Aerius Module theory
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
This functionality is currently unavailable or non-functional.
See the Aerius module overview for an overview of the general concept, input and output.
Calculation
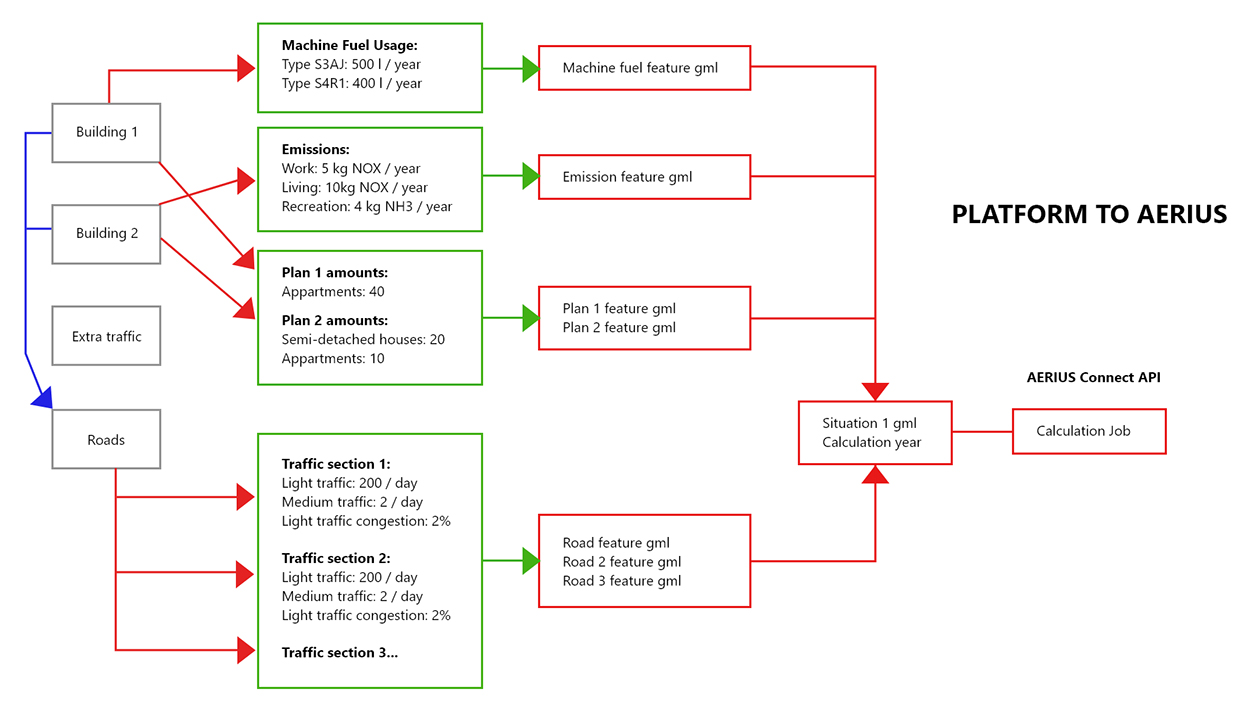
- Buildings are converted into one or more GML features for identifying by the Aerius Connect API.
- These features are represented as a line for roads, otherwise a center-point.
- These features are combined into a collection and put in a situation feature.
- This situation is sent to the Aerius Connect API and a calculation job is started
- This job is polled until completed.
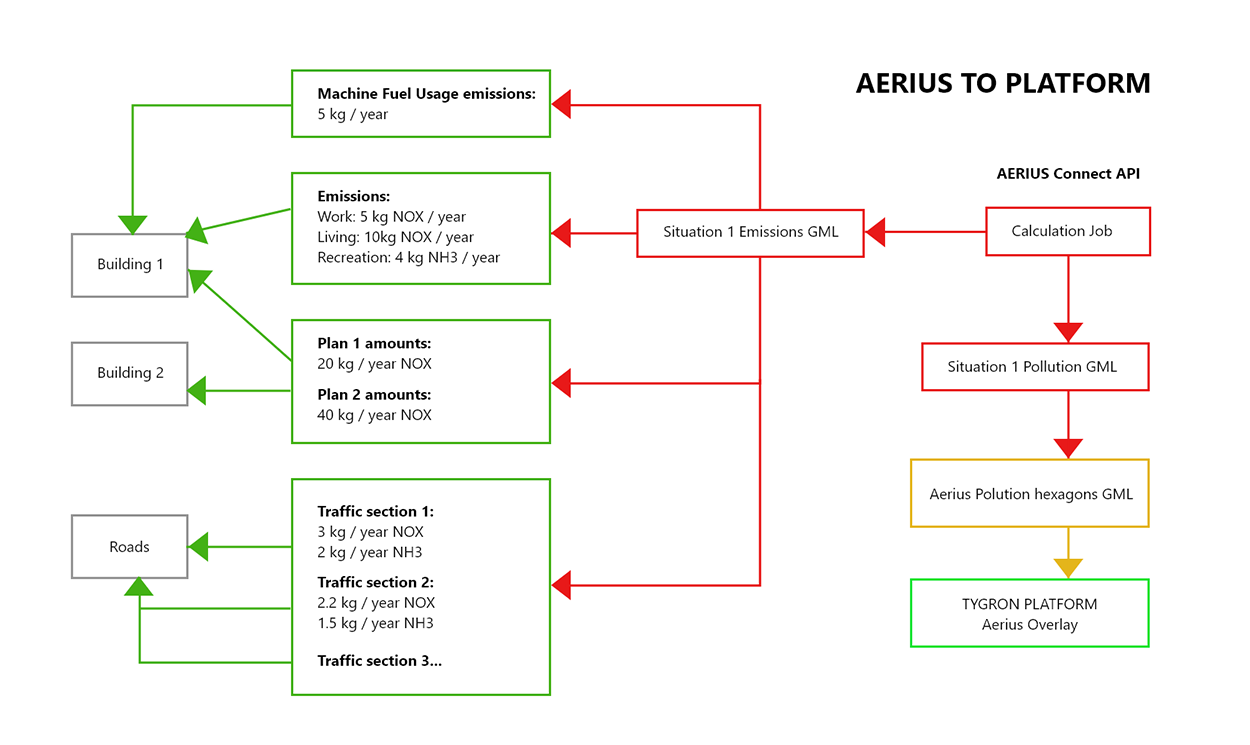
- When completed, the calculation results are retrieved and processed.
- Emissions for the various features related to a Building are stored under the NOX and NH3 attributes for that Building. If the Building is a road, the traffic emissions are shown. Otherwise, the emissions for plan, work and living and mobile machines are summed and shown here.
- Natura 2000 Hexagon polygons are converted to grid cells with their respective NOX and NH3 mol/ha/year values.
- Natura 2000 Hexagon polygons values are also stored as an array in the Aerius Overlay under the NOX and NH3 attributes.
Technical Overview
Considerations
- NOX and NH3 deposition is returned by the Aerius Connect API as hexagon features, which are stored in the Aerius Overlay's grid. Only when Natura 2000 areas are inside the project bounds, these hexagons can be seen. The array of individual values in mol/hectare/year per hexagon are also stored in the Aerius overlay under the NOX and NH3 keys respectively. These values are sorted by the highest 100 values for the hexagons and therefore not restricted by the project bounds.
- Only buildings are processed for specific attributes such as number of light traffic, office and shop area size, used fuel usage per year for buildings and direct emissions of NOX and NH3.
- Per sector these attributes are converted to individual Aerius features. These features are encoded using the GML-format, which is the primary data format the AERIUS Connect API accepts.
- A single building can therefore be send as multiple features, one for each sector. For some types of features, the Aerius Connect Api calculates NOX- and NH3-emission values, which are written back into the building.
- Only the sum of NOX emissions is stored per building, not per sector. Likewise for NH3 emissions. The traffic sector is an exception to this, traffic emissions are stored per road buildings.
- Depending on the amount of features send to the Aerius Connect API, the calculation jobs can take considerable time. The Aerius module stops waiting for a job after 5 minutes.