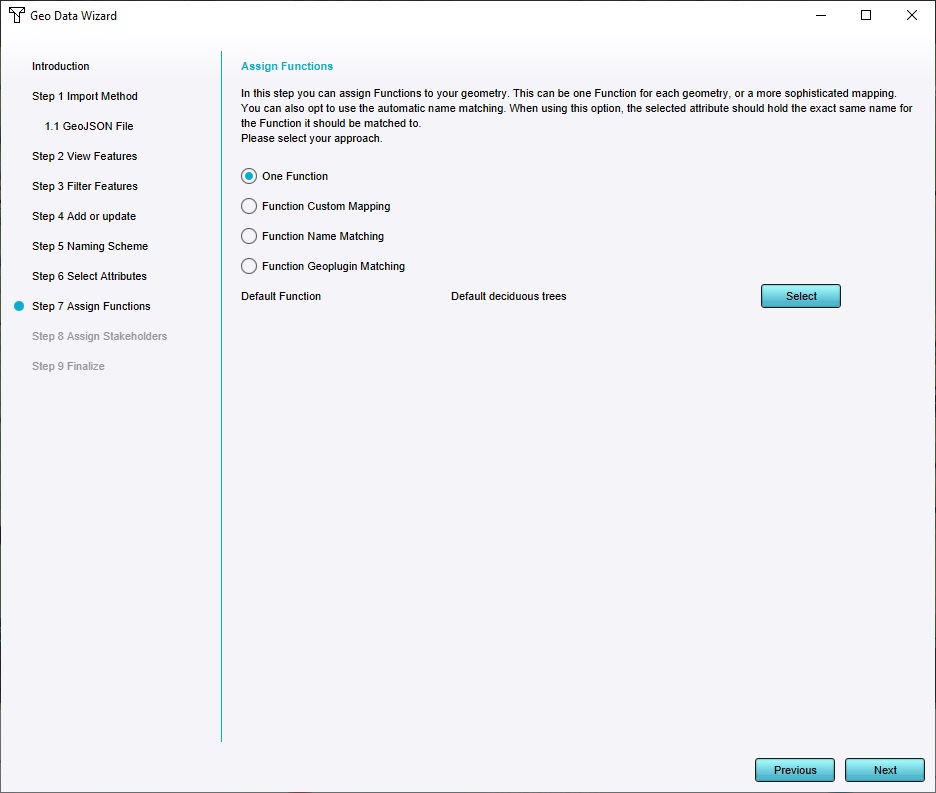
In the "Assign Functions" step, keep "One Function" selected, and click on "Select" to select the default function.
Select "Default Decidiuous Trees", and continue to the next step.
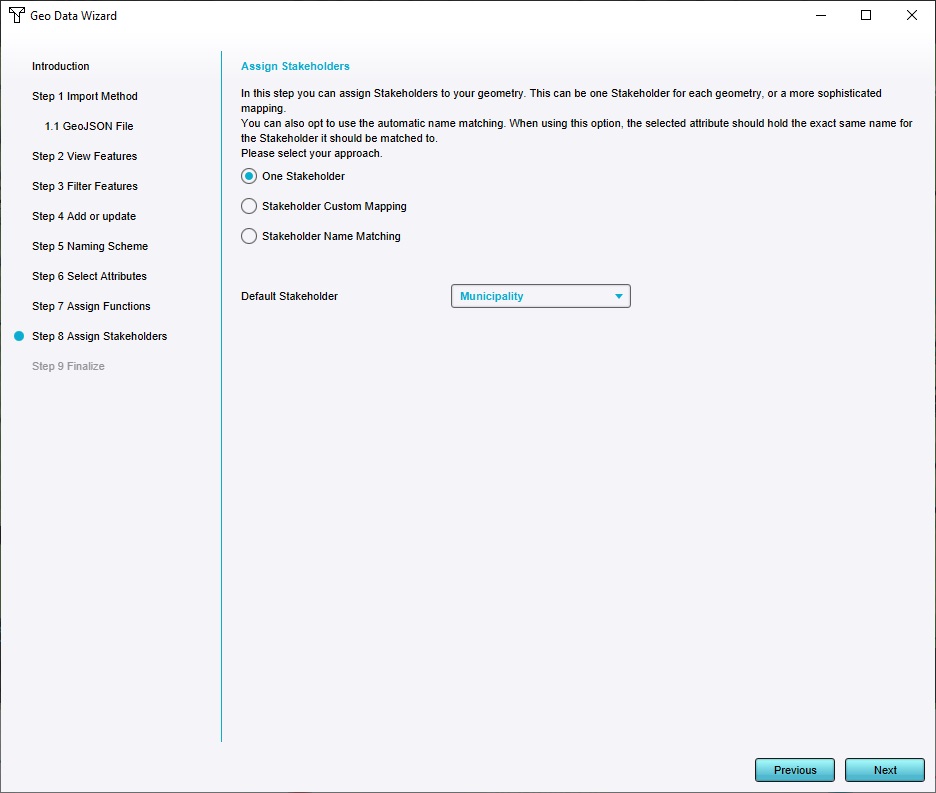
For the "Owner", select the Municipality.
Continue to the last step of the Wizard and click on "Finalize" to add the data to the Project.
Go to:
Click on "Update now" in the right panel to force the Overlay to recalculate.

Notice that in the areas where tree data was loaded in, the calculated temperature has dropped significantly.
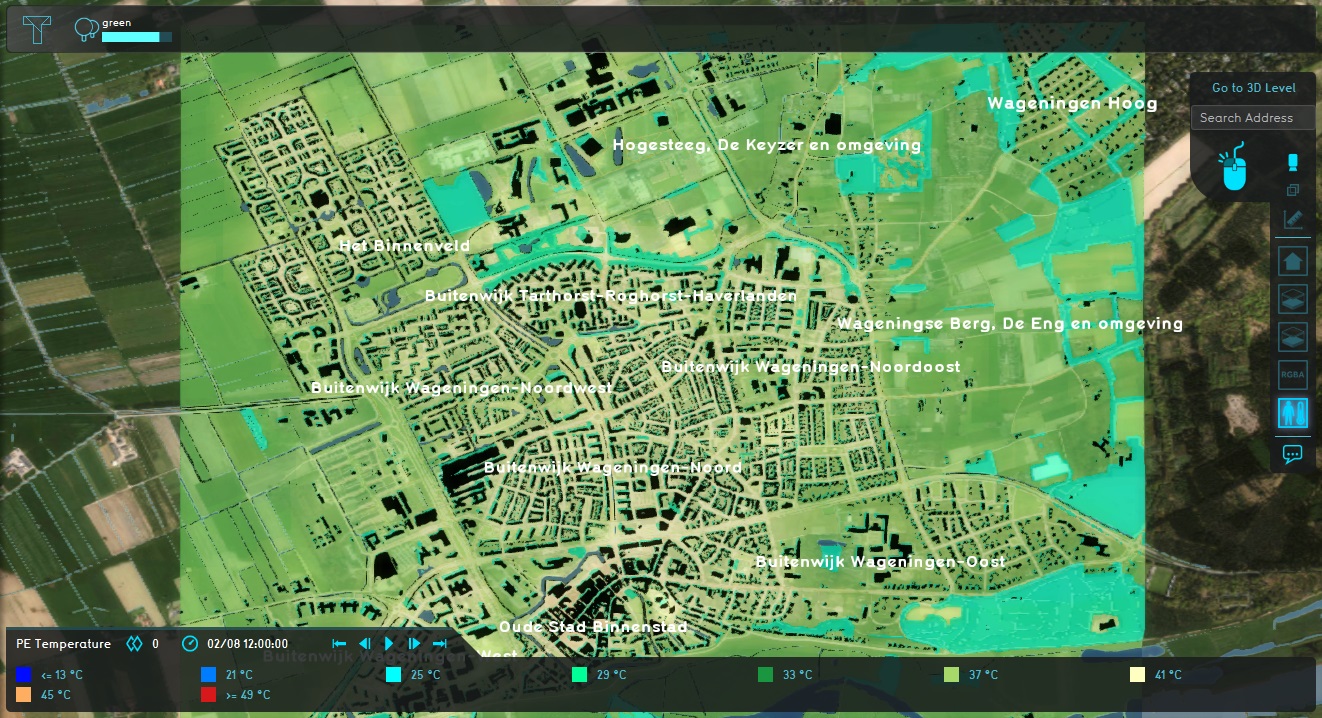
Also inspect the "Foliage" child Overlay of the Heat Overlay, which shows the presence of foliage.
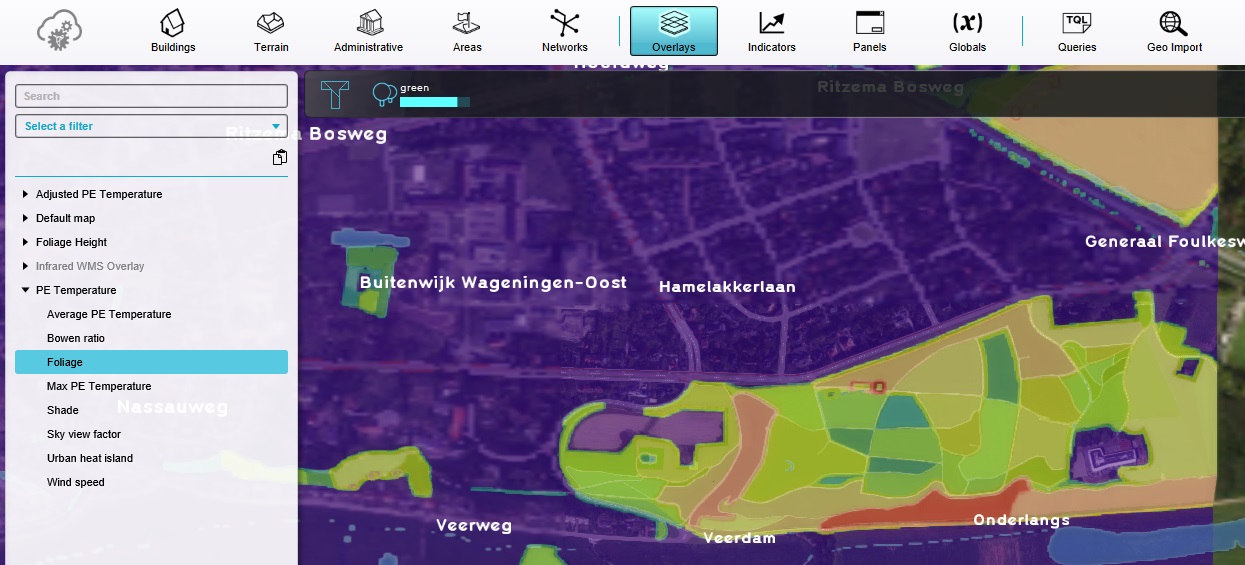
Using foliage grid data
Instead of relying on point data for trees, from which the Tygron Platform then extrapolates foliage coverage, it is also possible to supply a dataset of foliage directly. This is a grid of foliage heights which the Heat Overlay can then use for its calculations.
Importing foliage grid data
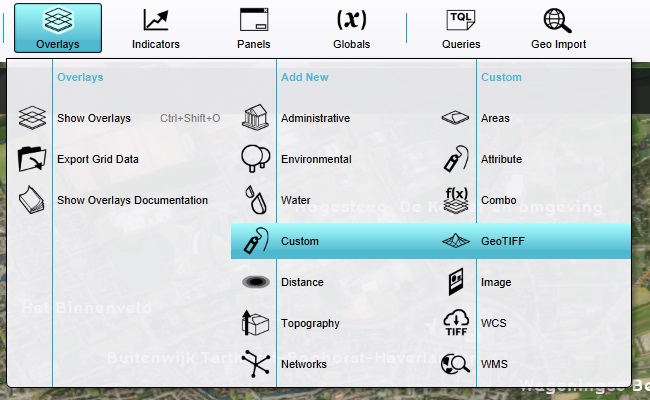
A GeoTiff Overlay is now added to the list of Overlays, and selected.
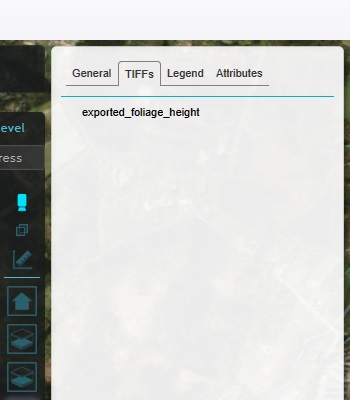
In the right panel, switch to the "TIFFs" tab.
At the bottom of the right panel, click on "Add".
A window appears which can be used to manage GeoTiff assets in a Project.
Click on "Add local file", and select the previously downloaded GeoTIFF file.
(Note that if the import of the file fails because you're working directly in the Demo Project, you can continue the rest of the steps with the already present "filteredtrees.tiff")
Select the imported tiff in the listing, and click "Ok".
The tiff is now added to the listing.
Connecting foliage grid to Heat Overlay
Go to:
In the right panel, click on "Configuration Wizard". This opens the Heat Overlay Wizard.
Continue to the step regarding Foliage.
Opt to use a Grid Overlay to define the Foliage.
In the next step, select the newly added "GeoTIFF", which contains the foliage data.
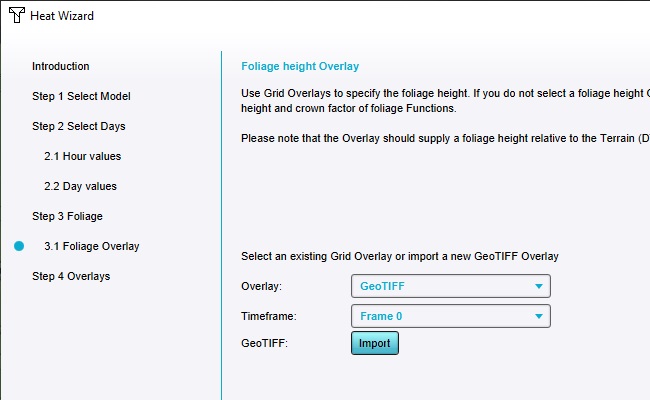
Close the Wizard, and click on "Update now" in the right panel.

Notice that in the areas with more foliage coverage according to the tiff, the calculated temperature has dropped significantly.

Also inspect the "Foliage" child Overlay of the Heat Overlay, which shows the presence of foliage.

Tutorial completed
Congratulations. You have now completed this tutorial. In it, you have learned how to import trees and foliage data, with an emphasis for use with the Heat Overlay..