Average calculation model (Heat Overlay): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
|} | |} | ||
{{article end | |||
|seealso= | |||
* [[Vegetation avg result type (Heat Overlay)|Vegetation fraction average result type]] | * [[Vegetation avg result type (Heat Overlay)|Vegetation fraction average result type]] | ||
* [[Sky view avg result type (Heat Overlay)|Sky view factor average result type]] | * [[Sky view avg result type (Heat Overlay)|Sky view factor average result type]] | ||
}} | |||
{{Template:HeatOverlay_formula_nav}} | {{Template:HeatOverlay_formula_nav}} | ||
Latest revision as of 17:01, 25 January 2023
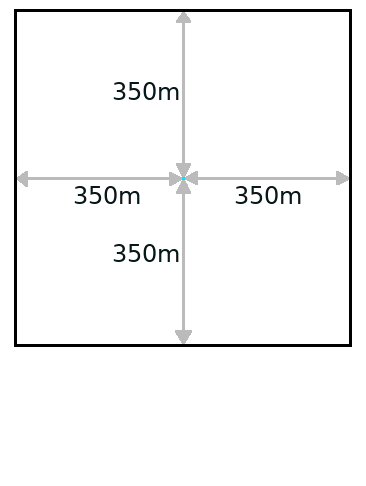
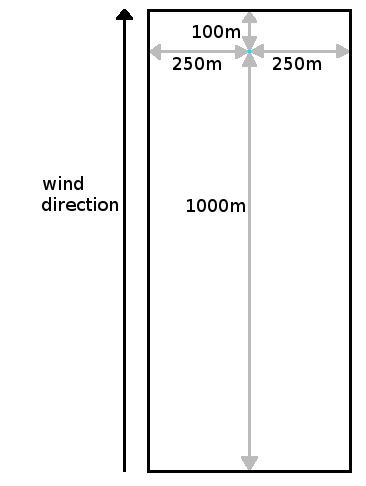
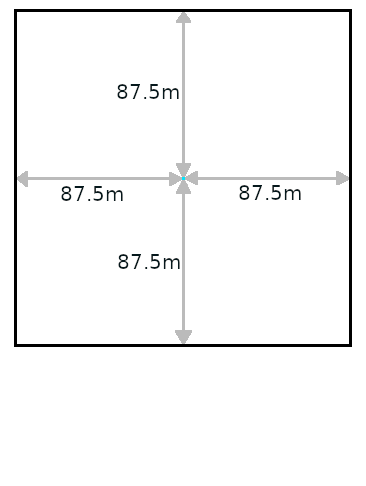
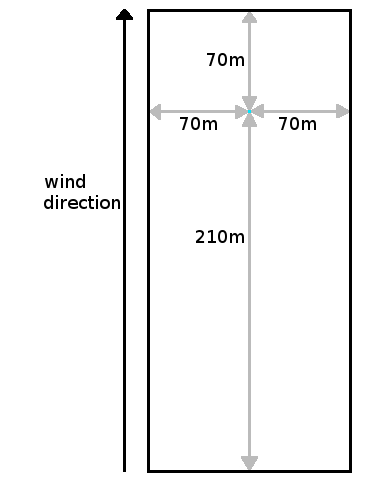
The wind speed and direction are used to determine the window for averaging values around a cell. Commonly, the values at a reference weather station are used. In calculations with a low wind speed, an cell-centered averaging window is used. In calculations with a high wind speed, an oblong rectangle is used for averaging, with the cell in question offset towards the far side along the line of the wind direction.
Wind speed:
- < 1.5 meter per second, the window is square and cell centered
- >= 1.5 meter per second, the window is oblong, and offset towards the wind direction, to account for the effect the wind has on factors which influence temperature.
The averaging
| Window | Model | Low wind speeds | High wind speeds |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large window |
|
 |
 |
| Small window |
|
 |
 |




