Radial well aquifer benchmark (Water Module): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
===Formulas=== | ===Formulas=== | ||
Stationary lowering of the ground water table in a closed water transmissive layer can be described by the following formula <ref name="verruijt70"/> | Stationary lowering of the ground water table in a closed water transmissive layer can be described by the following formula <ref name="verruijt70"/> | ||
<math>\phi(r) - \phi_0 = \frac {Q_0}{2\pi\cdot kD} \ln{\left ( \frac{r}{R} \right )}</math> | <math>\phi(r) - \phi_0 = \frac {Q_0}{2\pi\cdot kD} \ln{\left ( \frac{r}{R} \right )}</math> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
: <math>R</math>: distance of the considered stable water table edge to the well | : <math>R</math>: distance of the considered stable water table edge to the well | ||
: <math>Q_0</math>: amount of water pumped out in m³ / day | : <math>Q_0</math>: amount of water pumped out in m³ / day | ||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
Revision as of 14:53, 16 December 2020
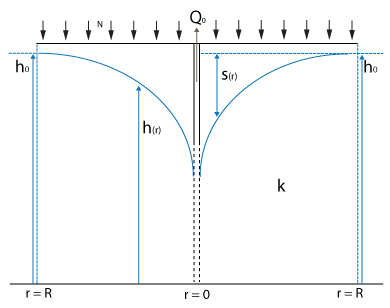
This testcase demonstrates a situation where a well is pumping up ground water. A characteristic ground water level curve will form over time.
Formulas
Stationary lowering of the ground water table in a closed water transmissive layer can be described by the following formula [1]
where:
- : stable water level at the considered stable water table edge
- : water level between the considered stable water table edge and the well
- : water level in the well
- : transmissivity of the aquifer in m² / day
- : distance to the well
- : distance of the considered stable water table edge to the well
- : amount of water pumped out in m³ / day
References
- ↑ Verruijt, A. (1970). Theory of Groundwater Flow. Macmillan, London.