Terrain height
Terrain height
- Terrain height is the whole of differences of terrain elevation in a given area, the quantitative measurement of vertical elevation change in a landscape. Terrain is used here as a general term in physical geography, referring to the lay of the land. This is usually expressed in terms of the elevation, slope, and orientation of terrain features. Terrain height - as element of a terrain - affects surface water flow and distribution. Over a large area, it can affect weather and climate patterns.
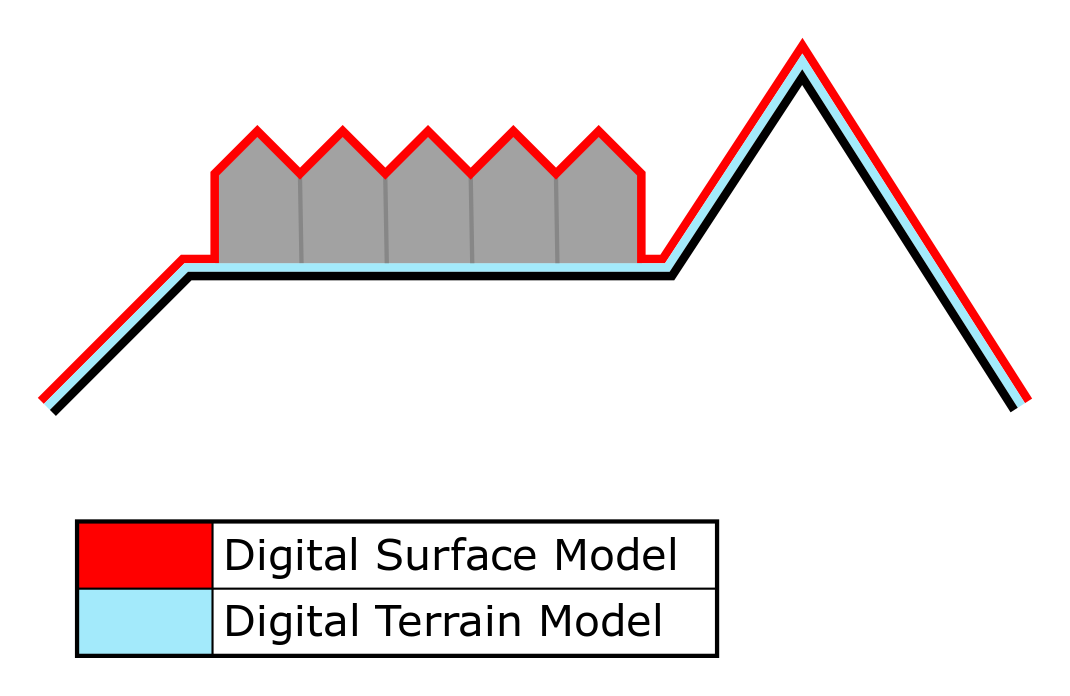
- In overlays, the user can select two types of elevation, the digital terrain model (DTM) and digital surface model (DSM). A DTM represents the bare ground surface without any objects like plants and buildings. In contrast; a DSM represents the earth's surface including all objects (e.g. houses, trees, etc.) on it.
- View original file here:[1]
Terrain height in the Tygron Platform
DTM for projects in The Netherlands
Data sources
In the Netherlands a DTM is constructed using the following data sources:
- A base DTM, with a cell size of 3mx3m, supplied by Rijkswaterstaat to ESRI, based on the AHN2.
- A DSM from AHN2 or AHN3 raw data (Actuele Hoogte Bestand) with a cell-size of 0.5x0.5m, 1x1m or 2.5x2.5m.
- A DTM from AHN2 or AHN3 containing interpolated ("maailveld") data from ESRI, with a cell-size of 0.5x0.5m, 1x1m or 2.5x2.5m.
- []Top10NL data.
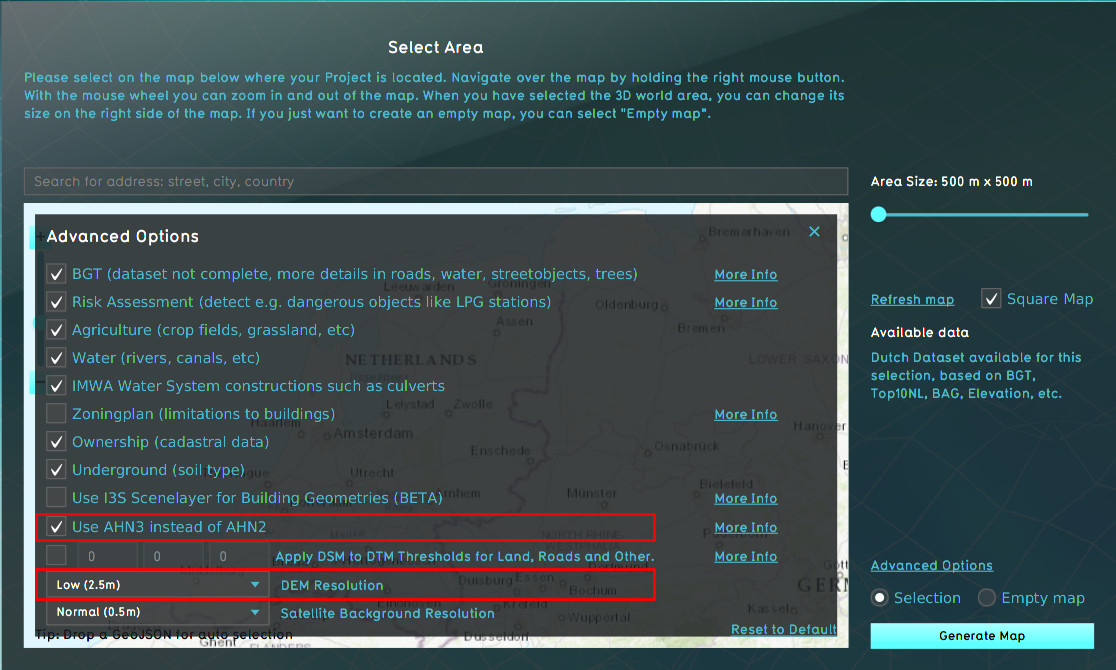
When defining a new project, you can choose whether the project should use AHN2 or AHN3 the DSM resolution under the Advanced Options at the wizard. These options influence the generation of the DTM:
- Use AHN3 DSM: if selected the AHN3 will be used, if not selected the AHN2.
- The AHN data will be available on 0.5m, 1m or 2.5m resolution in the project database for generating the elevation grid (see the image below).
DTM generation
By the following steps a project DTM is composed:
- The ESRI DTM and DSM are resampeled to the same resolution
- The difference between the resampeled DTM and DSM is computed
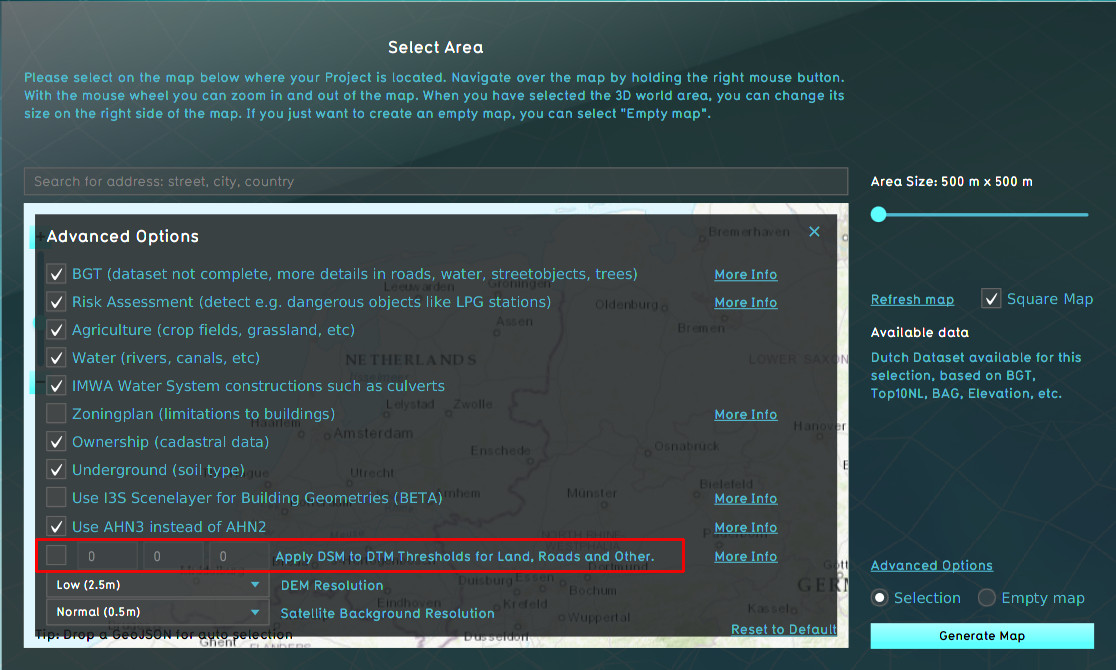
- Depending on the topography-value and a threshold either the value of the DTM or DSM is used to compose a DTM on high resolution:
- for bare lands the default threshold is 100cm, all cells with a difference <100cm between the DTM and DSM, the value will be taken from the DSM
- for roads the default threshold is 25cm, all cells with a difference <25cm between the DTM and DSM, the value will be taken from the DSM
- for crop-lands, scrup-land, etc the default threshold is 50cm, all cells with a difference <50cm between the DTM and DSM, the value will be taken from the DSM
It is possible to change the default thresholds. Therefore, change the corresponding value in the Advanced Options menu (see the image below). The first value is for bare lands, the second for the roads and the third for the crop-lands etc.
- Rooftops of buildings are getting an average height of the DSM of the polygon defining the buildings footprint. The footprint is split into sections using image recognition techniques; herewith the variability in rooftops can be taken into account in the elevation model
Waterdepth
Water bodies, found in terrain surface types, are lowered a few meters relative to the elevation of the surrounding surface. By default:
- Boezemwater: 3m lowered relative to the elevation of the surrounding surface
- Water: 2m lowered relative to the elevation of the surrounding surface
These values can be changed by changing the WATER_DEPTH_M attribute of the Terrain type. From the DEM a heightpoint in or as close to the wateredge is taken. On that point the Underground terrain type is determined. The slope (talud) of the sides of the water body is defined by the ANGLE_OF_REPOSE of this Underground Terrain Types and the maximum depth to which a water body is carved out is WATER_DEPTH_M as defined for the surface terrain type on this point. If the angle of repose is shallow enough and the water body thin enough, the angled sides may meet up before the maximum water depth is reached. In this case the water body will be appropriately shallower. The ANGLE_OF_REPOSE attribute can also be changed.
Changing terrain height
There are two options to change terrain height. One is to import a raster file with the new terrain height and the other option is to draw in the Tygron Platform where the terrain should be changed and to which height.
Importing a terrain height dataset
See how to import terrain height data.
Drawing terrain height
- Open the Terrain Height Brush Panel
- Select "Start Drawing"
- Adjust the Radius and Press sliders as desired
- Select the brush type Raise, Flatten or Lower
- Adjust terrain height by pressing and holding the left mouse button while drawing in the 3D world
- Confirm the changes by selecting "Apply changes"