Subsidence Overlay: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (112 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{deprecated}} | ||
[[File:Subsidence-Overlay.jpg|thumb|200px|right|The subsidence overlay]] | |||
[[File:Groundwater-Overlay.jpg|thumb|200px|right|The ground water overlay]] | |||
The Subsidence Overlay is an [[Grid overlay|overlay]] that shows which places in the [[project area]] are subject to subsidence due to oxidation and/or compaction of peat. The [[subsidence calculation|calculation]] results can provide insight into the subsidence taking place, and the effects it has on groundwater levels. | |||
The Subsidence Overlay can be used to calculate the amount of subsidence which takes place on peat soil, specifically due to peat oxidation and compaction. The calculations are specific for peat soil. Separate formulas for other soil types have not yet been implemented. Although it's possible to use the overlay to give an impression of subsidence resulting from other factors, the results will be less accurate. This means that results have a greater margin of error for different use-cases. | |||
It is possible to add multiple subsidence overlays to a project. By varying their configuration slightly, it is possible to calculate multiple scenario's or time-frames simultaneously. | |||
A project can be enriched with other overlays that are interesting in combination with the Subsidence Overlay. Examples are: | |||
The | * The initial [[Ground_watertable_result_type_(Water_Overlay)|Groundwater level]] calculated by the [[Groundwater Overlay]] | ||
* The [[Waterwijzer_Overlay|Waterwijzer Overlay]] which calculates the yield loss of crops based on [[Waterwijzer_Overlay#Considerations|several parameters such as Subsidence]] | |||
{{article end | |||
{{ | |howtos= | ||
* [[How to add and remove an Overlay]] | |||
* [[How to edit an overlay legend|Edit an overlay legend]] | |||
}} | }} | ||
==Module== | |||
A Subsidence Overlay can be configured by opening the Subsidence Overlay Wizard. More in-depth information can be found under each of the categories below. | |||
== | {{SubsidenceOverlay_nav}} | ||
[[Category:Overlays with result types]] | |||
Subsidence | {{Overlay nav}} | ||
Latest revision as of 05:48, 26 May 2025
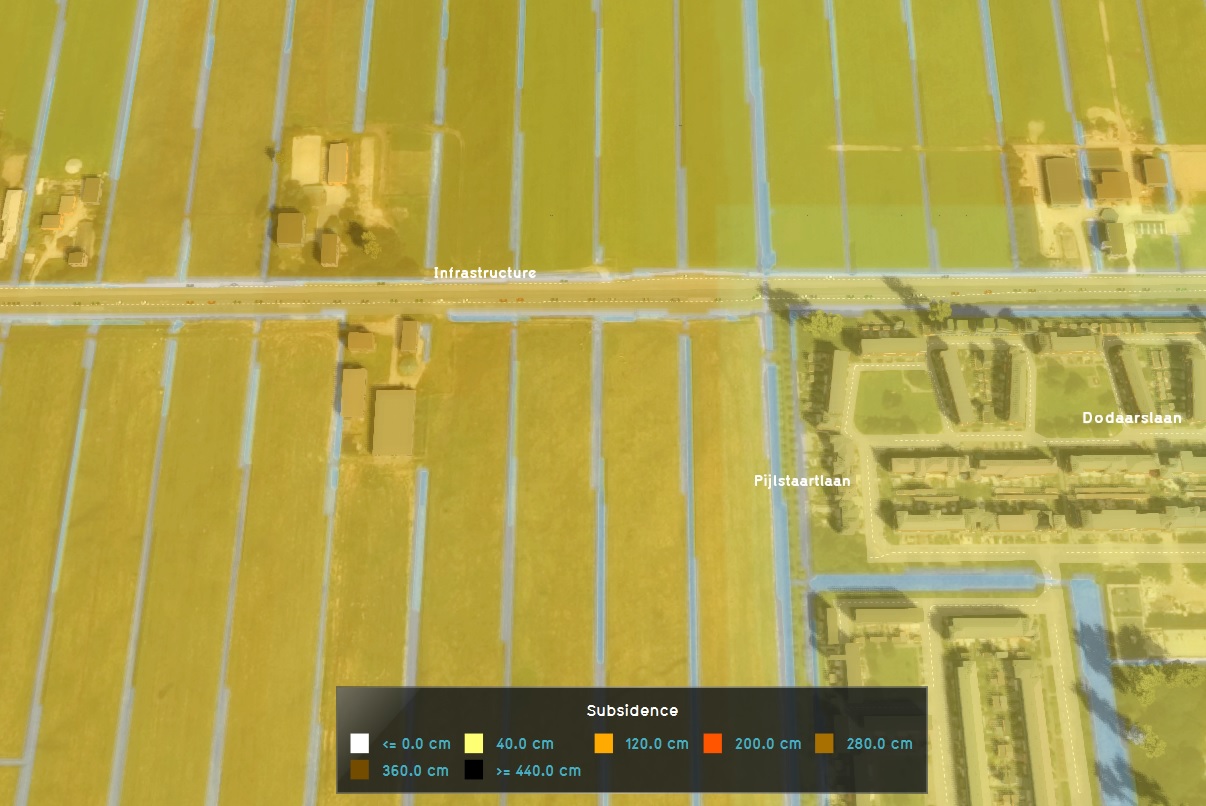

The Subsidence Overlay is an overlay that shows which places in the project area are subject to subsidence due to oxidation and/or compaction of peat. The calculation results can provide insight into the subsidence taking place, and the effects it has on groundwater levels.
The Subsidence Overlay can be used to calculate the amount of subsidence which takes place on peat soil, specifically due to peat oxidation and compaction. The calculations are specific for peat soil. Separate formulas for other soil types have not yet been implemented. Although it's possible to use the overlay to give an impression of subsidence resulting from other factors, the results will be less accurate. This means that results have a greater margin of error for different use-cases.
It is possible to add multiple subsidence overlays to a project. By varying their configuration slightly, it is possible to calculate multiple scenario's or time-frames simultaneously.
A project can be enriched with other overlays that are interesting in combination with the Subsidence Overlay. Examples are:
- The initial Groundwater level calculated by the Groundwater Overlay
- The Waterwijzer Overlay which calculates the yield loss of crops based on several parameters such as Subsidence
Module
A Subsidence Overlay can be configured by opening the Subsidence Overlay Wizard. More in-depth information can be found under each of the categories below.