Average Overlay: Difference between revisions
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
===Calculation=== | ===Calculation=== | ||
The way of averaging is defined by several [[Attribute]]s, and can most easily be set using the | The way of averaging is defined by several [[Attribute]]s, and can most easily be set using the ''Average Overlay Wizard''. | ||
The calculation can be configured via the following attributes: | The calculation can be configured via the following attributes: | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 10 January 2024
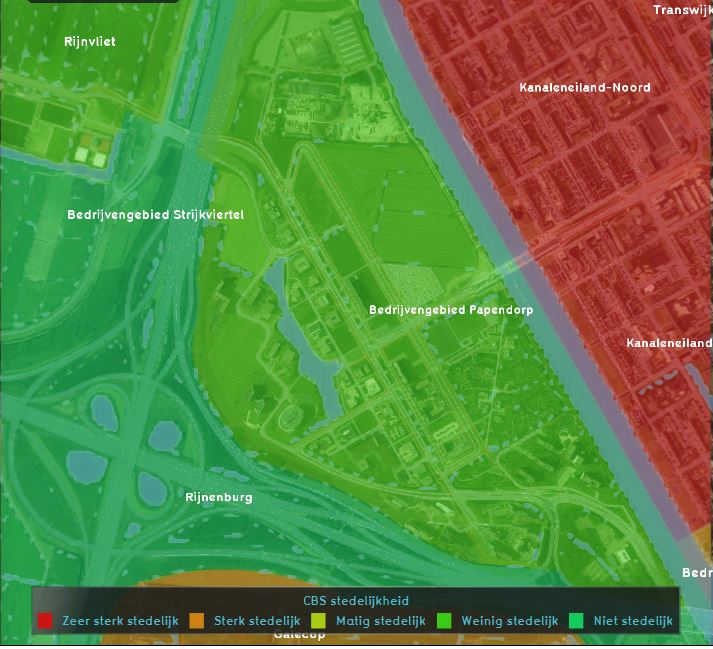
The Average Overlay is a multi purpose Grid Overlay which displays (smoothed) values. These values can originate from spatial features, such as buildings, terrains, areas and neighborhoods. Alternatively, the values can originate from an other Grid Overlay.
Another typical use-case of the Average Overlay is to visualize parameters of a simulation model (e.g. the rainfall overlay). A parameter assigned to a grid-cell can be related to one or more types of features in the project area: Buildings, Addresses, Terrains, Areas, Neighborhoods and Net Lines.
Thirdly the Average overlay supports replacing NO_DATA values with interpolated non NO_DATA values using surrounding cells within a specified distance.
Additional information displayed in hover panel
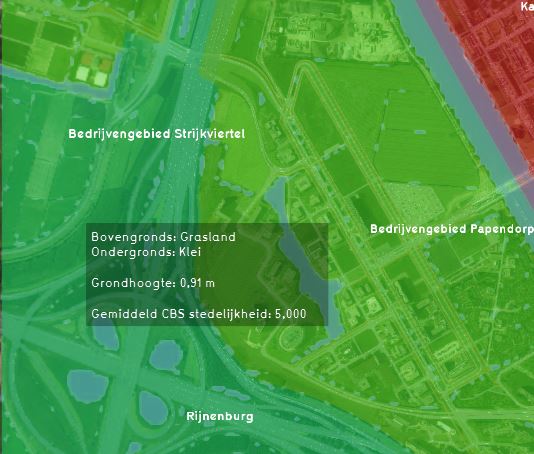
When clicking on a specific location in the map of the Average Overlay, the hover panel gives additional information over the actual value in that specific grid cell.
Calculation
The Average Overlay works by first computing a grid of input values. This depends on the input;
- Certain Vector data in the Project is rasterized into grid cells, depending on the configured MapLink (Average Overlay). Cells that do not contain Vector data are given a Default value.
- Grid is (re)rasterized if the dimensions are different from the requested dimensions, or used directly otherwise.
Next, it depends on the operator configured for the Average Overlay what happens next: for each grid cell, the values of all cells within a given radius from that one cell are summed up, and divided by the total amount of cells found in that radius. The output value of that one cell is that computed average.
The Average Overlay can be configured to fine-tune the exact data which should serve as input, and how the calculation should take place.
Average Operator
The Average Operator determines how a cells value is calculated. The following operators are supported for the Average Overlay:
- AVG: Averages rasterized values within the configured radius.
- MAX: Selects the maximum value of rasterized values within the configured radius.
- MIN: Selects the minimum value of rasterized values within the configured radius.
- AVG_INTERPOLATED: Replaces a cell's rasterized value when it contains NO_DATA, when its neighboring cell does contain a value. This process will be repeated multiple rounds based on the configured Distance m (Average Overlay) and the grid cell size.
Averaged Value Type
You can also configure in what way a value for this overlay will be selected:
- First: Selects the first value encountered among all considered Vector data types. See Rasterized Vector data for the order.
- Min: Selects the minimum value among all considered Vector data types.
- Max: Selects the maximum value among all considered Vector data types.
- Single layer: Only Vector data of the configured MapLink (Average Overlay) is rasterized.
- Grid: Indicates that this overlay uses its configured Input prequel (Average Overlay) as input instead of Vector data.
Rasterized Vector data
The Vector data that is rasterized is determined by two values: the configured layer MapLink (Average Overlay) of the Average overlay and the configured Average Type. If the Average Type is set to Grid, no vector data is rasterized for this overlay. When the MapLink is set to null, and the Average Type is set to anything other than Grid, all MapLink layers are considered. When the MapLink layer is set to a specific MapLink, only that type of data is rasterized.
The Average Overlay currently supports the following MapLinks (in order): Net Lines, Addresses, Buildings, Terrains, Areas, Neighborhoods.
Input
The Average Overlay requires an initial input, which it can then average out over a specified range. The input can be either an Attribute of vector data, or a Grid Overlay. The following options are available:
- Attribute First Layer
- Use the first value found among the layers of vector data which have the specified Attribute. If no such Attribute exists in a specific location, the used value is 0.
- Attribute Min Layer / Max Layer
- Use either the lowest or the highest value found among the layers of vector data which have the specified Attribute. If no such Attribute exists in a specific location, the used value is 0.
- Attribute Specific Layer
- Use the defined Attribute's value from the specific layer of vector data specified. Exactly one layer can be specified. If no such Attribute exists in a specific location, the used value is 0.
- Grid Overlay
- Use the values of another Grid Overlay when specified as input. No Attribute needs to be specified. NO_DATA values of the referenced Overlay result in NO_DATA values in the grid. The Average Overlay will have timeframes equal to the amount of timeframes of the Input Overlay. In case the input Grid Overlay does not have the same grid size as the Average Overlay, the input Grid Overlay 's value grid is automatically resized.
Calculation
The way of averaging is defined by several Attributes, and can most easily be set using the Average Overlay Wizard.
The calculation can be configured via the following attributes:
No data interpolation (Average Overlay)
| Icon | Attribute | Unit | Range | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
ATTRIBUTE_TIMEFRAMES | integer | 1 to 1000 | The amount of timeframes to display when basing input on Attribute arrays. | 1 |
| |
DEFAULT_VALUE | The default value used for a cell when no spatial data overlaps that cell. | 0 | ||
| |
DISTANCE_M | m | 0 to 2000.0 | The radius within which an average value must be computed. | 100 |
Input Overlay
Input Overlays are Average Overlays that supply additional insights in the data used for complex Overlay models (e.g the Water Overlay or Heat Stress Overlay). Input Overlays can be made visible in the 3D Visualization by selecting them in the Wizard or adding them manually.
Average Overlay Variants
There are four options to choose from:
- How to create an Average Overlay based on another Grid Overlay.
- How to fill NO_DATA values in a grid overlay by interpolation using and Average Overlay.
- How to create an Average Overlay based on feature attributes.
- How to configure an Average Overlay to gain insight into grid cell values.
How-to's
External links