Handout Water Module
This handout can be used for the Water Module training or as a recap of this training course.
How to use: Advice is to print this handout and use it during the training to take notes. Afterwards, you will have a summary of what you have learned during the training..
Project: The steps in the handout can be applied on any project.
Note: This handout is not a standalone tutorial but provides a guide during a training or can act as a summary. For a tutorial regarding the Water Module to practice with on your own, see the Rainfall Overlay tutorial.
The subjects in this handout are:
- Create a New Project
- Import water depth data
- Add the Rainfall Overlay
- Walkthrough of the Water overlay Wizard
Create New Project
- Click in the Main Menu on New Project
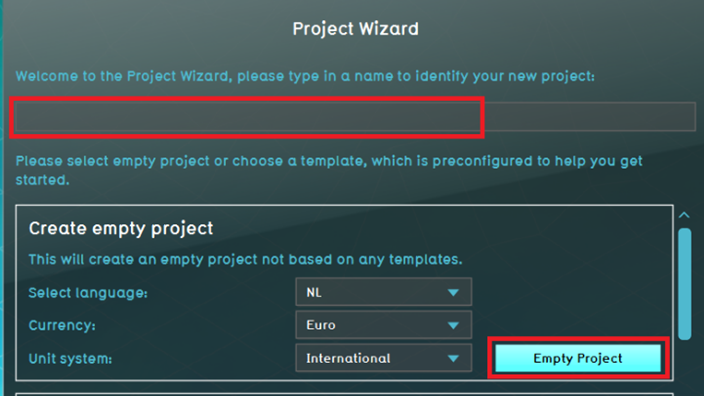
- Provide a name for the New Project (max 20 characters) and click on Empty Project.
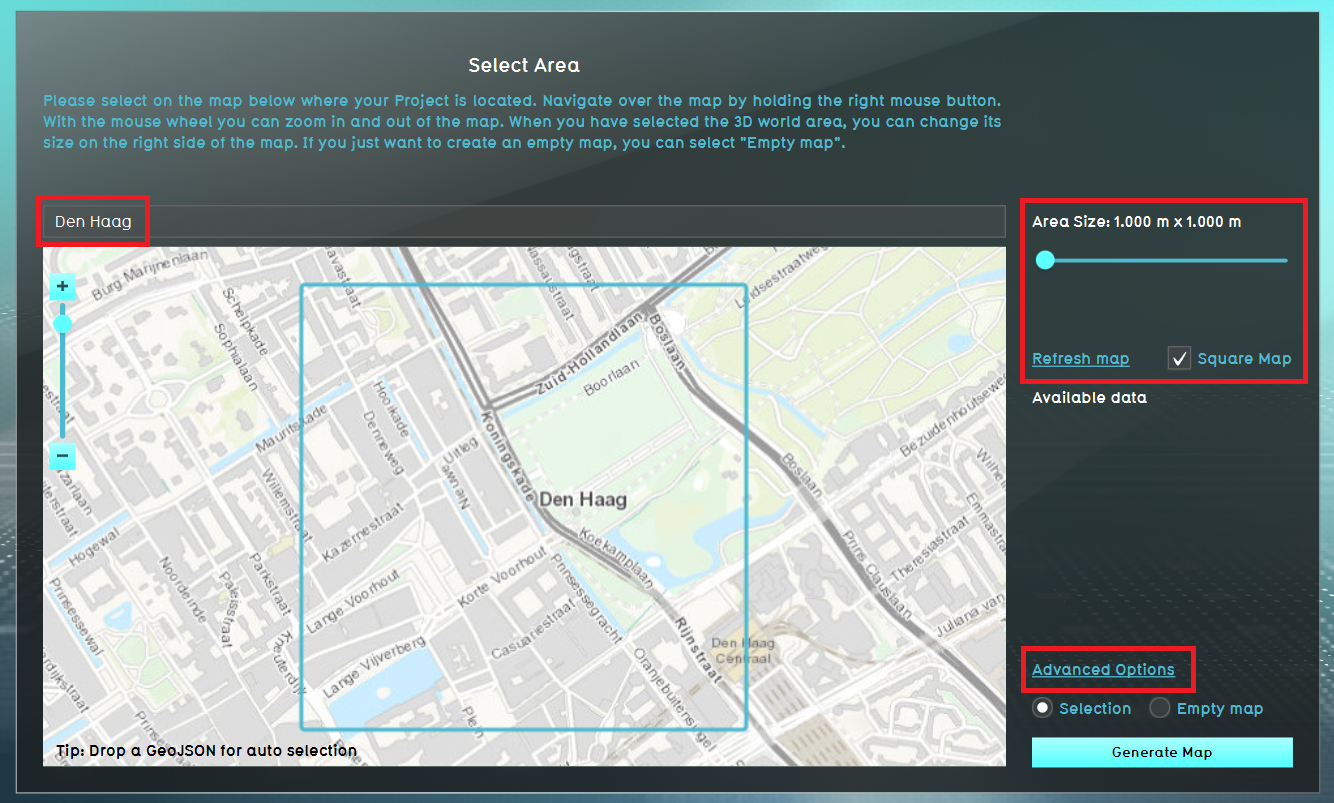
- For the location, fill in a location of your choice and click on Enter. Move the square with the left mouse button. The area of the map in the rectangle will be your new project area. With the sliders on the right side, it is possible to enlarge the square. However, the smaller the square is, the faster the project will be generated. For the following steps, choose a size of max 2 x 2 km.
- Then click on Advanced Options
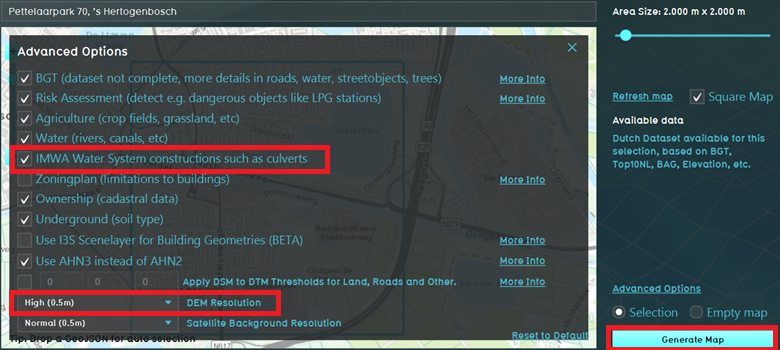
- Here you can check datasets that are used to generate the project. By default, the IMWA data source is checked where culverts are automatically imported from (if they are available for your location as open data). If you have your own culvert dataset, you can uncheck the IMWA data source. Also note the DEM resolution. Select a high DEM resolution to use the most accurate AHN data.
- Finally click on generate map to generate the project from open data.
Import water depth data
From open data, the depth of the bottom of a water body is not known. Read here how the Tygron Platform models water depths. Depending on the use case of your project, it can be important to add own data with the height of the water bottom.
Note that it is not possible to return to the original height data in the project. Therefore it is strongly advised to work with different versions of your project, to always have the possibility to go back to a previous version in case something went wrong with importing data.
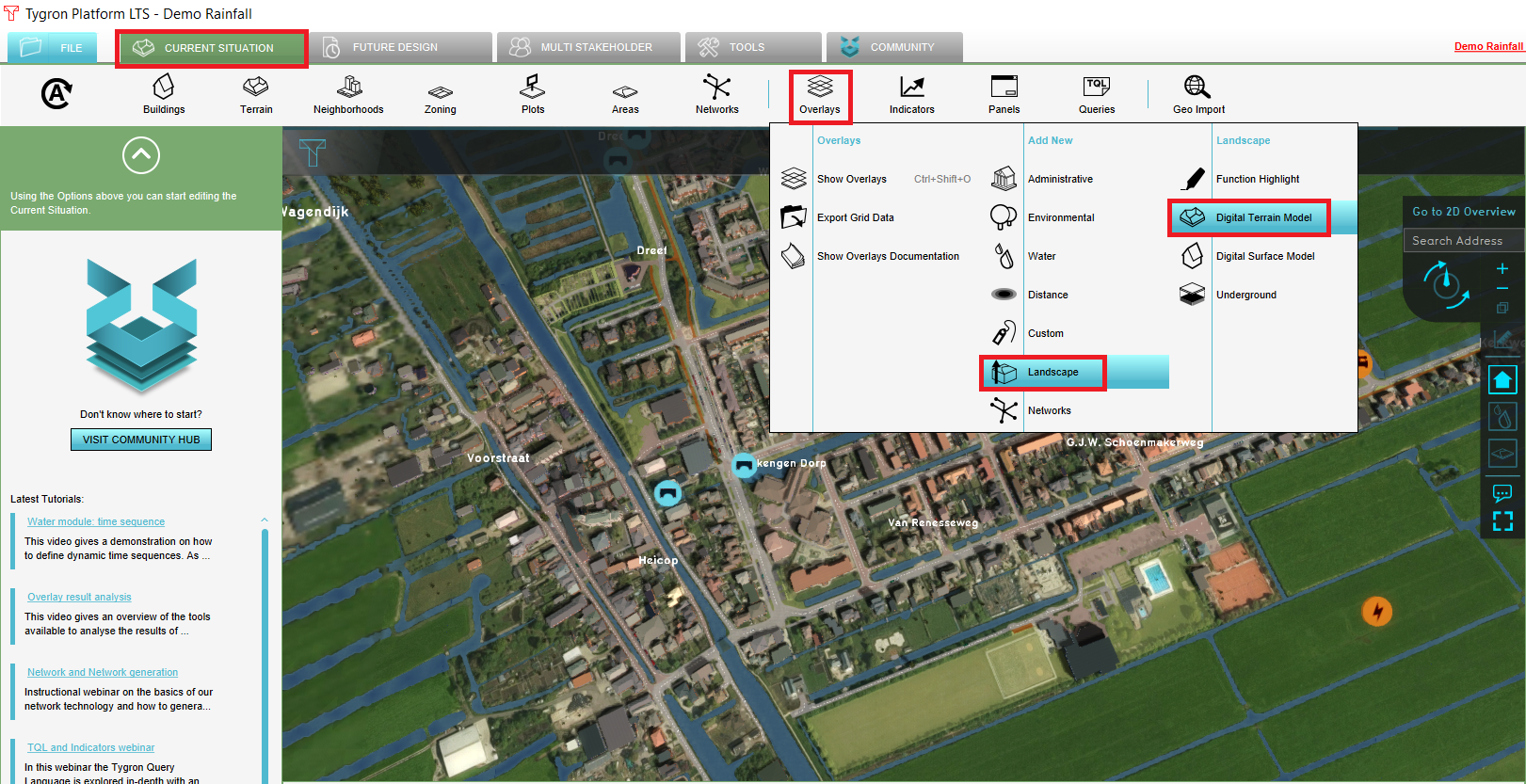
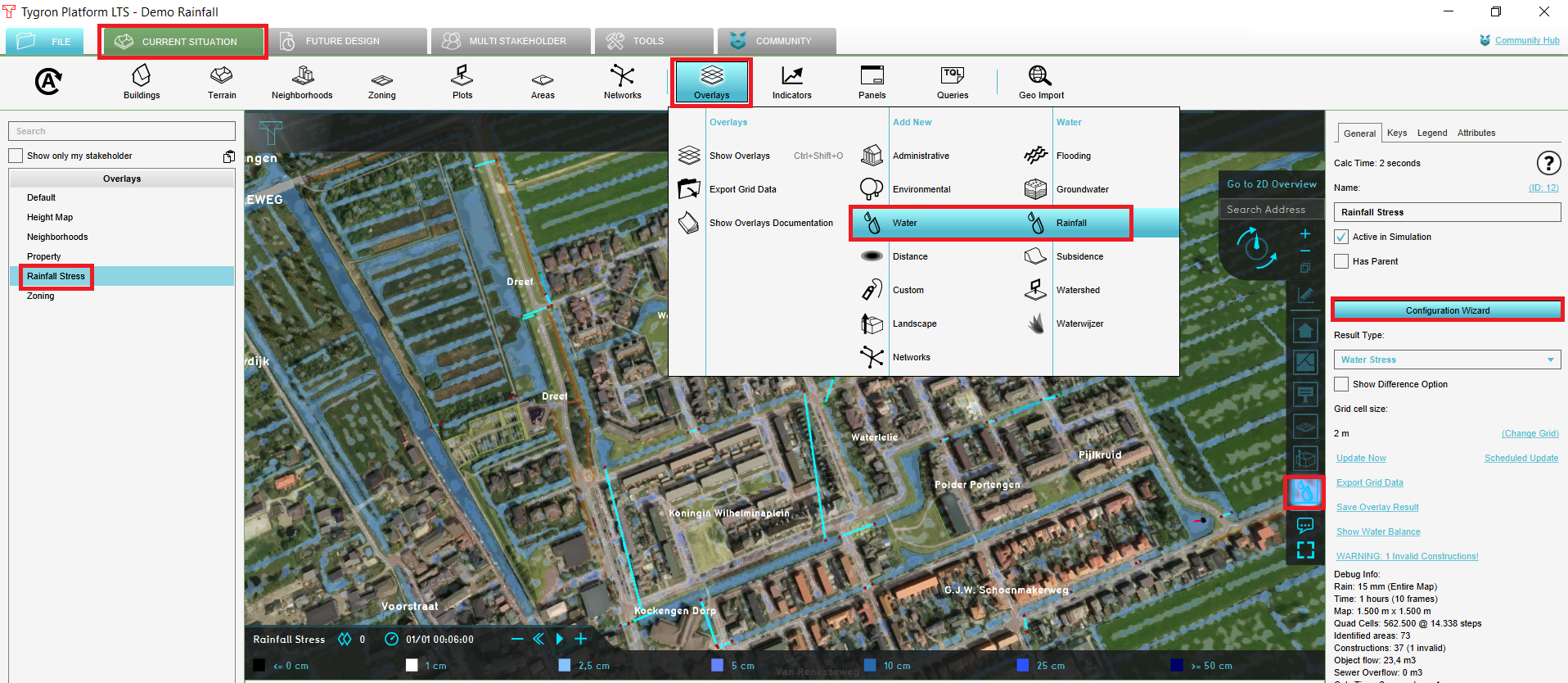
- Hover over the Overlays button in the Current Situation tab.
- From the Landscape category, add the Digital Terrain Model. Now a heightmap will be added to your project.
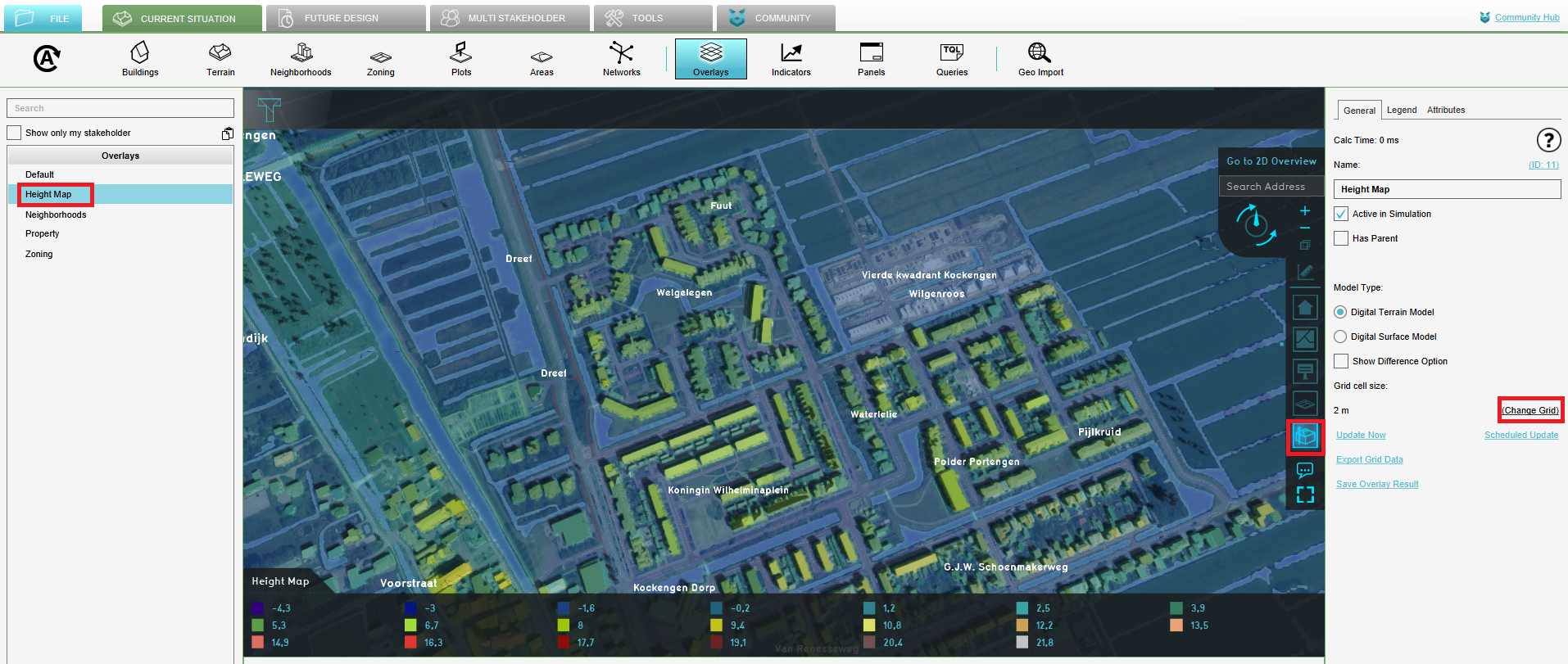
- In the left panel, see the overlays wich correspond with the Overlay bar. In the right panel, change the grid cell size by clicking on Change grid and fill in 2m.
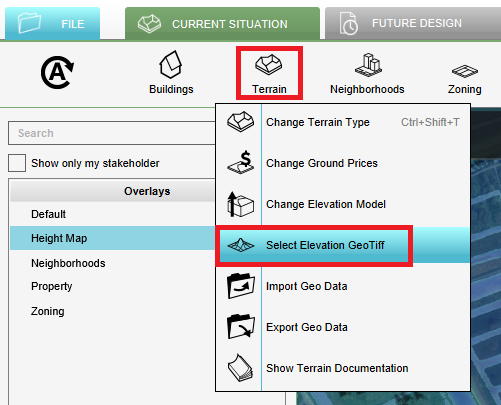
- Hover over the Terrain button in the Current Situation tab.
- Click on Select Elevation GeoTIFF.
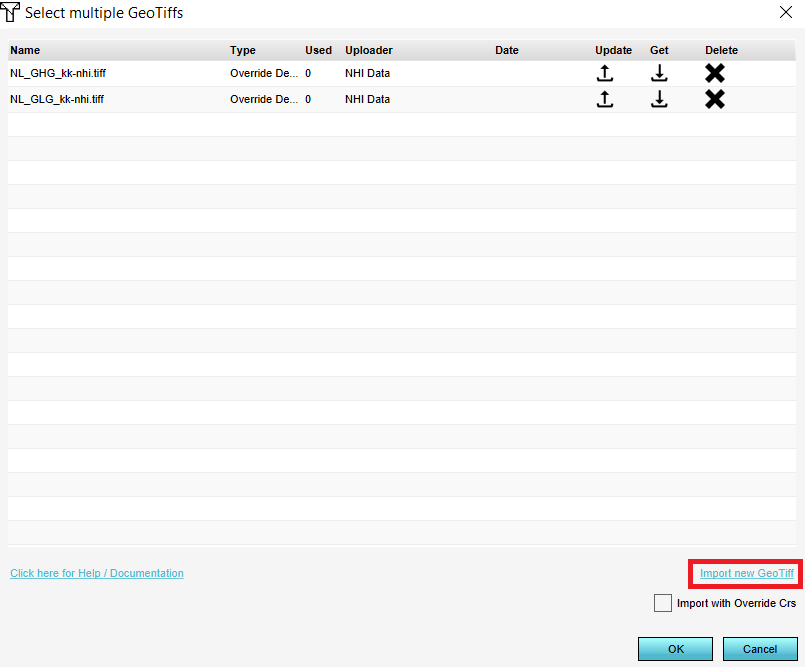
- In the panel that pops up, click on Import GeoTIFF and select your raster file. The file is now being uploaded.
- Select the file that is just uploaded and click on OK. The new heights will be applied to the project. Click on the Digital Terrain Model icon in the Overlay bar and notice the updated heightmap.
Add the Rainfall Overlay
For the following steps, you can practice with the Rainfall Overlay tutorial.
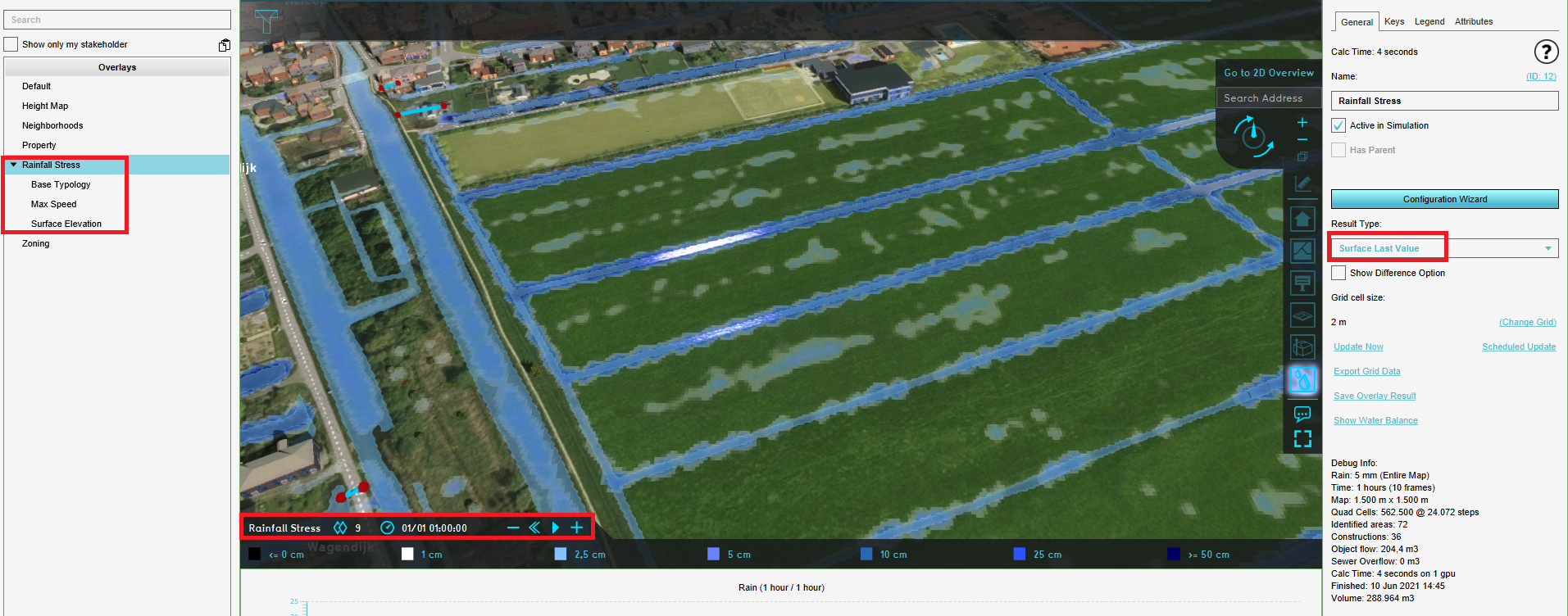
- In the Current Situation tab, hover over the Overlay button and add from the Water category the Rainfall Overlay.
- In the left panel, notice that the Rainfall Overlay is added to the project.
- In the left panel, select the Rainfall Overlay and click in the right panel on the Configuration wizard. In the following steps this Water Overlay Wizard will be completed to import the water system and configure settings for the Rainfall scenario.
Water Overlay Wizard
For the following steps, you can practice with the Rainfall Overlay tutorial.
Rainfall and simulation time
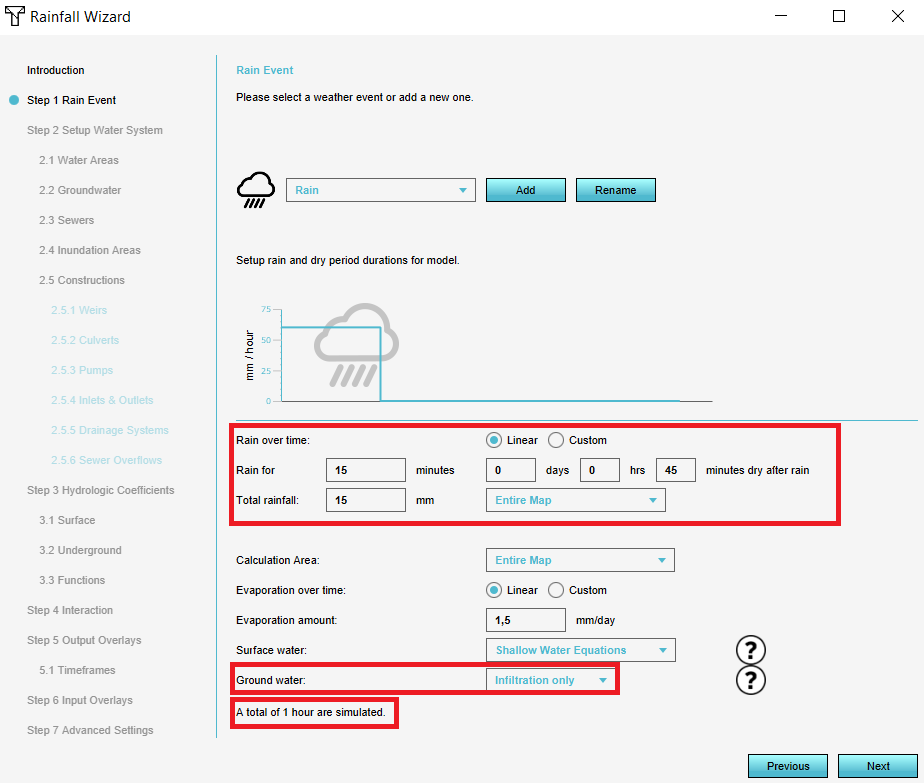
- In the first step of the wizard fill in the amount and the duration of the rain. Also fill in the simulation time.
- Leave the settings for Groundwater on the mode Infiltration only.
Water areas and Groundwater
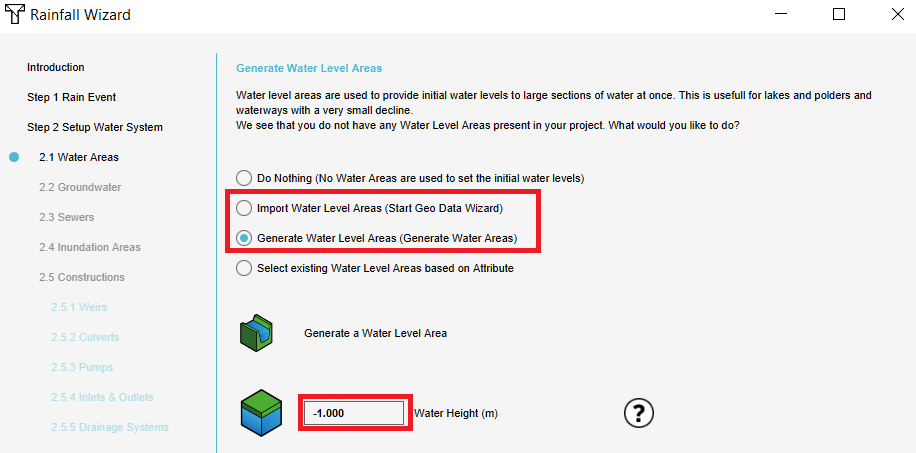
- In step 2.1 choose to generate or import Water areas. When choosing generate, one water area with the size of the entire project area is created. Enter the water level for this area. It is also possible to import own water area data.
- Check if there are no error messages by folding out the drop down menu. If a water area is marked red or orange, there is an error or warning. If there is an error, change the water level according to the error message. Click Next.
- In step 2.2 Groundwater click on Next
Sewer areas
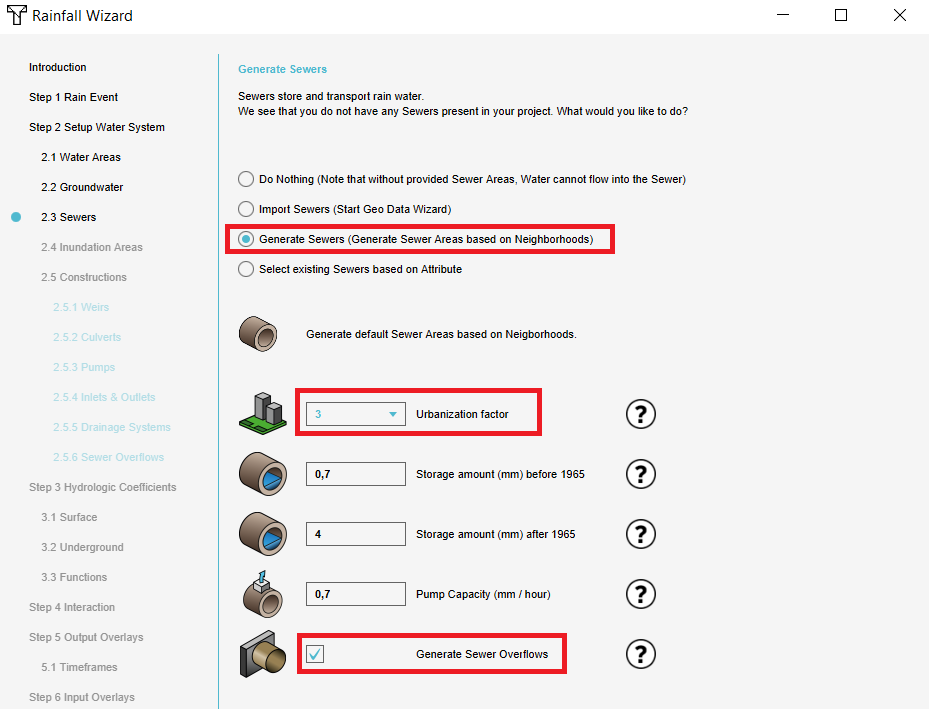
Depending on the use case, sewer areas can be imported to model the water system.
- In step 2.3 choose for the option to import your own Sewer area data or choose to Generate Sewers. Based on the Urbanization factor, sewer areas can be automatically generated for your project area.
- If you have a dataset with sewer overflows, uncheck the Generate Sewer overflows option and click on Next. If you do not have this dataset, then check this option to automatically create sewer overflows for every sewer area and click on Next.
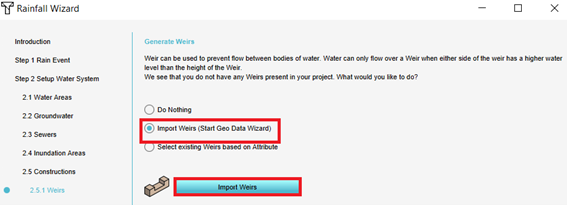
Import Weirs
- Choose in step 2.5.1 weirs for the option to import weirs and then click on the button Import weirs.
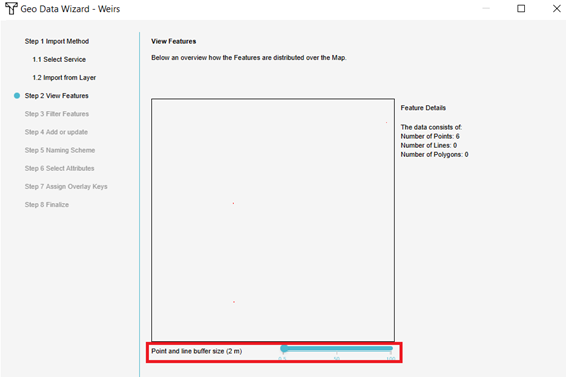
- Follow the steps in the Geo Data Wizard to import weirs. Take note of the the type of data you want to import. If the weirs are points, they should be buffered to create polygons. Choose a suitable name for the weirs to recognize them later on. In step 7 choose the names of the requested attributes that are used to calculate with.
- Finish the Geo Data Wizard
- Check if there are no error messages by folding out the drop down menu. If a weir is marked red or orange, there is an error or warning. If there is an error, change the attributes according to the error message. Then click on Next.
Import other Hydraulic structures
- Repeat the steps for weirs to import other hydraulic structures such as culverts, pumps, inlets and sewer overflows.
Culverts are automatically imported when the IMWA data source is checked. Note that it can occur that not all attributes have a value (from the open data) and that therefore default values can be used. When importing own culvert data, note that culverts is usually line data. The lines should be buffered to create polygons in the Geo Data Wizard. Pumps and inlets are usually point data which also need to be buffered.
- If you have generated sewer areas with sewer overflows, it is not needed to import own sewer overflows.
Result types
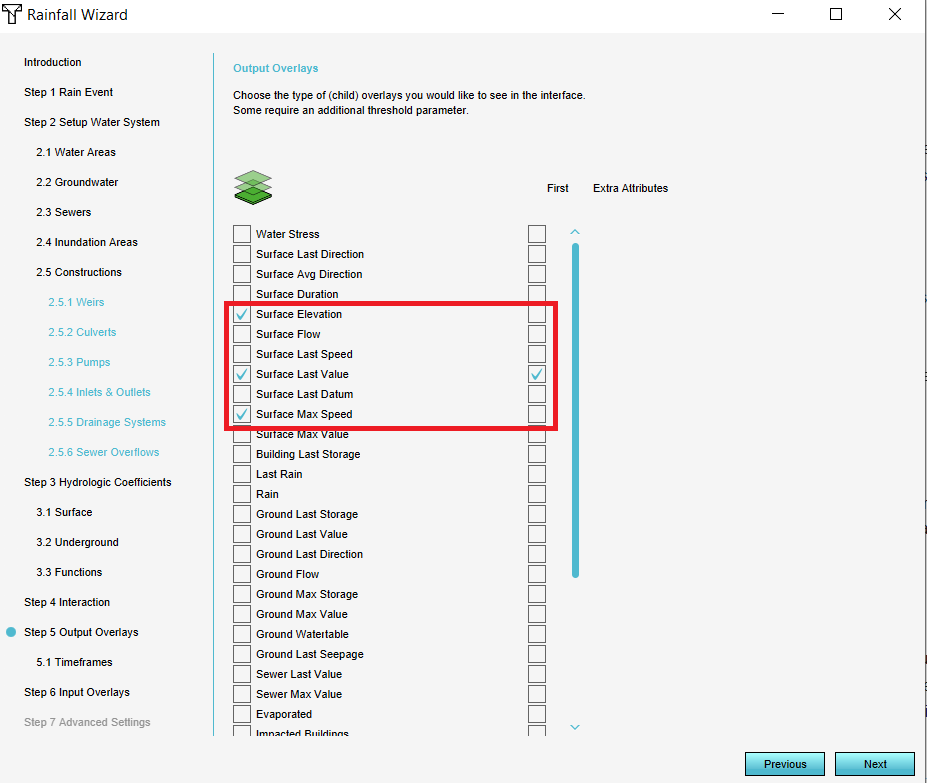
- Change, if desired, the attributes in step 3 and click on Next until you are at step 5.
- In step 5 select the result type maps you would like to see in your project. Useful result types are Surface elevation,Surface last value, Surface max speed and Base types.
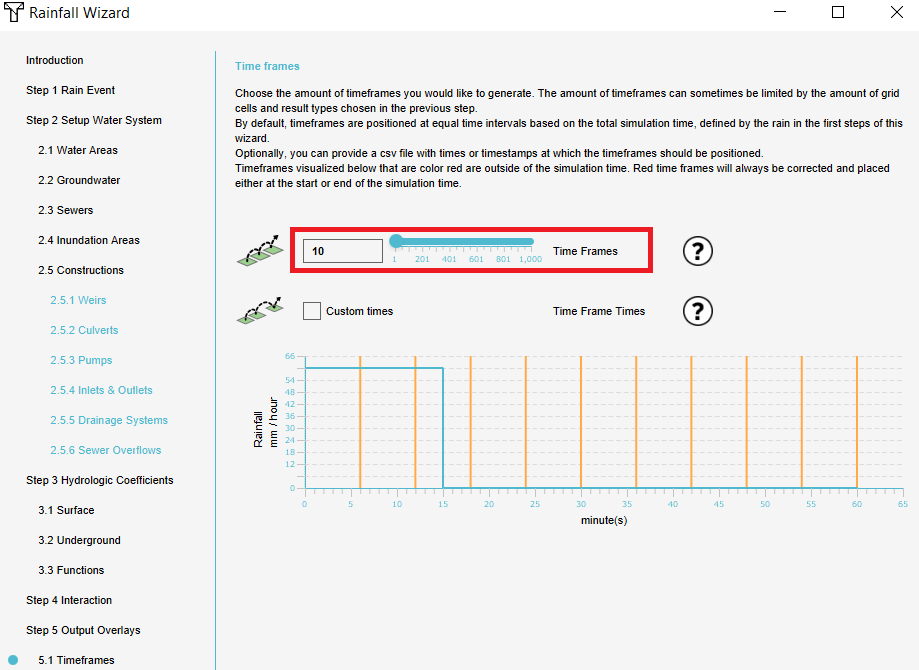
- Then select the amount of timeframes in the next step. Take into account the simulation time (step 1 of the wizard) and the use case, so that you have, for example, a timeframe every 15 minutes.
- Finish the wizard. The Rainfall will now be calculated. When the calculation is finished, see the result types in the left panel. In the right panel, more information can be found per result type. Click on the Play button to play the rainfall simulation.