Heat Module overview: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
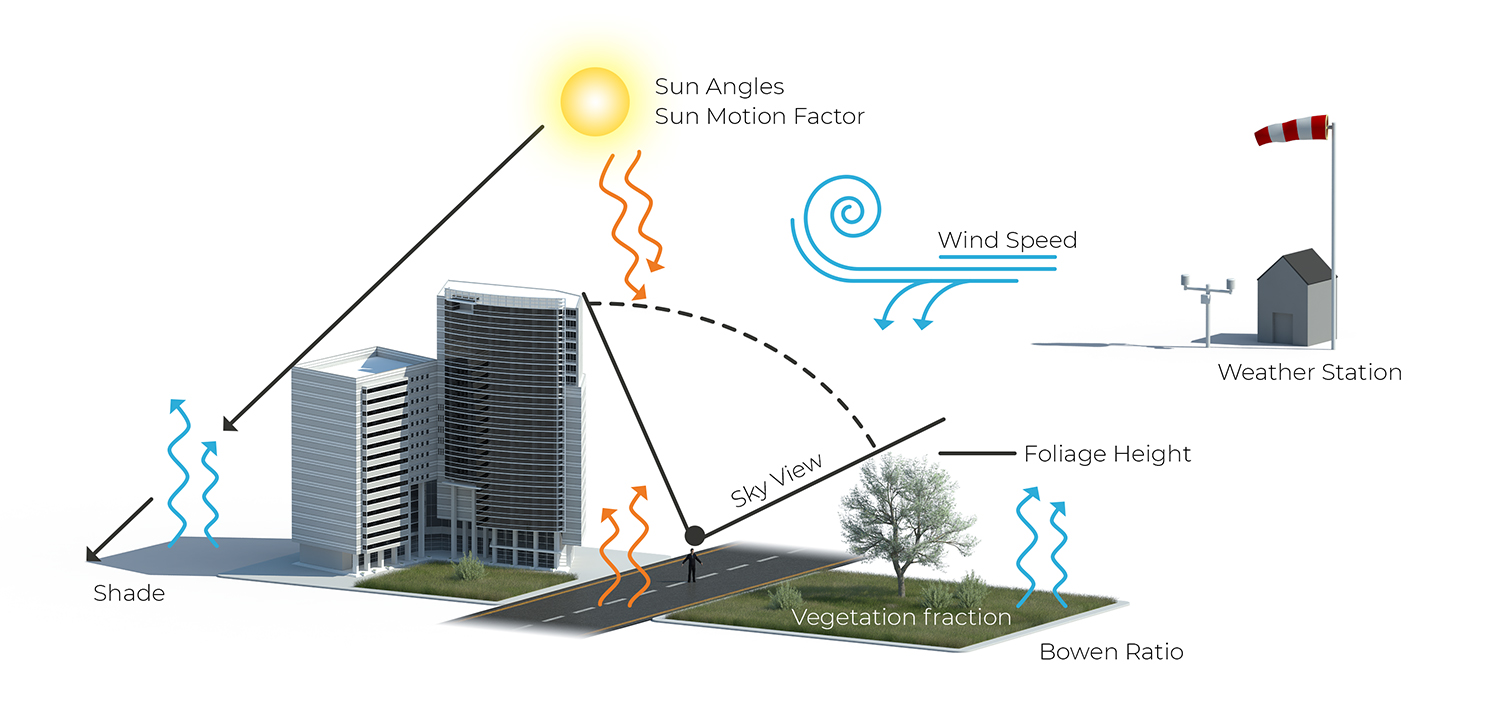
The [[DPRA Heat Module]] for the [[Heat Overlay]] can be used for heat stress calculations, based on geographical features and locale parameters. The final result is the [[Pet result type (Heat Overlay)|physiological equivalent temperature]], which is a measure of temperature which takes into account factors which can change the experience and effects of temperature. | |||
[[File:Overview_Heat_Module.jpg| | The module performs these calculations in accordance with the {{Heat DPRA Report}}. | ||
== | |||
[[File:Overview_Heat_Module.jpg|500px]] | |||
==Input factors== | |||
The calculation of the Heat Stress Overlays takes into account: | The calculation of the Heat Stress Overlays takes into account: | ||
* Meteorological circumstances such as: | * Meteorological circumstances such as: | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
* Spatial situation, such as: | * Spatial situation, such as: | ||
** Land use, for fraction vegetation and rate of evaporation ([[Bowen_ratio_(Heat_Overlay)|Bowen ratio]]). | ** Land use, for fraction vegetation and rate of evaporation ([[Bowen_ratio_(Heat_Overlay)|Bowen ratio]]). | ||
** Terrain, foliage and building heights | ** Terrain, [[Foliage_crown_factor_(Heat_Overlay)|foliage]] and building heights | ||
==Calculation of Physiological Equivalent Temperature== | ==Calculation of Physiological Equivalent Temperature== | ||
| Line 22: | Line 23: | ||
* Is a cell shaded? Calculated by the [[Shade_calculation_model_(Heat_Overlay)|shade calculation model]]; | * Is a cell shaded? Calculated by the [[Shade_calculation_model_(Heat_Overlay)|shade calculation model]]; | ||
===PET sun=== | |||
The following factors influence the [[PET_formulas_(Heat_Overlay)|Physiological Equivalent Temperature]] for locations directly in the sun: | The following factors influence the [[PET_formulas_(Heat_Overlay)|Physiological Equivalent Temperature]] for locations directly in the sun: | ||
* The [[Temperature_atmosphere_result_type_(Heat_Overlay)|atmospheric temperature]], calculated by the [[Temperature_formulas_(Heat_Overlay)#Atmospheric Temperature formula|atmospheric temperature formula]]; | * The [[Temperature_atmosphere_result_type_(Heat_Overlay)|atmospheric temperature]], calculated by the [[Temperature_formulas_(Heat_Overlay)#Atmospheric Temperature formula|atmospheric temperature formula]]; | ||
| Line 32: | Line 33: | ||
* The [[Sky_view_result_type_(Heat_Overlay)|sky view factor]], calculated by the [[Sky_view_factor_calculation_model_(Heat_Overlay)|sky view factor calculation model]]. | * The [[Sky_view_result_type_(Heat_Overlay)|sky view factor]], calculated by the [[Sky_view_factor_calculation_model_(Heat_Overlay)|sky view factor calculation model]]. | ||
===PET shade and night=== | |||
The following factors influence the [[PET_formulas_(Heat_Overlay)|Physiological Equivalent Temperature]] for locations directly in the shade or at night: | The following factors influence the [[PET_formulas_(Heat_Overlay)|Physiological Equivalent Temperature]] for locations directly in the shade or at night: | ||
* The [[Temperature_atmosphere_result_type_(Heat_Overlay)|atmospheric temperature]], calculated by the [[Temperature_formulas_(Heat_Overlay)#Atmospheric Temperature formula|atmospheric temperature formula]]; | * The [[Temperature_atmosphere_result_type_(Heat_Overlay)|atmospheric temperature]], calculated by the [[Temperature_formulas_(Heat_Overlay)#Atmospheric Temperature formula|atmospheric temperature formula]]; | ||
| Line 39: | Line 40: | ||
* The [[Sky_view_result_type_(Heat_Overlay)|sky view factor]], calculated by the [[Sky_view_factor_calculation_model_(Heat_Overlay)|sky view factor calculation model]]. | * The [[Sky_view_result_type_(Heat_Overlay)|sky view factor]], calculated by the [[Sky_view_factor_calculation_model_(Heat_Overlay)|sky view factor calculation model]]. | ||
* The diffuse radiation, calculated by the [[Diffuse_radiation_formula_(Heat_Overlay)|diffuse radiation formula]]. | * The diffuse radiation, calculated by the [[Diffuse_radiation_formula_(Heat_Overlay)|diffuse radiation formula]]. | ||
==Required information== | |||
In order to configure the [[Heat Overlay]] accurately additional data needs to be loaded in: | |||
* [[Dates (Heat Overlay)|Date(s) and time of day]]. Also multiple consecutive days can be used. Each day-hour combination will become a result. | |||
* Daily [[Weather station (Heat Overlay)|weather station]] data | |||
* Hourly weather station data | |||
* [[Foliage height calculation model (Heat Overlay)|Foliage height]]s (although a [[foliage crown factor (Heat Overlay)|means of estimation]] is available) | |||
==See also== | |||
* [[Getting started (Heat Overlay)]] | |||
* [[Heat Overlay Wizard (Heat Overlay)]] | |||
* [[Calculation models and formulas (Heat Overlay)]] | |||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
== | ==Getting started with the Heat Module== | ||
In order to get acquainted with configuring the Heat Overlay, follow our [[Tutorial_Heat_Overlay_(Heat_Overlay) |Heat Overlay Tutorial]] and/or the instructions on our . The process of configuring the Heat Overlay can be guided by the [[|Heat Overlay configuration wizard]]. | |||
====Date and time of day==== | ====Date and time of day==== | ||
| Line 79: | Line 85: | ||
* Buildings with [[Function|functions]] related to foliage. The [[Foliage_height_calculation_model_(Heat_Overlay)|foliage height calculation model]] will determine the foliage height using the height of the vegetation (as buildings) and the foliage crown factor attribute; | * Buildings with [[Function|functions]] related to foliage. The [[Foliage_height_calculation_model_(Heat_Overlay)|foliage height calculation model]] will determine the foliage height using the height of the vegetation (as buildings) and the foliage crown factor attribute; | ||
* Areas with as foliage height attribute, defining the foliage height for a whole area; | * Areas with as foliage height attribute, defining the foliage height for a whole area; | ||
* [[ | * [[GeoTIFF]], defining a foliage height value for each cell in its raster. | ||
\ | \ | ||
--> | --> | ||
{{HeatOverlay model attribute nav}} | |||
Latest revision as of 09:28, 2 March 2023
The DPRA Heat Module for the Heat Overlay can be used for heat stress calculations, based on geographical features and locale parameters. The final result is the physiological equivalent temperature, which is a measure of temperature which takes into account factors which can change the experience and effects of temperature.
The module performs these calculations in accordance with the DPRA Heat stress report.
Input factors
The calculation of the Heat Stress Overlays takes into account:
- Meteorological circumstances such as:
- Spatial situation, such as:
- Land use, for fraction vegetation and rate of evaporation (Bowen ratio).
- Terrain, foliage and building heights
Calculation of Physiological Equivalent Temperature
To calculate the Physiological Equivalent Temperature (PET), we first have to determine which formula (sun or shade/night) should be used. It is selected by:
- Day or night? Determined by the sun altitude angle;
- Is a cell shaded? Calculated by the shade calculation model;
PET sun
The following factors influence the Physiological Equivalent Temperature for locations directly in the sun:
- The atmospheric temperature, calculated by the atmospheric temperature formula;
- The hourly global radiation from the sun, supplied as weather station data;
- The wind speed at 1.2 meter above ground, calculate by the wind speed calculation model;
- The Wet-Bulb temperature, calculated by the Wet Bulb temperature formula;
- The sun altitude, calculated automatically based on the project area, date and time of day;
- The Bowen ratio, an attribute obtained from Buildings or Terrain on that specific location;
- The sky view factor, calculated by the sky view factor calculation model.
PET shade and night
The following factors influence the Physiological Equivalent Temperature for locations directly in the shade or at night:
- The atmospheric temperature, calculated by the atmospheric temperature formula;
- The wind speed at 1.2 meter above ground, calculate by the Wind speed calculation model;
- The Wet-Bulb temperature, calculated by the Wet Bulb temperature formula;
- The sky view factor, calculated by the sky view factor calculation model.
- The diffuse radiation, calculated by the diffuse radiation formula.
Required information
In order to configure the Heat Overlay accurately additional data needs to be loaded in:
- Date(s) and time of day. Also multiple consecutive days can be used. Each day-hour combination will become a result.
- Daily weather station data
- Hourly weather station data
- Foliage heights (although a means of estimation is available)
See also
- Getting started (Heat Overlay)
- Heat Overlay Wizard (Heat Overlay)
- Calculation models and formulas (Heat Overlay)