|
|
| (266 intermediate revisions by 12 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| {{learned|what the rainfall overlay is|how the rainfall overlay can be used|how the rainfall overlay can be configured|what principles govern its calculation|what formulas are used to perform the calculations}}
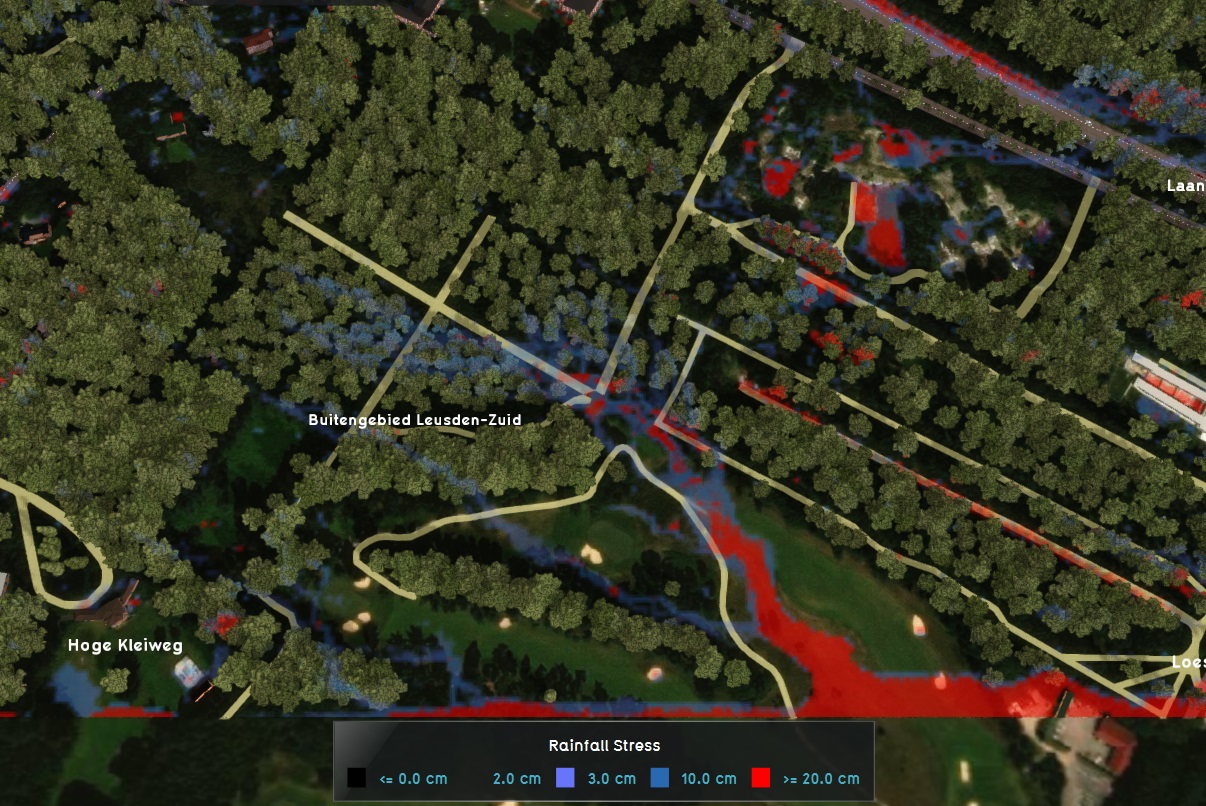
| | [[File:Rainfall-Overlay.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Rainfall overlay]] |
| | The Rainfall Overlay is a variant of the [[Water Overlay]], which in turn is a [[Grid overlay|grid overlay]]. Water overlays are connected to the [[Water Module]], a complex hydrological calculation module within the {{software}}. |
|
| |
|
| ==What is the rainfall overlay==
| | The Rainfall overlay specializes in displaying the hazard and impact of (heavy) rainfall over the project area. Based on the elevation model, terrain roughness and representations of the sewer and water systems, several result types can be generated by the accompanying Water Module. |
|
| |
|
| The rainfall overlay is a [[grid overlay]], which calculates where and how water would flow in situations where severe rainfall takes place. It does so by simulating water falling onto the [[3D world]] over the course of thousands of steps. During each step, water can, among other things, land on the ground, flow over the surface, infiltrate into the ground, flow underground, and end up in surface water.
| | A [[Rainfall_Overlay_tutorial|Rainfall Overlay Tutorial]] is available to get you started with this overlay. |
|
| |
|
| By repeating these simulation steps thousands of times, the influx and flows of water are accurately approximated.
| | In order to get more familiar with the different components of the Rainfall Overlay check out Quadrant 2 of the [[Testbed_water_module|Water Module Testbed]]. This Testbed is available to you as a project in the {{software}}. |
|
| |
|
| ==What can the rainfall overlay be used for== | | ==Rainfall overlay results== |
| The rainfall overlay is currently fit for simulating the flow and effects of severe rainfall on flat or mildly hilly areas, for map sizes of up to 5km. Larger maps, or calculations which involve an impulse of water such as levee breaches are not yet recommended. | | The Rainfall Overlay is a Water Overlay that is connected to the Water Module. This Water Module performs two dimensional grid based water simulations for a large set of input data and parameters, configured mostly through a related [[Water Overlay Wizard]]. When a simulation finishes, the module stores the result in the Rainfall overlay based on the selected result type. Only one result type can be stored per Rainfall overlay. |
|
| |
|
| The overlay can be configured to display various results of the simulated rainfall. For example it is possible to see the maximum amount of water certain locations had to endure, or the amount of water which has flowed across certain locations. | | The Water Module however, is not restricted to generating only one type of result. Instead it can produce multiple unique result types for one single simulation. |
| | Fortunately it is possible to add additional result type overlays which relate to a particular Rainfall overlay. These are known as [[Result Child Overlay]]s. Again, each child overlay only stores one particular result type. |
|
| |
|
| ==Adding and removing the overlay==
| | Apart from multiple result types, the Rainfall overlay can also store result data of multiple, intermediate simulation results, instead of just a single end result. These intermediate simulation results are known as [[timeframes (Water Overlay)|timeframes]]. |
| The rainfall overlay consists of several overlays or result types that show different analyses of the area after or during the extreme rainfall. The overlay can therefore be added to the project multiple times, to present different outcomes or different scenarios. For information on adding and removing the overlay to and from the [[project]], see the page on [[overlay#Adding and removing overlays|overlay]]s in general. These result types can be chosen via the Result type box or in the last step of the [[#Rain overlay wizard]]. Below they are listed and explained.
| |
|
| |
|
| ===Result types===
| | For the full list of result types, see [[Result type (Water Overlay)#List of Result Types|List of Result Types]]. |
| * '''BASE_GROUNDWATER_DISTANCE''': this overlay shows the distance between the groundwater level (obtained from the water area level data/ GxG map (*) and the surface level. For now, the height of the ground level is including the buildings and other objects on the ground (the height to the surface). This will be changed to the terrain height in a following release.
| |
| *'''BASE_TYPES''': from this overlay the division of the grid cells in water, land or sewer areas that are connected to the sewer are visible. Playing with the grid cell size, will make this division between areas/terrain types more or less accurate, which affect the calculation of the flooding.
| |
| *'''EVAPORATED''': shows how much water is evaporated after the rainfall in the defined simulation time. For more information on how this layer is calculated, see the [[Rainfall overlay calculations]] page.
| |
| *'''SEWER_LAST_VALUE''': The amount of water remaining in the sewer after the simulation is over
| |
| *'''SEWER_MAX_VALUE''': The largest amount of water that was in the sewer at any time during the simulation
| |
| *'''SURFACE_DURATION''': The total amount of time the surface has water on it
| |
| *'''SURFACE_FLOW''': The total amount of water which has flowed across the surface
| |
| *'''SURFACE_LAST_VALUE''': The amount of water remaining on the surface after the simulation is over
| |
| *'''SURFACE_MAX_VALUE''': The largest amount of water that was on the surface at any time during the simulation. Differs from WATER_STRESS in that water stored on bodies of water is always included.
| |
| *'''UNDERGROUND_FLOW''': The total amount of water which has flowed underground
| |
| *'''UNDERGROUND_LAST_VALUE''': the amount of water which has flowed underground after the rain simulation is over.
| |
| *'''UNDERGROUND_MAX_VALUE''': the largest amount of water that flowed underground at any time during the simulation
| |
| *'''WATER_STRESS''': The maximum amount of excess water at any time during the simulation. Differs from SURFACE_MAX_VALUE because water stored on bodies of water are not immediately deemed "excess", this depends on the threshold value which can be defined in the last step of the [[#Rain overlay wizard]]. If the amount of water exceeds this threshold value, the amount of water is visible on the water bodies.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Configuring the overlay==
| | For other results, which are not overlay results, but still related to the simulation for a particular Rainfall overlay, see [[Results (Water Overlay)|Rainfall overlay results]]. |
| The overlay can be configured to add additional data and adjust various values to change or enhance the way the calculations are made and make the model more reliable it calculates. The overlay itself contains a number of attributes which can be configured. Attributes in other parts of the project, such as the connected [[weather|rain definition]], buildings, terrains, and areas defining water level areas. To guide the user along these configurations, the rain overlay wizard can be used, where the user follows several steps to add own data or configure reference attributes.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Rain overlay wizard== | | ==Module== |
| | A Rainfall Overlay can be configured by opening the Rainfall Overlay Wizard. More in-depth information can be found under each of the categories below. |
| | {{Water Module buttons}} |
|
| |
|
| ===Data required=== | | ==References== |
| No data is explicitly required. The overlay is designed to provide initial calculations based on default values and minimal assumptions. However, the model can be refined with your own data:
| | # [[Water Module Theory#Formulas|Water model formulas]] |
| *Water level areas (peilgebieden)
| |
| *Weirs (stuwen)
| |
| *Sewers (rioleringsgebieden)
| |
| *Ground water level (grondwaterstanden)
| |
|
| |
|
| The wizard exists of several steps. First you start with configuring the rainfall. The third step is adding the water level areas.
| | {{WaterOverlay output nav}} |
| | | {{Overlay nav}} |
| ===Water level areas===
| |
| Here you can add your own dataset of "level areas" with a set water level. This file is loaded in as a [[geojson]] file as areas. The following attributed are needed for the calculations.
| |
| {| class="wikitable" | |
| ! Attribute
| |
| ! Description
| |
| ! Example
| |
| ! Remark
| |
| |-
| |
| | NAME
| |
| | The name of the water level area.
| |
| | PG 256
| |
| | This attribute is not loaded in as attribute, but can be used as name to identify the resulting area in the Engine later on.
| |
| |-
| |
| | WATER_LEVEL
| |
| | The height of the water, in meters, measured from Amsterdam Ordnance Datum (mNAP).
| |
| | 1.6
| |
| | For a water level area with infinite storage, this can be set to an extreme negative number (e.g. -9999). However, note that this would also place this area far below level areas with a proper height set.
| |
| |-
| |
| | OUTLET
| |
| | The amount of water which disappears from this level area in cubic meters per second (m3/s).
| |
| | 0.007
| |
| | This could also be the outlet of a ''gemaal''
| |
| |}
| |
| If you do not have any water level dataset, you can also generate a water level area. This will create one waterlevel area which covers the entire 3D world, with no OUTLET value and a WATER_LEVEL of -1000.
| |
| In the wizard the attributes which contain values for the water level and outlet need to be set. If they have different names, these can be chosen in the ''select attribute table''.
| |
| | |
| The next step asks for the weir dataset.
| |
| | |
| ===Weirs===
| |
| The weirs form connections between water level areas for the water to flow from higher water level areas to lower water level areas. The weir dataset is also loaded in as a [[geojson]] file. The following attributes need to be present.
| |
| {| class="wikitable" | |
| ! Attribute
| |
| ! Description
| |
| ! Example
| |
| ! Remark
| |
| |-
| |
| | NAME
| |
| | The name of the weir.
| |
| | PG 256
| |
| | This attribute is not loaded in as attribute, but can be used as name to identify the resulting contruction in the Engine later on.
| |
| |-
| |
| | WEIR_HEIGHT_M
| |
| | The height of the weir, in meters, measured from Amsterdam Ordnance Datum (mNAP).
| |
| | 1.8
| |
| | When using this model outside of the Netherlands, the height is in the same scale as the [[Terrain height]] of the project. When an extreme negative value is used, the construction acts like a culvert.
| |
| |-
| |
| | WEIR_SPEED
| |
| | The speed at which water is moved from one level area to the other, in cubic meters per second (m3/s).
| |
| | 0.007
| |
| | Once the water level exceeds the height of the weir, the water flows at this constant speed until the water level no longer exceeds the height of the weir.
| |
| |}
| |
| This file is loaded in as [[construction]]s. For now, the underground construction ''drainage system'' can be used. This will be updated with a construction resembling a weir in the future.
| |
| | |
| If no weirs exist, there are no connections between water level areas and water is not transferred between them.
| |
| | |
| Weirs must overlap with at most 2 water level areas. If a weir overlaps with more that 2 water level areas, 2 areas are selected at random which the weir pumps between. If a weir overlaps with only 1 water level area, only its outlet function is processed. Weirs which do not overlap with any water level areas have no effect.
| |
| | |
| ===Ground Water===
| |
| In step 5 of the wizard a raster file with ground water levels can be added. By default the ground water level of the water level areas is used. If you choose for the option to upload a GeoTiff file, you can add you own GxG map or use one of the already loaded in GxG maps.
| |
| | |
| ===Sewers===
| |
| The next step allows for the sewer areas to be uploaded. The file is loaded in as a [[geojson]] file as [[area]]s. The following attributes are needed:
| |
| {| class="wikitable"
| |
| ! Attribute
| |
| ! Description
| |
| ! Example
| |
| ! Remark
| |
| |-
| |
| | NAME
| |
| | The name of the sewer.
| |
| | Sewer North-East
| |
| | This attribute is not loaded in as attribute, but can be used as name to identify the resulting area in the Engine later on.
| |
| |-
| |
| | SEWER_PUMP_SPEED
| |
| | The speed at which water is pumped out of the sewer, in cubic meters per hour (m3/h).
| |
| | 1
| |
| | All areas which are not plots of this kind should either not have PERCEEL as an attribute, or should have it set to 0(*).
| |
| |-
| |
| | SEWER_STORAGE
| |
| | The amount of water which can be stored in this sewer, in meters (m).
| |
| | 0.007
| |
| | The total amount of storage for this sewer is the surface area of the [[construction]]s which are connected to the sewer in this particular sewer area, times this attribute.
| |
| |}
| |
| If no sewers exist, the model has no water flowing into sewer containers for storage. Therefore, you can automatically generate these areas. For more information on how the generation of these areas is done or about the sewer system in general, see the [[Rainfall overlay calculations#Sewer system|Rainfall overlay calculations]] page.
| |
| | |
| ===Reference values terrains===
| |
| In the next steps of the wizard the following reference values, regarding the surface and the underground terrain, can be edited.
| |
| *Water infiltration (m per day): the speed in which the water can infiltrate the underground. The speed is also determined by the underground water infiltration factor. From these two values, the lowest value is used.
| |
| *Water manning: the Gauckler Manning coefficient, often denoted as n, is an empirically derived coefficient, which is dependent on many factors, including surface roughness and sinuosity.
| |
| *Water evaporation factor: this factor will be multiplied with the general reference evaporation.
| |
| *Reference Evaporation (mm per day): The Makking reference evaporation factor. This value ranges from 0.5 mm per day in the winter till 3 mm per day in the summer for the weather station ‘ De Bilt’ in the Netherlands.
| |
| *Water storage fraction: the percentage of underground volume that can be used for the storage of water. This number is determined by the difference between the ground water level and the surface height times the surface area.
| |
| *Vertical to horizontal infiltration factor: The factor is the multiply factor to obtain the horizontal infiltration speed from the vertical infiltration speed. The speed which water moves horizontally underground is currently derived from the speed in which water infiltrates vertically.
| |
| | |
| ====Warnings====
| |
| * To calculate the correct flow use a grid size of max 2m.
| |
| * Use a hi-detail height map (1 point per 0.5m), select hi detail in the New Area Wizard under advanced options.
| |