Radial well aquifer benchmark (Water Module)
This testcase demonstrates a situation where a well is pumping up ground water. A characteristic ground water level curve will form over time.
Formulas
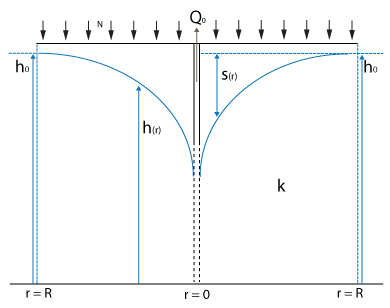
Stationary lowering of the ground water table in a closed water transmissive layer can be described by the following formula [1]
where:
- : stable water level at the considered stable water table edge
- : water level between the considered stable water table edge and the well
- : water level in the well
- : transmissivity of the aquifer in m² / day
- : distance to the well
- : distance of the considered stable water table edge to the well
- : amount of water pumped out in m³ / day
Setup
We use the following setup in our tests. The grid size used is 51 by 51, with a configurable cell size of in meters. There is one underground outlet, which pumps water away continuously with a default amount per second.
The outlet is placed on the cells x = 25 and y = 25 as an inlet with a negative inlet.
INLET Q is set to
UNDERGROUND is set to true (1.0) to place the outlet below the surface.
The simulation is run for 64 days with 0 rainfall, which is configured in the weather's rain attribute as:
References
- ↑ Verruijt, A. (1970). Theory of Groundwater Flow. Macmillan, London.