Global: Difference between revisions
Created page with "{{learned|what a global is|how to create Globals|what type of globals you can create|where globals currently applied for}} ==Global== A globals ia a number that is intecrated..." |
No edit summary |
||
| (91 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Api_current_situation_calculation.png|thumb|right|400px|[[Global]]s in comparison to [[Overlay]]s, [[Indicator]]s and [[Panel]]s]] | |||
A global is a value that exists in the project but is not necessarily connected to a specific component. The global can be used, for example in Excel calculations and influence the calculation of an Excel indicator. A global is similar to an [[attribute]] but for the entire project rather than for a specific component. The name of the global is also the global [[ID]] that can be used in queries. | |||
==Global== | ==Global uses== | ||
Globals can be used, broadly speaking, to store and recall values. The most common application of this is in combination with [[excel]] sheets. Using [[TQL]], the value of a global can be loaded into an excel sheet and used in calculations. The values of globals can also be [[TQL#Numeric_values|set using TQL]] from excels. Globals can also be used to directly influence the budget of a specific [[Stakeholder|stakeholder]]. Lastly, globals can be made visible in the [[3D Visualization]]. | |||
==Properties of globals== | |||
A global is always made up of a name and a number. Based on the purpose of the global the number represents an amount or a value which is specified by the name. | |||
===Output=== | |||
By using a <code>SELECT_GLOBAL_WHERE_NAME_IS_GLOBALID</code> query you can obtain the value of a global. This global's value can then be used in [[Excel|Excel]] calculations. | |||
It is also possible to connect the global to the budget of a specific stakeholder to directly influence the budget during a session. When the given value is a positive number it will increase the budget. When the given value is a negative number it will decrease the budget. | |||
| | |||
===Input=== | |||
There are 4 ways that a global's value can be set: | |||
* Each global has a starting value. At the start of a session, the global is set to this value. | |||
* A global can be updated using a TQL update statement, of the form <code>UPDATE_GLOBAL_WHERE_NAME_IS_X</code>. | |||
* A global's value can be changed by making use of a SET_GLOBAL_VALUE [[event]]. | |||
* A global can be directly linked to a TQL select statement, by setting the TQL property to a valid query. | |||
With the exception of linking a global directly to a TQL select statement, each method is a singular action to alter the global's value at one specific moment. Linking a global directly to a TQL select query will cause the global to be updated accordingly with every [[calculation cycle]]. This will easily overwrite any singular action such as an [[event]]. When using a TQL update statement in an excel to update a global, the effect will be similarly continuous, causing the global's value to update each calculation cycle. | |||
{{article end | |||
|howtos= | |||
* [[How to add and remove Globals]] | |||
* [[How to edit Global properties]] | |||
|seealso= | |||
[[File:YoutubeLogo1.jpg|link=https://youtu.be/IpQxzjzi1d0|thumb|left|200px|Panels en Globals (Dutch only)]] | |||
}} | |||
{{Editor current situation nav}} | |||
[[Category:Items]][[Category:Global]] | |||
Latest revision as of 10:22, 1 March 2023
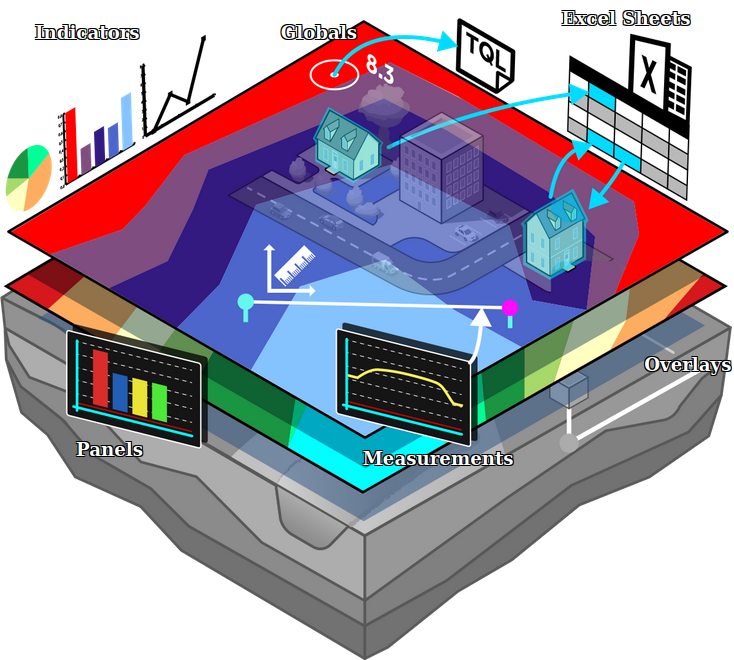
A global is a value that exists in the project but is not necessarily connected to a specific component. The global can be used, for example in Excel calculations and influence the calculation of an Excel indicator. A global is similar to an attribute but for the entire project rather than for a specific component. The name of the global is also the global ID that can be used in queries.
Global uses
Globals can be used, broadly speaking, to store and recall values. The most common application of this is in combination with excel sheets. Using TQL, the value of a global can be loaded into an excel sheet and used in calculations. The values of globals can also be set using TQL from excels. Globals can also be used to directly influence the budget of a specific stakeholder. Lastly, globals can be made visible in the 3D Visualization.
Properties of globals
A global is always made up of a name and a number. Based on the purpose of the global the number represents an amount or a value which is specified by the name.
Output
By using a SELECT_GLOBAL_WHERE_NAME_IS_GLOBALID query you can obtain the value of a global. This global's value can then be used in Excel calculations.
It is also possible to connect the global to the budget of a specific stakeholder to directly influence the budget during a session. When the given value is a positive number it will increase the budget. When the given value is a negative number it will decrease the budget.
Input
There are 4 ways that a global's value can be set:
- Each global has a starting value. At the start of a session, the global is set to this value.
- A global can be updated using a TQL update statement, of the form
UPDATE_GLOBAL_WHERE_NAME_IS_X. - A global's value can be changed by making use of a SET_GLOBAL_VALUE event.
- A global can be directly linked to a TQL select statement, by setting the TQL property to a valid query.
With the exception of linking a global directly to a TQL select statement, each method is a singular action to alter the global's value at one specific moment. Linking a global directly to a TQL select query will cause the global to be updated accordingly with every calculation cycle. This will easily overwrite any singular action such as an event. When using a TQL update statement in an excel to update a global, the effect will be similarly continuous, causing the global's value to update each calculation cycle.
